Conceptual Physics
... 3. What is the equation for speed? What are some possible units for speed? 4. Differentiate between speed and velocity. 5. Define constant velocity. When does an object have constant velocity? 6. Define acceleration. What is the equation for acceleration? 7. How are velocity and acceleration related ...
... 3. What is the equation for speed? What are some possible units for speed? 4. Differentiate between speed and velocity. 5. Define constant velocity. When does an object have constant velocity? 6. Define acceleration. What is the equation for acceleration? 7. How are velocity and acceleration related ...
work
... Recalling the definition of the scalar product of two vectors, we could also write a vector equation: ...
... Recalling the definition of the scalar product of two vectors, we could also write a vector equation: ...
Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. Contact forces are forces that result when two objects are physically in contact with one another. Example: push/pull, normal force, friction, spring force, tension, air resistance. Non-contact Forces: forces that result when two objects are not in physical contact. Example: gravitational force, ...
... 2. Contact forces are forces that result when two objects are physically in contact with one another. Example: push/pull, normal force, friction, spring force, tension, air resistance. Non-contact Forces: forces that result when two objects are not in physical contact. Example: gravitational force, ...
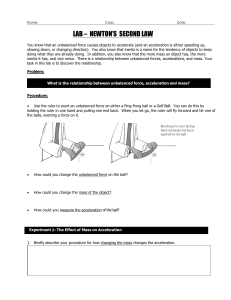
LAB – NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
... You know that an unbalanced force causes objects to accelerate (and an acceleration is either speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction). You also know that inertia is a name for the tendency of objects to keep doing what they are already doing. In addition, you also know that the more mass a ...
... You know that an unbalanced force causes objects to accelerate (and an acceleration is either speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction). You also know that inertia is a name for the tendency of objects to keep doing what they are already doing. In addition, you also know that the more mass a ...
Word File Sample for Question Bank Input Word Format
... supports A and B. The plank can slide against the supports (without friction) because of its weight Mg. With what acceleration and in what direction should a man of mass m should move so that the plank may mot move. On a smooth horizontal surface a block of mass m is attached with k F a spring as sh ...
... supports A and B. The plank can slide against the supports (without friction) because of its weight Mg. With what acceleration and in what direction should a man of mass m should move so that the plank may mot move. On a smooth horizontal surface a block of mass m is attached with k F a spring as sh ...
File
... Answer: False Newton’s First Law of Motion states: Objects in motion stay in motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an outside force. Outside forces such as friction, gravity, magnetic force, electrical, force, and air resistance slow/stop objects ...
... Answer: False Newton’s First Law of Motion states: Objects in motion stay in motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an outside force. Outside forces such as friction, gravity, magnetic force, electrical, force, and air resistance slow/stop objects ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... a fulcrum 1.40 m away from the left end. Find the forces that the bolt and the fulcrum exert on the board. ...
... a fulcrum 1.40 m away from the left end. Find the forces that the bolt and the fulcrum exert on the board. ...
Student Workbook
... 6. A crane lifts a (1100-kg) car vertically with an acceleration of 0.75 m/s2. If the car is raised a total height of 4.0-m during this acceleration determine: a) the value of the force needed to lift the car. c) the work done by gravity. b) the work done by this lifting force. d) the net work done ...
... 6. A crane lifts a (1100-kg) car vertically with an acceleration of 0.75 m/s2. If the car is raised a total height of 4.0-m during this acceleration determine: a) the value of the force needed to lift the car. c) the work done by gravity. b) the work done by this lifting force. d) the net work done ...
File
... Momentum, however, can be transferred from one object to another. The law of conservation of momentum states that if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t change. ...
... Momentum, however, can be transferred from one object to another. The law of conservation of momentum states that if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t change. ...