Newtons` second law is customarily presented to beginning students
... 1. Introduction. Center of gravity, center of mass, this concept seems very familiar. Indeed, many people including students of science have used the phrase in daily conversation. Yet, “what is the center of mass?”, and of more concern, what are its properties? We explore these ideas in the attempt ...
... 1. Introduction. Center of gravity, center of mass, this concept seems very familiar. Indeed, many people including students of science have used the phrase in daily conversation. Yet, “what is the center of mass?”, and of more concern, what are its properties? We explore these ideas in the attempt ...
1 - HCC Learning Web
... velocity of 10 m/s from rest. Find the average force exerted on the shot during this time. a. 175 N b. 350 N c. 525 N d. 700 N 12. In the terminology a 500-N block, the 500-N refers to the block’s: a. mass. b. force. c. weight. d. None of the above. 13. The statement by Newton that “for every action ...
... velocity of 10 m/s from rest. Find the average force exerted on the shot during this time. a. 175 N b. 350 N c. 525 N d. 700 N 12. In the terminology a 500-N block, the 500-N refers to the block’s: a. mass. b. force. c. weight. d. None of the above. 13. The statement by Newton that “for every action ...
Complete Inelastic Collisions in 1-D
... Elastic Collisions in 1-D One trick: Go into a coordinate system where one of the masses is initially at rest Change all velocities by one of the initial velocities Say we make: w2i= v2i-v2i=0 v1i ...
... Elastic Collisions in 1-D One trick: Go into a coordinate system where one of the masses is initially at rest Change all velocities by one of the initial velocities Say we make: w2i= v2i-v2i=0 v1i ...
Potential Energy and Equilibrium in 1D - FSU
... The Work-Energy Theorem: If work is the only form of energy transferred to a system, the law of conservation of energy becomes Wext = 4Esys where Wext is the work done on the system by external forces. ...
... The Work-Energy Theorem: If work is the only form of energy transferred to a system, the law of conservation of energy becomes Wext = 4Esys where Wext is the work done on the system by external forces. ...
5.1,2 Work and Energy Theorem. Work has different meaning in physics.
... Work is a scalar quantity. W2 SI unit is J (joule) Here we used equation of motion under a W1 W1 The U.S. customary unit is the foot-pound. constant acceleration to derive work-energy Work can be positive or negative. theorem. But this is a valid under all W1 W2 If a force and a displacement are i ...
... Work is a scalar quantity. W2 SI unit is J (joule) Here we used equation of motion under a W1 W1 The U.S. customary unit is the foot-pound. constant acceleration to derive work-energy Work can be positive or negative. theorem. But this is a valid under all W1 W2 If a force and a displacement are i ...
2014-15 1st Semester Physics Review
... d. a variable amount. e. a rate that depends on its initial speed. ____ 77. Whenever an object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of the same magnitude, but in the opposite direction to that of the first object. a. Sometimes true b. Always true c. Always false ____ 78 ...
... d. a variable amount. e. a rate that depends on its initial speed. ____ 77. Whenever an object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of the same magnitude, but in the opposite direction to that of the first object. a. Sometimes true b. Always true c. Always false ____ 78 ...
Student Review Sheet Physics Semester A Examination
... given the forces acting on an object and the mass of the object, determine the acceleration. given a vector diagram of an object’s velocity, determine the magnitude of its components. interpret a position versus time graph to determine the velocity and initial position of an object. given ve ...
... given the forces acting on an object and the mass of the object, determine the acceleration. given a vector diagram of an object’s velocity, determine the magnitude of its components. interpret a position versus time graph to determine the velocity and initial position of an object. given ve ...
DV_Matter-Teacher
... • There is a force exerted on an object as the result of the mass of the Earth – Therefore, the object is accelerated (I.e. the speed increases) when released At time = 0 seconds, an object is released with no velocity ...
... • There is a force exerted on an object as the result of the mass of the Earth – Therefore, the object is accelerated (I.e. the speed increases) when released At time = 0 seconds, an object is released with no velocity ...
Chapter Summary
... Introduction • Objects have been treated as “point particles” • Mass is located at a single point in space • This assumption is very useful • This is the correct way to deal with many situations • Not all types of motion can be dealt with using this approach • May have to consider the object as an ...
... Introduction • Objects have been treated as “point particles” • Mass is located at a single point in space • This assumption is very useful • This is the correct way to deal with many situations • Not all types of motion can be dealt with using this approach • May have to consider the object as an ...
CTEnergyAnsFa06
... CTEnergy-19. A hockey puck sliding on an ice rink is moving at 1 m/s when it slides onto a carpet that someone left on the ice. The puck comes to rest after moving 1m on the carpet. How far along the carpet would the puck go, if its initial speed was 2m/s? ...
... CTEnergy-19. A hockey puck sliding on an ice rink is moving at 1 m/s when it slides onto a carpet that someone left on the ice. The puck comes to rest after moving 1m on the carpet. How far along the carpet would the puck go, if its initial speed was 2m/s? ...
Physics Final Review Sheet Name
... 21. If a force of 10 N is applied to an object with a mass of 1 kg, the object will accelerate at ...
... 21. If a force of 10 N is applied to an object with a mass of 1 kg, the object will accelerate at ...
kinetic energy
... THE WORK OF A FORCE (Section 18.2) Recall that the work done by a force can be written as: ...
... THE WORK OF A FORCE (Section 18.2) Recall that the work done by a force can be written as: ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
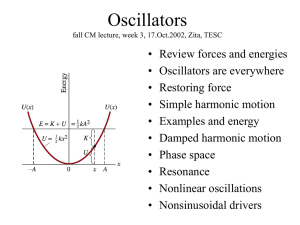
... Find x0 for minimum V0 (at dV/dx=0) Think about how to find x(t) near the bottom of potential well. ...
... Find x0 for minimum V0 (at dV/dx=0) Think about how to find x(t) near the bottom of potential well. ...