Formation of Gems and Minerals
... becomes concentrated in the molten rock because it does not get incorporated into most minerals that crystallize. Consequently, the last, uncrystallized fraction is rich water and other unusual elements that also do not like to go into ordinary minerals. – When this water-rich magma is expelled in t ...
... becomes concentrated in the molten rock because it does not get incorporated into most minerals that crystallize. Consequently, the last, uncrystallized fraction is rich water and other unusual elements that also do not like to go into ordinary minerals. – When this water-rich magma is expelled in t ...
Volcano Directed Reading
... c. Magma is harder than the rock around it d. Magma is tricky 11. What is the name of a mountain chain created by lava from undersea rift zones? a. Divergent boundary c. Mid-ocean ridge b. Tectonic plate d. Hot springs Mantle plumes Convergent boundary ...
... c. Magma is harder than the rock around it d. Magma is tricky 11. What is the name of a mountain chain created by lava from undersea rift zones? a. Divergent boundary c. Mid-ocean ridge b. Tectonic plate d. Hot springs Mantle plumes Convergent boundary ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Chapter 13 Study Guide 1. What is soil
... The three main layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost layer and the least dense. It contains both continental and oceanic crust. The mantle is the largest layer and contains both the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. The core is the center-most layer made up ...
... The three main layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost layer and the least dense. It contains both continental and oceanic crust. The mantle is the largest layer and contains both the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. The core is the center-most layer made up ...
6. geology - Discovering Antarctica
... blocks, Madagascar and the Seychelles, separated from India as it migrated northwards away from Africa and Antarctica. Finally, in mid-Tertiary times the break up of Gondwana was completed when the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula separated from southern South America by sea-floor spreading i ...
... blocks, Madagascar and the Seychelles, separated from India as it migrated northwards away from Africa and Antarctica. Finally, in mid-Tertiary times the break up of Gondwana was completed when the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula separated from southern South America by sea-floor spreading i ...
ScienceChapter6Study..
... How do earthquakes help scientist find out about what is deep inside Earth? Certain types of seismic waves travel through liquid, solids, or both. So scientists have been able to use earthquakes to help figure out the make up of Earth’s interior. ...
... How do earthquakes help scientist find out about what is deep inside Earth? Certain types of seismic waves travel through liquid, solids, or both. So scientists have been able to use earthquakes to help figure out the make up of Earth’s interior. ...
Plate Tectonics Unit(poster)
... mid-ocean ridge, it comes from Volcanoes and makes the ocean floor of every ocean * 3 Ocean floor was found to be sinking below continents or other crust at the trenches… this process was named subduction ...
... mid-ocean ridge, it comes from Volcanoes and makes the ocean floor of every ocean * 3 Ocean floor was found to be sinking below continents or other crust at the trenches… this process was named subduction ...
Perspective - Elements Magazine
... seafloor where geochemists can sample and analyze the lavas so as to better understand mantle and bulk-Earth evolution. But structural and metamorphic geology are equally necessary, since ridge magmatism is necessarily synkinematic. The brittle carapace is dissected by multiple generations of faults ...
... seafloor where geochemists can sample and analyze the lavas so as to better understand mantle and bulk-Earth evolution. But structural and metamorphic geology are equally necessary, since ridge magmatism is necessarily synkinematic. The brittle carapace is dissected by multiple generations of faults ...
Notes-Stress, Faults and Folds
... Rocks don’t always bend, sometimes they break. When the rock moves and breaks it is called a _______________. There are several different kinds of faults. There are two sides to a fault. The side that is above the fault plane is called the ____________________ ___________________. When the hanging ...
... Rocks don’t always bend, sometimes they break. When the rock moves and breaks it is called a _______________. There are several different kinds of faults. There are two sides to a fault. The side that is above the fault plane is called the ____________________ ___________________. When the hanging ...
Earthquake Waves - davis.k12.ut.us
... • We have a fault line running through our area called the Wasatch Fault • Because we are close to a lake, another concern is something called “liquefaction”, which is when loose, sandy soil behaves like a liquid when shaken • After class if interested I have a map up front of Davis County’s fault l ...
... • We have a fault line running through our area called the Wasatch Fault • Because we are close to a lake, another concern is something called “liquefaction”, which is when loose, sandy soil behaves like a liquid when shaken • After class if interested I have a map up front of Davis County’s fault l ...
The Ring of Fire - American Red Cross
... Scientists have discovered that the surface of the Earth is made up of tectonic plates — gigantic slabs of rock that fit together like the pieces of a puzzle. Some of these slabs are bigger than a continent, and the biggest is at the bottom of the Pacific Ocean. Unlike the pieces of a puzzle, the te ...
... Scientists have discovered that the surface of the Earth is made up of tectonic plates — gigantic slabs of rock that fit together like the pieces of a puzzle. Some of these slabs are bigger than a continent, and the biggest is at the bottom of the Pacific Ocean. Unlike the pieces of a puzzle, the te ...
Earth`s plates
... pieces called tectonic plates They float on the mantle Different sizes and shapes ...
... pieces called tectonic plates They float on the mantle Different sizes and shapes ...
3.0 Landforms provide evidence of change
... After more than a billion years of sediment buildup the collision of two plates happened. The North American Plate and the Pacific Plate met. The Pacific Plate was forced down and the North American Plate rode above it. But the force and pressure of the collision cause the edge of the North American ...
... After more than a billion years of sediment buildup the collision of two plates happened. The North American Plate and the Pacific Plate met. The Pacific Plate was forced down and the North American Plate rode above it. But the force and pressure of the collision cause the edge of the North American ...
crust - Madison County Schools
... samples give insight into the conditions present at those depths. ...
... samples give insight into the conditions present at those depths. ...
Chapter 4 volcanoes powerpoint notes
... 3. Volcanoes create fertile soils which enhance agriculture. 4. Volcanoes, depending on number, frequency, and eruption size, could contribute to global cooling and the origin of ice ages, due to the blocking out of the sun. Plants failing to photosynthesize could result in total collapse of food we ...
... 3. Volcanoes create fertile soils which enhance agriculture. 4. Volcanoes, depending on number, frequency, and eruption size, could contribute to global cooling and the origin of ice ages, due to the blocking out of the sun. Plants failing to photosynthesize could result in total collapse of food we ...
relative age dating
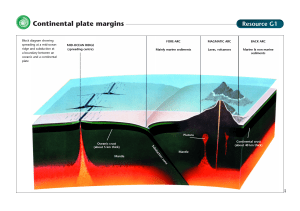
... LITHOSPHERE (PLATES) 1. DIVERGENT BOUNDARY 2. CONVERGENT BOUNDARY 3. TRANSFORM BOUNDARY ...
... LITHOSPHERE (PLATES) 1. DIVERGENT BOUNDARY 2. CONVERGENT BOUNDARY 3. TRANSFORM BOUNDARY ...
Quiz- Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks
... a. the rock has well-defined layers b. the rock is about 50 percent plagioclase feldspar c. the rock is light in color and low in density d. the rock has large crystals ...
... a. the rock has well-defined layers b. the rock is about 50 percent plagioclase feldspar c. the rock is light in color and low in density d. the rock has large crystals ...
Volcano Webquest
... What happens to the finest ash particles that get ejected from the volcano during an eruption? ...
... What happens to the finest ash particles that get ejected from the volcano during an eruption? ...
Study Guide / Notes 11
... 10. There are no abrupt breaks in the seismic velocities through the lower mantle. This suggests that the lower mantle is homogeneous. 11. Shear waves (S-waves) cannot travel through a liquid. S-waves passing through the earth that intercept the outer core are blocked. This indicates that the outer ...
... 10. There are no abrupt breaks in the seismic velocities through the lower mantle. This suggests that the lower mantle is homogeneous. 11. Shear waves (S-waves) cannot travel through a liquid. S-waves passing through the earth that intercept the outer core are blocked. This indicates that the outer ...
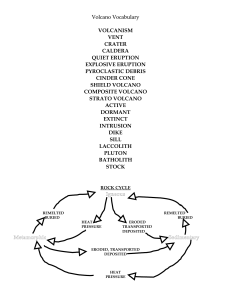
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... grain, or crystal, size. The deeper the intrusion, the larger the grain size 1. Volcanic Neck- is an intrusive structure composed of cooled magma trapped in the throat or vent of a volcano. 2. Dike- is a tabular, typically vertical intrusion ...
... grain, or crystal, size. The deeper the intrusion, the larger the grain size 1. Volcanic Neck- is an intrusive structure composed of cooled magma trapped in the throat or vent of a volcano. 2. Dike- is a tabular, typically vertical intrusion ...
Name - saddlespace.org
... •When a volcano is done erupting, there is usually a funnel-shaped in the ground from which the lava erupted. This is called a ...
... •When a volcano is done erupting, there is usually a funnel-shaped in the ground from which the lava erupted. This is called a ...
Variations in the structure and rheology of the lithosphere.
... young orogenic belts and the ancient Precambrian shields are responsible for first-order variations in tectonic history seen at the Earth’s surface over geological time. The last decade has seen a number of developments in the understanding of the lithosphere, some of which have challenged previousl ...
... young orogenic belts and the ancient Precambrian shields are responsible for first-order variations in tectonic history seen at the Earth’s surface over geological time. The last decade has seen a number of developments in the understanding of the lithosphere, some of which have challenged previousl ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.