study guide for test - OldTurnpikeGradeEightScience
... Weight is a force calculated with Newton’s Second Law. It is measured in Newtons and is the product of g and mass. 13. 560 N 14. c 15. b 16. a 17. The chimp and the banana would hit the ground together in a vacuum. There is no air resistance to balance gravity, so both would be in free fall. Gravita ...
... Weight is a force calculated with Newton’s Second Law. It is measured in Newtons and is the product of g and mass. 13. 560 N 14. c 15. b 16. a 17. The chimp and the banana would hit the ground together in a vacuum. There is no air resistance to balance gravity, so both would be in free fall. Gravita ...
Unit 5 Review
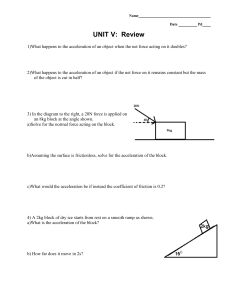
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
Work Power Energy Exams1 (Work) and Problem Solutions 1. In the
... Since masses of the objects are equal, and distance taken by the objects are equal, work done on gravity of three objects are equal. 4. In the picture given below, forces act on objects. Works done on objects during time t are W1, W2 and W3. Find the relation of the works. ...
... Since masses of the objects are equal, and distance taken by the objects are equal, work done on gravity of three objects are equal. 4. In the picture given below, forces act on objects. Works done on objects during time t are W1, W2 and W3. Find the relation of the works. ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... Newton’s second law of motion is perhaps his most famous. This leaflet will discuss this law and give some examples of its use. ...
... Newton’s second law of motion is perhaps his most famous. This leaflet will discuss this law and give some examples of its use. ...
work and energy
... The ability to do work (an imperfect definition) Many types exist: mechanical (potential, kinetic), heat, light, electrical, magnetic, nuclear They can change from one to another The sum of all of them (total energy)is conserved ...
... The ability to do work (an imperfect definition) Many types exist: mechanical (potential, kinetic), heat, light, electrical, magnetic, nuclear They can change from one to another The sum of all of them (total energy)is conserved ...
Final Exam Practice questions
... 10) A 100 N traffic light is suspended by two wires of length L1 and L2 as shown in the figure. If L1 = 3.0 m and L2 = 5.0 m and the distance x = 2.0 m, then the tension in the wire of length L1 is, a) 125 N b) 101 N c) 90 N d) 82 N e) 75 N 11) You are designing a soap-box derby race car that will r ...
... 10) A 100 N traffic light is suspended by two wires of length L1 and L2 as shown in the figure. If L1 = 3.0 m and L2 = 5.0 m and the distance x = 2.0 m, then the tension in the wire of length L1 is, a) 125 N b) 101 N c) 90 N d) 82 N e) 75 N 11) You are designing a soap-box derby race car that will r ...
Physics - CSUN.edu
... how to resolve two-dimensional vectors into their components and calculate the magnitude and direction of a vector from its components. k.* how to solve two-dimensional problems involving balanced forces (statics). l.* how to solve problems in circular motion, using the formula for centripetal accel ...
... how to resolve two-dimensional vectors into their components and calculate the magnitude and direction of a vector from its components. k.* how to solve two-dimensional problems involving balanced forces (statics). l.* how to solve problems in circular motion, using the formula for centripetal accel ...
Chapter 7 - s3.amazonaws.com
... A property of the state of an object Scalar quantity – no direction Conserved – cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change from one form to another or be exchanged from one object to another Units: Joule = kg m2/s2 ...
... A property of the state of an object Scalar quantity – no direction Conserved – cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change from one form to another or be exchanged from one object to another Units: Joule = kg m2/s2 ...
Energy of Interaction
... If we rename (r1 – r2) as r, we finally have: Wtot -dr U (r) -dU . Let’s pause to appreciate this result. It says that if the force of interaction between two particles is conservative, then we can define a potential energy throughout space. As the particles move, the potential energy changes ...
... If we rename (r1 – r2) as r, we finally have: Wtot -dr U (r) -dU . Let’s pause to appreciate this result. It says that if the force of interaction between two particles is conservative, then we can define a potential energy throughout space. As the particles move, the potential energy changes ...
physics140-f07-lecture5 - Open.Michigan
... You assume all responsibility for use and potential liability associated with any use of the material. Material contains copyrighted content, used in accordance with U.S. law. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact [email protected] with any questions, correction ...
... You assume all responsibility for use and potential liability associated with any use of the material. Material contains copyrighted content, used in accordance with U.S. law. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact [email protected] with any questions, correction ...
Chapter 8 and 9 Study Guide
... 2. A 30-kg girl and a 50-kg boy face each other on friction-free roller skates. The girl pushes the boy, who moves away at a speed of 3 m/s. What is the girl's speed? 3. A 40-kg football player leaps through the air to collide with and tackle a 50-kg player heading toward him, also in the air. If th ...
... 2. A 30-kg girl and a 50-kg boy face each other on friction-free roller skates. The girl pushes the boy, who moves away at a speed of 3 m/s. What is the girl's speed? 3. A 40-kg football player leaps through the air to collide with and tackle a 50-kg player heading toward him, also in the air. If th ...
Sects. 12.3 through 12.4
... horizontal force of 20.0 N is required to hold the object at rest when it is pulled 0.200 m from its equilibrium position (the origin of the x axis). The object is now released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) th ...
... horizontal force of 20.0 N is required to hold the object at rest when it is pulled 0.200 m from its equilibrium position (the origin of the x axis). The object is now released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) th ...