A solid disk with mass = 0
... c) If the skater decreases her rotational inertia to 25 kg.m2, what will be the skater’s new rotational speed? ...
... c) If the skater decreases her rotational inertia to 25 kg.m2, what will be the skater’s new rotational speed? ...
Second Law of Motion - St. Paul School | San Pablo, CA
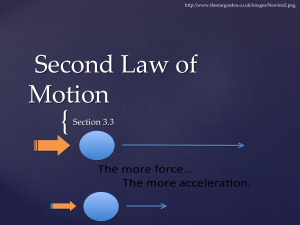
... Newton’s second law shows the relationship between what values? What does Newton’s second law state? How does the weight of an object affect its acceleration? How would increasing the force applied to an object affect the acceleration? a. ...
... Newton’s second law shows the relationship between what values? What does Newton’s second law state? How does the weight of an object affect its acceleration? How would increasing the force applied to an object affect the acceleration? a. ...
Elastic potential energy
... 3.3 Power: The rate of doing work. The rate at which energy is transferred or transformed. Work done divided by the time. Energy transferred divided by the time. P[watt] =W[J]/t[s] ...
... 3.3 Power: The rate of doing work. The rate at which energy is transferred or transformed. Work done divided by the time. Energy transferred divided by the time. P[watt] =W[J]/t[s] ...
Solutions to
... A block of mass 0.500 kg is pushed against a horizontal spring of negligible mass until the spring is compressed a distance x (Fig. P8.61). The force constant of the spring is 450 N/m. When it is released, the block travels along a frictionless, horizontal surface to point B, the bottom of a vertica ...
... A block of mass 0.500 kg is pushed against a horizontal spring of negligible mass until the spring is compressed a distance x (Fig. P8.61). The force constant of the spring is 450 N/m. When it is released, the block travels along a frictionless, horizontal surface to point B, the bottom of a vertica ...
1st Day of Physics!!
... Using an animal could help, but what they really needed were some clever ways to either make work easier or faster. ...
... Using an animal could help, but what they really needed were some clever ways to either make work easier or faster. ...
Lec 11 - Mr. Lee at Hamilton High School
... Practice: A rifle can shoot a 4.20-g bullet at a speed of 965 m/s. a) Find the kinetic energy of the bullet. b) What work is done on the bullet if it starts from rest? c) If the work is done over a distance of 0.75 m, what is the average force on the bullet? d) If the bullet comes to rest by pushin ...
... Practice: A rifle can shoot a 4.20-g bullet at a speed of 965 m/s. a) Find the kinetic energy of the bullet. b) What work is done on the bullet if it starts from rest? c) If the work is done over a distance of 0.75 m, what is the average force on the bullet? d) If the bullet comes to rest by pushin ...
Newton`s Laws - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... In most situations, there is more than one force acting on an object at any given time When we draw the FBD we should label all forces that are acting on an object and also determine which would cancel each other out Ones that do not completely cancel out will be used to determine the net force ...
... In most situations, there is more than one force acting on an object at any given time When we draw the FBD we should label all forces that are acting on an object and also determine which would cancel each other out Ones that do not completely cancel out will be used to determine the net force ...
Mechanics 1: Newton`s Laws
... In terms of units, we can give a definition of force. A dyne is the force that will give a 1 gm mass an acceleration of 1 cm/sec2 . A newton is the force that will give a 1 kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/sec2 . Inertial Frames of Reference and Absolute Motion. It needs to be stated that in the cours ...
... In terms of units, we can give a definition of force. A dyne is the force that will give a 1 gm mass an acceleration of 1 cm/sec2 . A newton is the force that will give a 1 kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/sec2 . Inertial Frames of Reference and Absolute Motion. It needs to be stated that in the cours ...
On the Shoulders of Giants”
... Since x, y, and z are orthogonal and linearly independent, I can write a Lagrange’s EOM for each. In order to conserve space, I call x, y, and z to be dimensions 1, 2, and 3. ...
... Since x, y, and z are orthogonal and linearly independent, I can write a Lagrange’s EOM for each. In order to conserve space, I call x, y, and z to be dimensions 1, 2, and 3. ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... • If an object is in vertical equilibrium (ie it is confined to a stationary horizontal surface) then (Fnet)y = 0. The sum of y-components of all forces = 0. • If an object is in horizontal equilibrium (ie freefall) then (Fnet)x = 0. ...
... • If an object is in vertical equilibrium (ie it is confined to a stationary horizontal surface) then (Fnet)y = 0. The sum of y-components of all forces = 0. • If an object is in horizontal equilibrium (ie freefall) then (Fnet)x = 0. ...