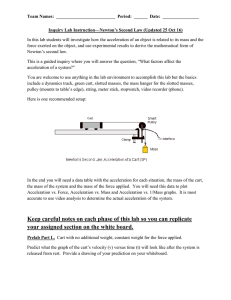
7 - MIT
... What is the minimum total mechanical energy that the particle can have if you know that it has traveled over the entire region of X shown? ...
... What is the minimum total mechanical energy that the particle can have if you know that it has traveled over the entire region of X shown? ...
Chapter 3 Review - tylerparkerphysicalscience
... Law of conservation of momentum-states that as long as interacting objects are not influenced by outside forces (like friction), their momentum before the interaction will equal their momentum after the interaction. Newton’s first law of motion-states any object at rest will remain at rest unless ac ...
... Law of conservation of momentum-states that as long as interacting objects are not influenced by outside forces (like friction), their momentum before the interaction will equal their momentum after the interaction. Newton’s first law of motion-states any object at rest will remain at rest unless ac ...
Rotation of Rigid Bodies - wbm
... An airplane propeller (I=(1/12)ML2) is 2.08 m in length (from tip to tip) with mass 117 kg. The propeller is rotating at 2400 rev/min about an axis through it’s center. ...
... An airplane propeller (I=(1/12)ML2) is 2.08 m in length (from tip to tip) with mass 117 kg. The propeller is rotating at 2400 rev/min about an axis through it’s center. ...
Physics Lecture Notes (abridged)
... 1. occurs when there is a constant acceleration at right angles to the velocity 2. constant perimeter (tangential) speed: vt = 2r/T a. distance = circumference of the circle: 2r b. time = time for one revolution: T (period) 3. constant inward (centripetal) acceleration: ac = v2/r G. Newton’s laws ...
... 1. occurs when there is a constant acceleration at right angles to the velocity 2. constant perimeter (tangential) speed: vt = 2r/T a. distance = circumference of the circle: 2r b. time = time for one revolution: T (period) 3. constant inward (centripetal) acceleration: ac = v2/r G. Newton’s laws ...
4 Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... • A heavy truck is harder to stop than a small car moving at the same speed. We say that the truck has more momentum than the car. • A small bullet moving at a high speed can have the same large momentum as a huge ship moving at a small speed. By Momentum we mean inertia in motion Momentum = mass ...
... • A heavy truck is harder to stop than a small car moving at the same speed. We say that the truck has more momentum than the car. • A small bullet moving at a high speed can have the same large momentum as a huge ship moving at a small speed. By Momentum we mean inertia in motion Momentum = mass ...
Document
... Mechanical energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion or its position. Radiant energy includes light, microwaves, radio waves, x-rays, and other forms of ...
... Mechanical energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion or its position. Radiant energy includes light, microwaves, radio waves, x-rays, and other forms of ...
ENERGY
... remains of organisms that lived millions of years ago. C. The use of fossil fuels presents several disadvantages. 1. Oil and natural gas reserves will not last indefinitely. 2. Although coal reserves will last several hundred more years, mining coal is dangerous, and burning coal creates environment ...
... remains of organisms that lived millions of years ago. C. The use of fossil fuels presents several disadvantages. 1. Oil and natural gas reserves will not last indefinitely. 2. Although coal reserves will last several hundred more years, mining coal is dangerous, and burning coal creates environment ...
Work & Energy - Christos N. Hadjichristidis
... Work done by a force=F x distance moved in the direction of force Be Extra Careful: Work is not always Force x Distance: If the acting force has no component in the direction of the movement (or if the force is acting perpendicular at the direction of the movement) then the force does not cause the ...
... Work done by a force=F x distance moved in the direction of force Be Extra Careful: Work is not always Force x Distance: If the acting force has no component in the direction of the movement (or if the force is acting perpendicular at the direction of the movement) then the force does not cause the ...
CBSE Class 9 Work Energy and Power Quick Study Chapter...
... Water stored in reservoir has large amount of potential energy due to which it can drive a water turbine when allowed to fall down. This is the principle of production of hydro electric energy. Expression for potential energy of a body above the ground level Consider an object of mass m. It is raise ...
... Water stored in reservoir has large amount of potential energy due to which it can drive a water turbine when allowed to fall down. This is the principle of production of hydro electric energy. Expression for potential energy of a body above the ground level Consider an object of mass m. It is raise ...
Chapter2_2
... The units of power are joule/sec (J/s) = Watt (W) James Watt (1736-1819); Scottish inventor and engineer whose improvements to the steam engine were fundamental to the changes wrought by the Industrial Revolution. (from Wikipedia) ...
... The units of power are joule/sec (J/s) = Watt (W) James Watt (1736-1819); Scottish inventor and engineer whose improvements to the steam engine were fundamental to the changes wrought by the Industrial Revolution. (from Wikipedia) ...
document
... Reading Quiz Review • Choose the correct response: According to Newton's Third Law • If you push on a chair, the chair must push back on you." • "The sum of all forces on an object must be zero." • "Accelerations are caused by forces." • "None of the above." ...
... Reading Quiz Review • Choose the correct response: According to Newton's Third Law • If you push on a chair, the chair must push back on you." • "The sum of all forces on an object must be zero." • "Accelerations are caused by forces." • "None of the above." ...