Volcano
... Volcano-an opening in Earth’s crust through which lava may flow. Focus- the point where an earthquake starts. Lava- hot, melted rock that reaches Earth’s surface. Hot spot- a stationary location in Earth’s mantle where magma melts through a tectonic plate. 5. Epicenter- the point on Earth’s surface ...
... Volcano-an opening in Earth’s crust through which lava may flow. Focus- the point where an earthquake starts. Lava- hot, melted rock that reaches Earth’s surface. Hot spot- a stationary location in Earth’s mantle where magma melts through a tectonic plate. 5. Epicenter- the point on Earth’s surface ...
Three distinct margins of the North American and Eurasian Plates
... dependent on near-surface geology; all of Lisbon’s 40 churches were damaged and 35 were destroyed; only 10 out of the 75 convents remained and 33 palaces, the Arsenal, the Royal Library and the Patriarchal Palace were destroyed. Only 3000 of ~20,000 dwellings housing 38,000 families could be used af ...
... dependent on near-surface geology; all of Lisbon’s 40 churches were damaged and 35 were destroyed; only 10 out of the 75 convents remained and 33 palaces, the Arsenal, the Royal Library and the Patriarchal Palace were destroyed. Only 3000 of ~20,000 dwellings housing 38,000 families could be used af ...
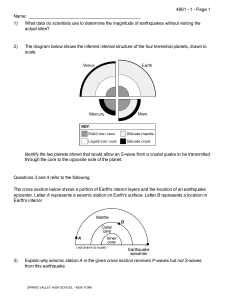
Name: 1) What data do scientists use to determine the magnitude of
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
The evolution of Middle America and the Gulf of l\tfexico
... units of Late Jurassic (Callovian to early Oxfordian) age in the Gulf Basin probably occurred contemporaneously with the arrival of these blocks at their present positions. Clastic units that interfinger with some of the youngest salt units and rim the Gulf of Mexico have not recorded major recogniz ...
... units of Late Jurassic (Callovian to early Oxfordian) age in the Gulf Basin probably occurred contemporaneously with the arrival of these blocks at their present positions. Clastic units that interfinger with some of the youngest salt units and rim the Gulf of Mexico have not recorded major recogniz ...
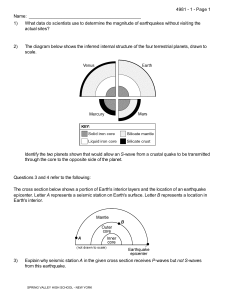
Name: 1) What data do scientists use to determine the magnitude of
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
It is my opinion that the Earth is very nob le and admirable ••• and if it
... Thus, we can identify three outer layers in the Earth; the buoyant crust, containing low density crustal minerals including quartz and feldspar; the shallow mantle containing high-temperature minerals and minerals that settle out of magma mushs rising to the surface - these minerals are primarily ol ...
... Thus, we can identify three outer layers in the Earth; the buoyant crust, containing low density crustal minerals including quartz and feldspar; the shallow mantle containing high-temperature minerals and minerals that settle out of magma mushs rising to the surface - these minerals are primarily ol ...
AUGUSTA COUNTY SCHOOLS CURRICULUM MAP Submitted by
... shale, sandstone, and coal), using a rock classification key. ...
... shale, sandstone, and coal), using a rock classification key. ...
Rock Cycling - Minerals Council of Australia
... The crust of the Earth is made up of rocks and minerals from the tallest mountains to the floor of the deepest ocean. It makes up less than 1% of the Earth’s mass. The continental crust is up to 50km thick while the oceanic crust is, at most, 15 km thick. Most of the rocky crust is covered by either ...
... The crust of the Earth is made up of rocks and minerals from the tallest mountains to the floor of the deepest ocean. It makes up less than 1% of the Earth’s mass. The continental crust is up to 50km thick while the oceanic crust is, at most, 15 km thick. Most of the rocky crust is covered by either ...
10_Volcanoes_and_Hazards
... In the Pacific Northwest, the Juan de Fuca Plate plunges beneath the North American Plate. As the denser plate of oceanic crust is forced deep into the Earth's interior beneath the continental plate, a process known as subduction, it encounters high temperatures and pressures that partially melt sol ...
... In the Pacific Northwest, the Juan de Fuca Plate plunges beneath the North American Plate. As the denser plate of oceanic crust is forced deep into the Earth's interior beneath the continental plate, a process known as subduction, it encounters high temperatures and pressures that partially melt sol ...
3 The Theory of Plate Tectonics Key Terms
... Review “Cause and Effect” (Q) What do scientists think causes the movement of Earth’s plates? “Write out answer in complete sentences” ...
... Review “Cause and Effect” (Q) What do scientists think causes the movement of Earth’s plates? “Write out answer in complete sentences” ...
Mountain Building DOC
... The major types of mountains include volcanic mountains, folded mountains, fault-block mountains, and dome mountains. • Geologists refer to the collection of processes involved in mountain building as orogenesis. • Mountains that are formed primarily by compressional stresses, which create folds in ...
... The major types of mountains include volcanic mountains, folded mountains, fault-block mountains, and dome mountains. • Geologists refer to the collection of processes involved in mountain building as orogenesis. • Mountains that are formed primarily by compressional stresses, which create folds in ...
Igneous rocks
... Origins of Magma Factors That Affect Magma Formation – Mineral content also impacts how magma is formed as different minerals have different melting points. – In general, oceanic crust is rich in iron and magnesium and therefore melts at higher temperatures than continental crust, which contains hig ...
... Origins of Magma Factors That Affect Magma Formation – Mineral content also impacts how magma is formed as different minerals have different melting points. – In general, oceanic crust is rich in iron and magnesium and therefore melts at higher temperatures than continental crust, which contains hig ...
Evolution of continents, cratons and supercontinents: building the
... Jordan23 proposed the term 'tectosphere' for the highly depleted and relatively low-density upper mantle layer, and tomographic images beneath old cratons clearly show high-velocity roots extending to at least 200 km depth, and in some cases even up to 300 km (ref. 24). Tectosphere, also known as co ...
... Jordan23 proposed the term 'tectosphere' for the highly depleted and relatively low-density upper mantle layer, and tomographic images beneath old cratons clearly show high-velocity roots extending to at least 200 km depth, and in some cases even up to 300 km (ref. 24). Tectosphere, also known as co ...
Test Review Building Up and Wearing Down the Surface
... Plate Tectonics. You are to include in your discussion who the scientist was that was a major contributor of the theory, then provide an explanation of how the crustal plates move, what happens at plate boundaries, what geologic activity occurs there and why. Draw a fully labelled diagram of how con ...
... Plate Tectonics. You are to include in your discussion who the scientist was that was a major contributor of the theory, then provide an explanation of how the crustal plates move, what happens at plate boundaries, what geologic activity occurs there and why. Draw a fully labelled diagram of how con ...
Chapter 21.1 PPT - Madison County Schools
... Plate Tectonics, continued • Alignment of oceanic rocks supports the theory of moving plates. – Iron in molten rock aligns itself with Earth’s magnetic field as it cools. – The Earth’s magnetic field reverses polarity about every 200,000 years. – The process is recorded as magnetic bands in rock, ba ...
... Plate Tectonics, continued • Alignment of oceanic rocks supports the theory of moving plates. – Iron in molten rock aligns itself with Earth’s magnetic field as it cools. – The Earth’s magnetic field reverses polarity about every 200,000 years. – The process is recorded as magnetic bands in rock, ba ...
Can a Horizontal Astronomical Driving Force and an
... buckle wavelength in simulations in which the radius of the Earth and the thicknesses of the sublithospheric mantle and the lithosphere were varied, as well as the ratio of the moduli of the two layers over a range consistent with observed variance of these parameters on Earth. The wavelength of the ...
... buckle wavelength in simulations in which the radius of the Earth and the thicknesses of the sublithospheric mantle and the lithosphere were varied, as well as the ratio of the moduli of the two layers over a range consistent with observed variance of these parameters on Earth. The wavelength of the ...
Inside the Earth
... same processes that are at work today were at work in the past. Summarized by “The present is the key to the past.” Hutton recognized that time is the critical element to the formation of common geologic structures. Uniformitarianism is a basic foundation of modern geology. ...
... same processes that are at work today were at work in the past. Summarized by “The present is the key to the past.” Hutton recognized that time is the critical element to the formation of common geologic structures. Uniformitarianism is a basic foundation of modern geology. ...
Chapter 3 Understanding the `big ideas`: major concepts that
... sideways away from these ridges until it sank into oceanic trenches. This was his ‘Sea Floor Spreading’ theory, but Hess was able to publish no strong evidence to support his theory, apart from the shapes of the ocean floors. It was a year later, in 1963, that two British geologists, Fred Vine and D ...
... sideways away from these ridges until it sank into oceanic trenches. This was his ‘Sea Floor Spreading’ theory, but Hess was able to publish no strong evidence to support his theory, apart from the shapes of the ocean floors. It was a year later, in 1963, that two British geologists, Fred Vine and D ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.