File - PHYSICS AP/DUAL
... 12. A cart with mass m has a velocity v before it strikes another cart of mass 3m at rest. The two carts couple and move off together with a velocity of (A) v/5 (B) 2v/5 (C) 3v/5 (D) 2v/3 (E) v/4 13. A 40 kg skater at rest on a frictionless rink throws a 3 kg ball, giving the ball a velocity of 10 m ...
... 12. A cart with mass m has a velocity v before it strikes another cart of mass 3m at rest. The two carts couple and move off together with a velocity of (A) v/5 (B) 2v/5 (C) 3v/5 (D) 2v/3 (E) v/4 13. A 40 kg skater at rest on a frictionless rink throws a 3 kg ball, giving the ball a velocity of 10 m ...
Momentum
... A property of a moving body that determines the length of time required to bring it to rest when under the action of a constant force or moment. ...
... A property of a moving body that determines the length of time required to bring it to rest when under the action of a constant force or moment. ...
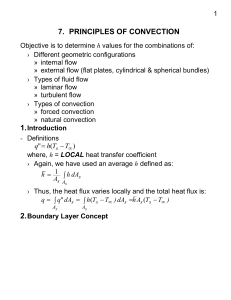
Convection Principles
... The distance from the wall to a point where u( y) 0.99u - Thermal Boundary Layer › The thermal BL develops because of the temperature difference between the free stream and the plate wall ...
... The distance from the wall to a point where u( y) 0.99u - Thermal Boundary Layer › The thermal BL develops because of the temperature difference between the free stream and the plate wall ...
List of Topics for the Final Exam
... of C has a mass number of 13 and therefore, 6 protons, 7 neutrons and 6 electrons periodic table: s and p blocks, alkali metals, halogens, noble gases, groups (vertical) vs. periods (horizontal) groups are similar because they have the same number of valence electrons flame test lab, quantization of ...
... of C has a mass number of 13 and therefore, 6 protons, 7 neutrons and 6 electrons periodic table: s and p blocks, alkali metals, halogens, noble gases, groups (vertical) vs. periods (horizontal) groups are similar because they have the same number of valence electrons flame test lab, quantization of ...
Geograph2
... is always true: If a stationary object breaks up into a number of parts then the sum of all their momenta - when due account is taken of their various directions - will be zero, which was the momentum of the object before it broke up. On the other hand, if a moving object breaks up while in motion, ...
... is always true: If a stationary object breaks up into a number of parts then the sum of all their momenta - when due account is taken of their various directions - will be zero, which was the momentum of the object before it broke up. On the other hand, if a moving object breaks up while in motion, ...
for reference Name Period ______ Date ______ Motion Notes from
... Acceleration: The rate of change in velocity. To calculate acceleration, use this equation: Acceleration = (Final Velocity) - (Original Velocity) / Time Deceleration: A term commonly used to mean a decrease in speed. Force: any push or pull. Forces cause a change in motion. Friction: a force tha ...
... Acceleration: The rate of change in velocity. To calculate acceleration, use this equation: Acceleration = (Final Velocity) - (Original Velocity) / Time Deceleration: A term commonly used to mean a decrease in speed. Force: any push or pull. Forces cause a change in motion. Friction: a force tha ...
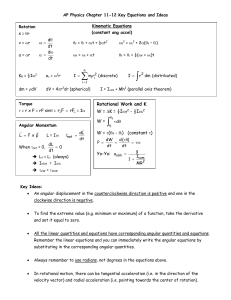
AP Physics Chapter 11-12 Key Equations and Ideas Rotation s = qr
... the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
... the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...