1: How does the process of mountain building begin
... 24: As erosion reduces the summits of newly formed mountains, and reduces their weight, what happens to the crust beneath the mountain? At what point will it stop rising? ...
... 24: As erosion reduces the summits of newly formed mountains, and reduces their weight, what happens to the crust beneath the mountain? At what point will it stop rising? ...
File
... An example of the cause of an Earthquake • For example as two plates move towards each other, one can be pushed down under the other one into the mantle. • If this plate gets stuck it causes a lot of pressure on surrounding rocks. • When this pressure is released it produces shock waves. These are ...
... An example of the cause of an Earthquake • For example as two plates move towards each other, one can be pushed down under the other one into the mantle. • If this plate gets stuck it causes a lot of pressure on surrounding rocks. • When this pressure is released it produces shock waves. These are ...
Chapter 6 lesson 1-4
... Index Fossils- fossils of an organism that lived during a relatively short, well-defined time span. ...
... Index Fossils- fossils of an organism that lived during a relatively short, well-defined time span. ...
3 - Greene ESC
... Earth. This includes demonstrating an understanding of the composition of the universe, the solar system and Earth. In addition, it includes understanding the properties and the interconnected nature of Earth’s systems, processes that shape Earth and Earth’s history. Students also demonstrate an und ...
... Earth. This includes demonstrating an understanding of the composition of the universe, the solar system and Earth. In addition, it includes understanding the properties and the interconnected nature of Earth’s systems, processes that shape Earth and Earth’s history. Students also demonstrate an und ...
Earthquakescrossword
... 3. break in Earth’s crust along which portions of Earth’s crust move relative to one another 4. the study of earthquakes 5. point inside Earth where an earthquake begins 8. point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s starting point 10. the fastest seismic waves 11. secondary seismic wave ...
... 3. break in Earth’s crust along which portions of Earth’s crust move relative to one another 4. the study of earthquakes 5. point inside Earth where an earthquake begins 8. point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s starting point 10. the fastest seismic waves 11. secondary seismic wave ...
Chapter 5 Section 1
... 2. What is the difference between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere? 3. How do temperature and pressure change as you go deeper into the Earth? 4. How are oceanic and continental crusts alike and different? 5. Place these terms in correct order so they begin at Earth’s surface and move toward th ...
... 2. What is the difference between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere? 3. How do temperature and pressure change as you go deeper into the Earth? 4. How are oceanic and continental crusts alike and different? 5. Place these terms in correct order so they begin at Earth’s surface and move toward th ...
Life and the Evolution of Earth`s Atmosphere
... would have supplied less solar radiation to warm the early Earth. To keep the Earth from starting out as a frozen wasteland, with no hope for beginning life to take hold, an atmospheric “greenhouse” must have kept the surface zone warm enough to maintain water in liquid form. Liquid water is the pre ...
... would have supplied less solar radiation to warm the early Earth. To keep the Earth from starting out as a frozen wasteland, with no hope for beginning life to take hold, an atmospheric “greenhouse” must have kept the surface zone warm enough to maintain water in liquid form. Liquid water is the pre ...
Plate Tectonics Picture Study Guide File
... Mid-ocean ridges create new land when: Sea-floor spreading happens and causes magma to rise to the surface ...
... Mid-ocean ridges create new land when: Sea-floor spreading happens and causes magma to rise to the surface ...
Earth Materials – Progress Test 4
... Read all the questions carefully. Answer all questions on the paper provided. Do not write on the test paper. Question 1 The earth’s atmosphere was originally formed by volcanic activity. The early atmosphere contained carbon dioxide, ammonia, water vapour and methane. (a) Explain how the amount ...
... Read all the questions carefully. Answer all questions on the paper provided. Do not write on the test paper. Question 1 The earth’s atmosphere was originally formed by volcanic activity. The early atmosphere contained carbon dioxide, ammonia, water vapour and methane. (a) Explain how the amount ...
No Slide Title - NSCC NetID: Personal Web Space
... You will be learning a new language! Geology is a broad, interdisciplinary science with a rich vocabulary. The terminology we will use throughout this course will require that you learn a new language; in fact, this is true of most introductory science courses. You will learn nearly the same vocabu ...
... You will be learning a new language! Geology is a broad, interdisciplinary science with a rich vocabulary. The terminology we will use throughout this course will require that you learn a new language; in fact, this is true of most introductory science courses. You will learn nearly the same vocabu ...
REVISED EXAM 3 STUDY GUIDE – PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
... b. Outer core c. Mesosphere d. Asthenosphere ...
... b. Outer core c. Mesosphere d. Asthenosphere ...
Earth*s Formation and Interior Earth Science Notes Unit 1: Studying
... 2. Outer layers beginning to compresspressure increasing temperature 3. Radioactive materials emitting high-energy particles-when surrounding rocks absorbed the particles, the energy of the particles’ motion led to higher temperatures. ...
... 2. Outer layers beginning to compresspressure increasing temperature 3. Radioactive materials emitting high-energy particles-when surrounding rocks absorbed the particles, the energy of the particles’ motion led to higher temperatures. ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... discovered undersea mountain running north to south down the length of the Atlantic Ocean, which they named the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. ...
... discovered undersea mountain running north to south down the length of the Atlantic Ocean, which they named the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. ...
Eighth Grade Science Essential Knowledge 1. Matter – anything that
... 122. Asexual reproduction – a type of reproduction – fission, budding and regeneration – in which a new organism is produced from one organism and has DNA identical to the parent organism 123. Evolution – change of living things over time 124. Fossil – trace or remains of a plant or an animal in sed ...
... 122. Asexual reproduction – a type of reproduction – fission, budding and regeneration – in which a new organism is produced from one organism and has DNA identical to the parent organism 123. Evolution – change of living things over time 124. Fossil – trace or remains of a plant or an animal in sed ...
10-25 miles
... degrees F to 9000 degrees F 11. Made of Nickel and Iron 12. This liquid core produces a magnetic field that helps protect earth from coronal mass ejections (CME’s) produced by the sun. ...
... degrees F to 9000 degrees F 11. Made of Nickel and Iron 12. This liquid core produces a magnetic field that helps protect earth from coronal mass ejections (CME’s) produced by the sun. ...
IGNEOUS and METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY
... PETROLOGY – comes from petros for rock – hence the study of rocks Sedimentary – deposition of material from water or air ...
... PETROLOGY – comes from petros for rock – hence the study of rocks Sedimentary – deposition of material from water or air ...
Earth`s Interior
... minerals (also magnesium, silicon) 3. surrounded by crust of relatively light silicon-rich minerals. (You are here.) Earth is differentiated. ...
... minerals (also magnesium, silicon) 3. surrounded by crust of relatively light silicon-rich minerals. (You are here.) Earth is differentiated. ...
Unit 1: Structure of the Earth
... • At first, the Earth gets a little cooler as you go deeper. • But at 20 meters depth, the temperature starts rising. • For every 40 meters you descend, the temperature rises about 1° Celsius. After a few kilometers this rate slows a bit, but it gets hotter the deeper you travel inside the Earth. ...
... • At first, the Earth gets a little cooler as you go deeper. • But at 20 meters depth, the temperature starts rising. • For every 40 meters you descend, the temperature rises about 1° Celsius. After a few kilometers this rate slows a bit, but it gets hotter the deeper you travel inside the Earth. ...
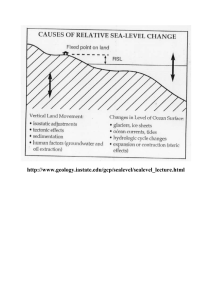
Eustatic Sea Level Change Mechanisms
... Eustatic Sea Level Change Mechanisms Eustatic sea-level changes occur on an oceanic to worldwide scale. They result from either a change in the volume of seawater, or a change in the size of the ocean basin that contains it. Even in these large-scale cases, however, mean sea level can vary from pla ...
... Eustatic Sea Level Change Mechanisms Eustatic sea-level changes occur on an oceanic to worldwide scale. They result from either a change in the volume of seawater, or a change in the size of the ocean basin that contains it. Even in these large-scale cases, however, mean sea level can vary from pla ...
Which type of heat transfer is taking place?
... First, let’s start with the part of the Earth that we live on, the outermost layer called the crust. It is made up of loose material, like rocks, soil, and seabed. The crust is about five miles deep beneath the oceans and about twenty-five miles thick below the continents. Beyond the crust is the ma ...
... First, let’s start with the part of the Earth that we live on, the outermost layer called the crust. It is made up of loose material, like rocks, soil, and seabed. The crust is about five miles deep beneath the oceans and about twenty-five miles thick below the continents. Beyond the crust is the ma ...
Earth`s Interior
... 19. What are convection currents? Please give examples: _________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 20. Describe how convection currents work within the e ...
... 19. What are convection currents? Please give examples: _________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 20. Describe how convection currents work within the e ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... • Geologists cannot observe Earth’s interior directly. Instead, they must rely on indirect methods of observation. Scientists record seismic waves and how they travel through the Earth in order to make some inferences about the Earth’s interior. ...
... • Geologists cannot observe Earth’s interior directly. Instead, they must rely on indirect methods of observation. Scientists record seismic waves and how they travel through the Earth in order to make some inferences about the Earth’s interior. ...
The Four Spheres of Earth and Their Influence - geography-bbs
... a smaller function within the environment. It is the unique interaction between the living and non-living elements. An ecosystem is a community functioning together as one unit. ...
... a smaller function within the environment. It is the unique interaction between the living and non-living elements. An ecosystem is a community functioning together as one unit. ...
Slide 1
... • metallic and non-metallic minerals Earth Science deals with the formation and occurrence as well as maintaining the supply and impact to the environment. ...
... • metallic and non-metallic minerals Earth Science deals with the formation and occurrence as well as maintaining the supply and impact to the environment. ...