SOLUTION
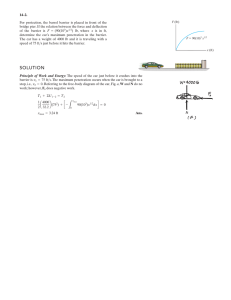
... 4-lb block, which is sliding toward it at v = 9 ft>s. As shown, the spring is confined by the plate P and wall using cables so that its length is 1.5 ft. If the stiffness of the spring is k = 50 lb>ft, determine the required unstretched length of the spring so that the plate is not displaced more th ...
... 4-lb block, which is sliding toward it at v = 9 ft>s. As shown, the spring is confined by the plate P and wall using cables so that its length is 1.5 ft. If the stiffness of the spring is k = 50 lb>ft, determine the required unstretched length of the spring so that the plate is not displaced more th ...
laws of motion
... For object sliding on a smooth inclined plane • The acceleration depends on the inclination of the plane only. It does not depend on the mass. Objects of different masses slide on the inclined plane with the same acceleration. • The acceleration always points down-slope, independent of the directio ...
... For object sliding on a smooth inclined plane • The acceleration depends on the inclination of the plane only. It does not depend on the mass. Objects of different masses slide on the inclined plane with the same acceleration. • The acceleration always points down-slope, independent of the directio ...
HonorsReview
... Similarly throughout the school year we have used many line graphs to determine the relations between different variables. The intention was to derive a relation rather than memorize a formula. When you solve a problem always relate to FBD, energy bar graphs, graphs, or motion diagrams to get a basi ...
... Similarly throughout the school year we have used many line graphs to determine the relations between different variables. The intention was to derive a relation rather than memorize a formula. When you solve a problem always relate to FBD, energy bar graphs, graphs, or motion diagrams to get a basi ...
Potential Energy
... Summary of Types of Collisions In an elastic collision, both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. In an inelastic collision, momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not. In a perfectly inelastic collision, momentum is conserved, kinetic energy is not, and the two objects stick togethe ...
... Summary of Types of Collisions In an elastic collision, both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. In an inelastic collision, momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not. In a perfectly inelastic collision, momentum is conserved, kinetic energy is not, and the two objects stick togethe ...
June 10
... Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the spaces provided on the Answer Booklet. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. ...
... Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the spaces provided on the Answer Booklet. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. ...
Physics 6010, Fall 2010 Symmetries and Conservation Laws
... By a conservation law we mean a quantity constructed from the coordinates, velocities, accelerations, etc. of the system that does not change as the system evolves in time. When the equations of motion are second order, conservation laws typically arise as functions on the velocity phase (possibly w ...
... By a conservation law we mean a quantity constructed from the coordinates, velocities, accelerations, etc. of the system that does not change as the system evolves in time. When the equations of motion are second order, conservation laws typically arise as functions on the velocity phase (possibly w ...
CH6-10 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... 24. A rubber ball with a speed of 5.0 m/s collides head-on elastically with an identical ball at rest. What is the speed of the initially stopped ball after the collision? a) zero b) 1.0 m/s c) 2.5 m/s d) 5.0 m/s 25. A 3.0-kg object moves to the right with a speed of 4.0 m/s. It collides in a perfec ...
... 24. A rubber ball with a speed of 5.0 m/s collides head-on elastically with an identical ball at rest. What is the speed of the initially stopped ball after the collision? a) zero b) 1.0 m/s c) 2.5 m/s d) 5.0 m/s 25. A 3.0-kg object moves to the right with a speed of 4.0 m/s. It collides in a perfec ...
Grade 8 Physical Science 2015 Unit 1
... o The term “heat” as used in everyday language refers both to thermal energy (the motion of atoms or molecules within a substance) and the transfer of that thermal energy from one object to another. In science, heat is used only for this second meaning; it refers to the energy transferred due to the ...
... o The term “heat” as used in everyday language refers both to thermal energy (the motion of atoms or molecules within a substance) and the transfer of that thermal energy from one object to another. In science, heat is used only for this second meaning; it refers to the energy transferred due to the ...
Review 2012
... a. TRUE- Momentum is a vector quantity. Like all vector quantities, the momentum of an object is not fully described until the direction of the momentum is identified. Momentum, like other vector quantities, is subject to the rules of vector operations. b. FALSE- The Joule is the unit of work and en ...
... a. TRUE- Momentum is a vector quantity. Like all vector quantities, the momentum of an object is not fully described until the direction of the momentum is identified. Momentum, like other vector quantities, is subject to the rules of vector operations. b. FALSE- The Joule is the unit of work and en ...
8th Grade Physical Science Final Study Guide
... 111. The path of a crate sliding along flat ground is/is not an example of projectile motion. Is Not 112. If dropped at the same time from the same height, a tennis ball/a solid rubber ball/a solid steel ball would hit the ground first. (Assume no air resistance) The same time 113. An empty shopping ...
... 111. The path of a crate sliding along flat ground is/is not an example of projectile motion. Is Not 112. If dropped at the same time from the same height, a tennis ball/a solid rubber ball/a solid steel ball would hit the ground first. (Assume no air resistance) The same time 113. An empty shopping ...
Lecture 12
... A roller coaster of mass m starts at rest at height y1 and falls down the path with friction, then back up until it hits height y2 (y1 > y2). An odometer tells us that the total scalar distance traveled is d. Assuming we don’t know anything about the friction or the path, how much work is done by fr ...
... A roller coaster of mass m starts at rest at height y1 and falls down the path with friction, then back up until it hits height y2 (y1 > y2). An odometer tells us that the total scalar distance traveled is d. Assuming we don’t know anything about the friction or the path, how much work is done by fr ...
Part IV
... “Every object continues in a state of rest or uniform motion (constant velocity) in a straight line unless acted on by a net force.” ...
... “Every object continues in a state of rest or uniform motion (constant velocity) in a straight line unless acted on by a net force.” ...
Potential Energy Conservation of Energy
... The total mechanical energy is conserved and remains the same at all times ...
... The total mechanical energy is conserved and remains the same at all times ...