$doc.title
... Problem 7. The figure below is a graph of the energy of a system of a planet interacting with a star. The gravitational potential energy Ug is shown as the thick curve, and plotted along the ...
... Problem 7. The figure below is a graph of the energy of a system of a planet interacting with a star. The gravitational potential energy Ug is shown as the thick curve, and plotted along the ...
Energy
... Draw energy bar charts that describe energy transfers between objects at different points in time. Write and solve conservation of energy problems that are consistent with these bar chart diagrams. State and apply the Law of Conservation of Energy. Distinguish between total energy and change in ener ...
... Draw energy bar charts that describe energy transfers between objects at different points in time. Write and solve conservation of energy problems that are consistent with these bar chart diagrams. State and apply the Law of Conservation of Energy. Distinguish between total energy and change in ener ...
Newton Review
... Use Chapters 1 & 2 in your book to help you find the answers to the questions below. 1. Write Newton’s first law. Law of Inertia: objects remain in motion, or at rest, until a force acts upon them. 2. Give an example of Newton’s first law using a rocket in your example. A rocket lifts off until grav ...
... Use Chapters 1 & 2 in your book to help you find the answers to the questions below. 1. Write Newton’s first law. Law of Inertia: objects remain in motion, or at rest, until a force acts upon them. 2. Give an example of Newton’s first law using a rocket in your example. A rocket lifts off until grav ...
Momentum and Energy
... Although it sounds intimidating, the WorkEnergy Theorem is not a difficult concept. In short, if you do work on an object, you change that object’s total energy by exactly the same amount of work you put into it. Here, you are pushing the block ...
... Although it sounds intimidating, the WorkEnergy Theorem is not a difficult concept. In short, if you do work on an object, you change that object’s total energy by exactly the same amount of work you put into it. Here, you are pushing the block ...
FREE ENERGY & Antigravity
... General Relativity. He stated “there is no experiment a person could conduct in a small volume of space that would distinguish between a gravitational field and an equivalent uniform acceleration”. Is that so??? ...
... General Relativity. He stated “there is no experiment a person could conduct in a small volume of space that would distinguish between a gravitational field and an equivalent uniform acceleration”. Is that so??? ...
Einstein and Relativity 0.1 Overview 0.2 Discrepancies With
... Eventually, through the further work of Galileo, Newton, and others, people came to speak about frames of reference. A frame of reference is any frame of experience that is moving at a constant speed. We refer to this unaccelerated frame as an inertial frame. When in a frame of reference, you can on ...
... Eventually, through the further work of Galileo, Newton, and others, people came to speak about frames of reference. A frame of reference is any frame of experience that is moving at a constant speed. We refer to this unaccelerated frame as an inertial frame. When in a frame of reference, you can on ...
Microsoft Word - SPH 3U, T2L6, Newton`s Second Law.doc
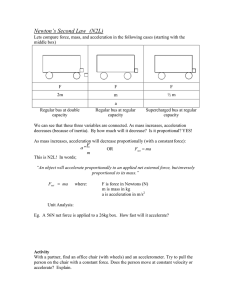
... Newton’s Second Law (N2L) Lets compare force, mass, and acceleration in the following cases (starting with the middle box) ...
... Newton’s Second Law (N2L) Lets compare force, mass, and acceleration in the following cases (starting with the middle box) ...
Unit 4 SG
... 5. Draw a velocity versus time graph showing the following: A zebra moves from rest to a constant speed of 2 m/s for 2 seconds, then it stops for 4 seconds to drink water, and then takes off running at 4 m/s for 2 ...
... 5. Draw a velocity versus time graph showing the following: A zebra moves from rest to a constant speed of 2 m/s for 2 seconds, then it stops for 4 seconds to drink water, and then takes off running at 4 m/s for 2 ...
Document
... _____ 6. When a soccer ball is kicked, the action and reaction forces do not cancel each other out because a. the forces are not equal in size. b. the forces act on different objects. c. the forces act at different times. d. All of the above ______ 7. .Newton’s first law of motion applies to a. movi ...
... _____ 6. When a soccer ball is kicked, the action and reaction forces do not cancel each other out because a. the forces are not equal in size. b. the forces act on different objects. c. the forces act at different times. d. All of the above ______ 7. .Newton’s first law of motion applies to a. movi ...
Energy of the universe is conserved Mechanical Energy
... without air drag with respect to both time and position. a. Find the work done by the person on the box for the first 6 meters of pushing. ...
... without air drag with respect to both time and position. a. Find the work done by the person on the box for the first 6 meters of pushing. ...