Question Identical constant forces push two identical objects A
... What is the minimum total mechanical energy that the particle can have if you know that it has traveled over the entire region of X shown? ...
... What is the minimum total mechanical energy that the particle can have if you know that it has traveled over the entire region of X shown? ...
AP B MC Midterm Answers 2004
... a) It is equal to h/2 b) It is equal to h/4 c) It is equal to h/2 d) It is equal to h e) It is between zero and h; height depends on how much energy is lost to friction. 34. A ball falls straight down through the air under the influence of gravity. There is a retarding force F on the ball with magn ...
... a) It is equal to h/2 b) It is equal to h/4 c) It is equal to h/2 d) It is equal to h e) It is between zero and h; height depends on how much energy is lost to friction. 34. A ball falls straight down through the air under the influence of gravity. There is a retarding force F on the ball with magn ...
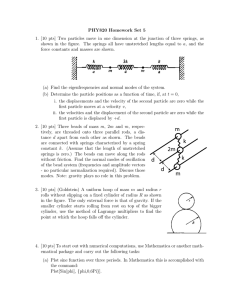
PHY820 Homework Set 5
... 1. [10 pts] Two particles move in one dimension at the junction of three springs, as shown in the figure. The springs all have unstretched lengths equal to a, and the force constants and masses are shown. ...
... 1. [10 pts] Two particles move in one dimension at the junction of three springs, as shown in the figure. The springs all have unstretched lengths equal to a, and the force constants and masses are shown. ...
Regular Physics Mid-Term Review Packet
... 31. The acceleration of an object acted upon by a force is directly proportional to the applied force and inversely proportional to the mass. 32. Based on Newton’s 2nd law, if mass of an object doubles, for the same applied force, what happens to its acceleration. 33. For the same mass if the force ...
... 31. The acceleration of an object acted upon by a force is directly proportional to the applied force and inversely proportional to the mass. 32. Based on Newton’s 2nd law, if mass of an object doubles, for the same applied force, what happens to its acceleration. 33. For the same mass if the force ...
Potoourii of Interia Demos - Otterbein Neutrino Research Group
... The bicycle wheel, you, and the chair comprise a system that obeys the principle of conservation of angular momentum. This means that any change in angular momentum within the system must be accompanied by an equal and opposite change, so the net effect is zero. Suppose you are now sitting on the st ...
... The bicycle wheel, you, and the chair comprise a system that obeys the principle of conservation of angular momentum. This means that any change in angular momentum within the system must be accompanied by an equal and opposite change, so the net effect is zero. Suppose you are now sitting on the st ...
Chapter 4
... Gravity- is an attractive force between any two objects that depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. The force increases as the mass of either object increases, or as the objects move closer. There are 4 basic forces. They are Electromagnetic-electricity and magneti ...
... Gravity- is an attractive force between any two objects that depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. The force increases as the mass of either object increases, or as the objects move closer. There are 4 basic forces. They are Electromagnetic-electricity and magneti ...
chapter 2 - UniMAP Portal
... Initially, the internal energy of the fluid is 800 kJ. During the cooling process, the fluid loses 500 kJ of heat, and the paddle wheel does 100 kJ of work on the fluid. Determine the final internal energy of the fluid. Neglect the energy stored in the paddle wheel. ...
... Initially, the internal energy of the fluid is 800 kJ. During the cooling process, the fluid loses 500 kJ of heat, and the paddle wheel does 100 kJ of work on the fluid. Determine the final internal energy of the fluid. Neglect the energy stored in the paddle wheel. ...
Newton`s Second Law NOTES
... 24.) A 5000 kg truck is traveling along a straight road at 10 m/s. Two seconds later its speed is 9 m/s. What is the magnitude of the net force acting on the truck during this time? ...
... 24.) A 5000 kg truck is traveling along a straight road at 10 m/s. Two seconds later its speed is 9 m/s. What is the magnitude of the net force acting on the truck during this time? ...
1. In the absence of air friction, an object dropped near the surface of
... (A) It oscillates with maximum position x2 and minimum position x0. (B) It moves to the right of x3 and does not return. (C) It moves to the left of x0 and does not return. (D) It comes to rest at either x0 or x2. (E) It cannot reach either x0 or x2. 16. A balloon of mass M is floating motionless in ...
... (A) It oscillates with maximum position x2 and minimum position x0. (B) It moves to the right of x3 and does not return. (C) It moves to the left of x0 and does not return. (D) It comes to rest at either x0 or x2. (E) It cannot reach either x0 or x2. 16. A balloon of mass M is floating motionless in ...
8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics
... (b) [5 pts] Show that if m << M then to first order the rotation rate depends linearly on both x and v. (c) [5 pts] Derive an expression for IT in terms of M and R. Warning! This is a difficult problem, so save it for last! ...
... (b) [5 pts] Show that if m << M then to first order the rotation rate depends linearly on both x and v. (c) [5 pts] Derive an expression for IT in terms of M and R. Warning! This is a difficult problem, so save it for last! ...
Name_________________Date___________Period_____ Num
... 11. What happens to an object when there is a balanced force applied? ...
... 11. What happens to an object when there is a balanced force applied? ...
No Slide Title
... The path taken (longer or shorter) does not matter: only the displacement does! PHY 231 ...
... The path taken (longer or shorter) does not matter: only the displacement does! PHY 231 ...
Serway_PSE_quick_ch08
... an initial speed v. It slides until it stops due to the friction force between the block and the surface. The surface is now tilted at 30°, and the block is projected up the surface with the same initial speed v. Assume that the friction force remains the same as when the block was sliding on the ho ...
... an initial speed v. It slides until it stops due to the friction force between the block and the surface. The surface is now tilted at 30°, and the block is projected up the surface with the same initial speed v. Assume that the friction force remains the same as when the block was sliding on the ho ...
Do now
... writing the formula and then explaining if there is a direct or inverse relationship between the force and the acceleration (1 pt), what happens to the acceleration if the mass changes (1 pt), and then explain what conditions must be necessary for equilibrium to exist in the system (1 pt). ...
... writing the formula and then explaining if there is a direct or inverse relationship between the force and the acceleration (1 pt), what happens to the acceleration if the mass changes (1 pt), and then explain what conditions must be necessary for equilibrium to exist in the system (1 pt). ...