Geology of National Parks
... Explain how the chemical composition of magmas relates to plate tectonics and affects the geometry, structure, and explosivity of volcanoes. E3.4 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Plate motions result in potentially catastrophic events (earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, mass wasting) that affect humanity. T ...
... Explain how the chemical composition of magmas relates to plate tectonics and affects the geometry, structure, and explosivity of volcanoes. E3.4 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Plate motions result in potentially catastrophic events (earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, mass wasting) that affect humanity. T ...
Lecture 2 Summer 2011
... 34. Columnar joints are due to the cooling of A.granite batholiths B.gabbro batholiths C.basalt lava flows D.all of the above may form columnar joints 35. ? rocks form from pre-existing rocks through solid-state transformation. A.igneous B.metamorphic C.sedimentary 36. Calderas are depressions that ...
... 34. Columnar joints are due to the cooling of A.granite batholiths B.gabbro batholiths C.basalt lava flows D.all of the above may form columnar joints 35. ? rocks form from pre-existing rocks through solid-state transformation. A.igneous B.metamorphic C.sedimentary 36. Calderas are depressions that ...
Deforming the Earth*s crust
... causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks. When sedimentary rock layers are tilted up by ...
... causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks. When sedimentary rock layers are tilted up by ...
Lesson 2 - Plate Tectonics - Hitchcock
... • Scientists have proposed three mechanisms to explain how tectonic plates move: mantle convection, ridge push, and slab pull. • Hotter parts of the mantle rise as cooler, denser parts sink. This kind of movement of material due to differences in density is called convection. • Mantle convection dra ...
... • Scientists have proposed three mechanisms to explain how tectonic plates move: mantle convection, ridge push, and slab pull. • Hotter parts of the mantle rise as cooler, denser parts sink. This kind of movement of material due to differences in density is called convection. • Mantle convection dra ...
Unit 4 Lesson 2 Plate Tectonics
... • Scientists have proposed three mechanisms to explain how tectonic plates move: mantle convection, ridge push, and slab pull. • Hotter parts of the mantle rise as cooler, denser parts sink. This kind of movement of material due to differences in density is called convection. • Mantle convection dra ...
... • Scientists have proposed three mechanisms to explain how tectonic plates move: mantle convection, ridge push, and slab pull. • Hotter parts of the mantle rise as cooler, denser parts sink. This kind of movement of material due to differences in density is called convection. • Mantle convection dra ...
Notes - Volcanoes
... What is a Volcano? • A volcano is a weak spot in the crust where molten material, magma, from the mantle comes to Earth’s surface. – Magma – a molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases and water. • When magma reaches the surface of Earth it is called lava. – When lava cools it creates new so ...
... What is a Volcano? • A volcano is a weak spot in the crust where molten material, magma, from the mantle comes to Earth’s surface. – Magma – a molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases and water. • When magma reaches the surface of Earth it is called lava. – When lava cools it creates new so ...
Presnall, D. C. (1980) A double partial melt zone in the mantle beneath mid-ocean ridges, Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 23, 103-111.
... 1978; Walker eta!., 1978) and Anderson and Minster (1980) have pointed out that the thickness of the lithosphere depends on whether seismic, thermal, or rheological properties are being considered. It will be seen in the following discussion that if the model of Presnall et a!. (1979) for the genera ...
... 1978; Walker eta!., 1978) and Anderson and Minster (1980) have pointed out that the thickness of the lithosphere depends on whether seismic, thermal, or rheological properties are being considered. It will be seen in the following discussion that if the model of Presnall et a!. (1979) for the genera ...
View/Open
... trench along the line where the subducted slab disappears, with a line of volcanic islands paralleling the trench on the overriding slab. Because of the geometry of a spherical planet, volcanoes associated with oceanic subduction zones tend to form broadly curving archipelagos ("arcs") of volcanic i ...
... trench along the line where the subducted slab disappears, with a line of volcanic islands paralleling the trench on the overriding slab. Because of the geometry of a spherical planet, volcanoes associated with oceanic subduction zones tend to form broadly curving archipelagos ("arcs") of volcanic i ...
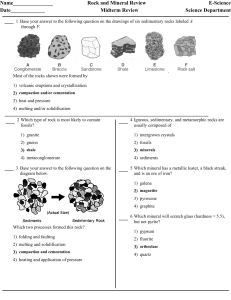
Rocks and Minerals Midterm Rev
... 20 In the simple rock-cycle diagram, which processes along path X would change the schist (stage C) directly into a pile of sediments (stage A)? 1) uplift, weathering, and erosion of the schist 2) cementing of sediment grains followed by compaction 3) melting of the schist followed by cooling 4) hea ...
... 20 In the simple rock-cycle diagram, which processes along path X would change the schist (stage C) directly into a pile of sediments (stage A)? 1) uplift, weathering, and erosion of the schist 2) cementing of sediment grains followed by compaction 3) melting of the schist followed by cooling 4) hea ...
Rock Cycle
... • First, students will make edible igneous rocks. In order to do this, the teacher must first melt approximately one bowl of chocolate chips in a microwave (or another heat source such as an Easy Bake Oven). ...
... • First, students will make edible igneous rocks. In order to do this, the teacher must first melt approximately one bowl of chocolate chips in a microwave (or another heat source such as an Easy Bake Oven). ...
Igneous Rocks Intrusions and Volcanoes
... example of these mixture. The more sodium, the more felsic the magma melt and the lighter the igneous rock( look at the chart on page 113). Mafic Rocks a have large amounts of olivine and pyroxenes giving the rocks their characteristic dark colors. There may be a small to moderate amount of calcium ...
... example of these mixture. The more sodium, the more felsic the magma melt and the lighter the igneous rock( look at the chart on page 113). Mafic Rocks a have large amounts of olivine and pyroxenes giving the rocks their characteristic dark colors. There may be a small to moderate amount of calcium ...
Env. Geol Entrance Exam Part 1 – Multiple Choice / True
... a. do not have more than one isotope. b. are found naturally in the earth. c. are common in rocks of the United States. d. occur as minerals consisting of a single element. 8. Magma that is erupted at the earth's surface is termed: a. lava. b. coarse-grained. c. sedimentary. d. granite. 9. The locat ...
... a. do not have more than one isotope. b. are found naturally in the earth. c. are common in rocks of the United States. d. occur as minerals consisting of a single element. 8. Magma that is erupted at the earth's surface is termed: a. lava. b. coarse-grained. c. sedimentary. d. granite. 9. The locat ...
Evidence for Plate Tectonics
... could not fly or swim between continents – Continents were together when these animals lived, so they could walk from one continent to another ...
... could not fly or swim between continents – Continents were together when these animals lived, so they could walk from one continent to another ...
Why is our earth unstable?
... What is the structure of the earth? Our earth can be divided into _______ three layers. From the surface to the centre, they are: ...
... What is the structure of the earth? Our earth can be divided into _______ three layers. From the surface to the centre, they are: ...
Jeopardy Game (ppt 9 MB)
... assemblages are not randomly distributed, but rather succeed one another in an orderly way across broad areas ...
... assemblages are not randomly distributed, but rather succeed one another in an orderly way across broad areas ...
Volcano Notes
... flat on the ground. It is composed of thinner more mafic lavas. Shield volcanoes have gentle and gradual eruptions. These erupt the most often. Example: Kilauea Other formations: Caldera – large crater-shaped basin that results from a big volcanic eruption. Lakes may be found in these. Rift Eruption ...
... flat on the ground. It is composed of thinner more mafic lavas. Shield volcanoes have gentle and gradual eruptions. These erupt the most often. Example: Kilauea Other formations: Caldera – large crater-shaped basin that results from a big volcanic eruption. Lakes may be found in these. Rift Eruption ...
Volcano
... Volcano-an opening in Earth’s crust through which lava may flow. Focus- the point where an earthquake starts. Lava- hot, melted rock that reaches Earth’s surface. Hot spot- a stationary location in Earth’s mantle where magma melts through a tectonic plate. 5. Epicenter- the point on Earth’s surface ...
... Volcano-an opening in Earth’s crust through which lava may flow. Focus- the point where an earthquake starts. Lava- hot, melted rock that reaches Earth’s surface. Hot spot- a stationary location in Earth’s mantle where magma melts through a tectonic plate. 5. Epicenter- the point on Earth’s surface ...
Plate Tectonics as a Far- From- Equilibrium Self
... organization and reorganization require; an open system, a large steady outside source of matter or energy, non-linear interconnectedness of system components, dissipation and a mechanism for exporting entropy products (19). Under these conditions the system responds as a whole, and in such a way as ...
... organization and reorganization require; an open system, a large steady outside source of matter or energy, non-linear interconnectedness of system components, dissipation and a mechanism for exporting entropy products (19). Under these conditions the system responds as a whole, and in such a way as ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.