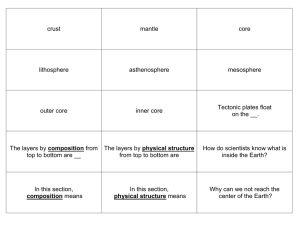
7.1.2 Study: The Mantle and Crust
... Use the spaces below to take notes on the key concepts presented in this study. Main Idea #1: Scientists can collect information on the surface of Earth that gives them a hint as to what is below the surface. ...
... Use the spaces below to take notes on the key concepts presented in this study. Main Idea #1: Scientists can collect information on the surface of Earth that gives them a hint as to what is below the surface. ...
Exam Study Guide
... formation (including climate) and deposition. (Small well sorted grains – far from source, poorly sorted far from source). E3.1d Explain how the crystal sizes of igneous rocks indicate the rate of cooling and whether the rock is extrusive (small grained) or intrusive (large grained). E3.1e Expla ...
... formation (including climate) and deposition. (Small well sorted grains – far from source, poorly sorted far from source). E3.1d Explain how the crystal sizes of igneous rocks indicate the rate of cooling and whether the rock is extrusive (small grained) or intrusive (large grained). E3.1e Expla ...
Earth
... New mountains can be formed when land masses are being pushed together due to plate tectonics, and also from volcanic activity. Mount Everest and the rest of the Himalayas make up a ...
... New mountains can be formed when land masses are being pushed together due to plate tectonics, and also from volcanic activity. Mount Everest and the rest of the Himalayas make up a ...
The Geosphere
... • Geosphere – consists of all the rock, soils and sediments on the Earth • Atmosphere – consists of the air that surrounds the Earth • Hydrosphere – consists of all water, fresh or saltwater • Biosphere – all living things on the planet ...
... • Geosphere – consists of all the rock, soils and sediments on the Earth • Atmosphere – consists of the air that surrounds the Earth • Hydrosphere – consists of all water, fresh or saltwater • Biosphere – all living things on the planet ...
The Geosphere
... • Geosphere – consists of all the rock, soils and sediments on the Earth • Atmosphere – consists of the air that surrounds the Earth • Hydrosphere – consists of all water, fresh or saltwater • Biosphere – all living things on the planet ...
... • Geosphere – consists of all the rock, soils and sediments on the Earth • Atmosphere – consists of the air that surrounds the Earth • Hydrosphere – consists of all water, fresh or saltwater • Biosphere – all living things on the planet ...
Earth Science Notes
... _______________: _____ of Earth’s volume, _____ of Earth’s mass o 2 regions Solid _______________ core – iron, nickel, high density Liquid _______________ core – iron, nickel, sulfur, oxygen _______________: _____ of Earth’s volume; _____ of Earth’s mass o Magnesium and iron-rich minerals o ...
... _______________: _____ of Earth’s volume, _____ of Earth’s mass o 2 regions Solid _______________ core – iron, nickel, high density Liquid _______________ core – iron, nickel, sulfur, oxygen _______________: _____ of Earth’s volume; _____ of Earth’s mass o Magnesium and iron-rich minerals o ...
File
... 10. What are the 2 rules of magnetism? Fossils: 11. What are fossils? 12. List at least 3 ways they are formed or found 13. Draw a diagram showing how the fossils of a bird would be found if they were 10 years old, 25 years old, and 50 years old 14. What does the term geological history refer to? 15 ...
... 10. What are the 2 rules of magnetism? Fossils: 11. What are fossils? 12. List at least 3 ways they are formed or found 13. Draw a diagram showing how the fossils of a bird would be found if they were 10 years old, 25 years old, and 50 years old 14. What does the term geological history refer to? 15 ...
the earth`s spheres
... the huge icecaps in Greenland and Antarctica. It has two major components: continental or land ice and sea ice. 4. The Biosphere (life sphere) includes all living things. The biosphere is a life-supporting global ecosystem, where each living things depends on each other and the environment. The ecos ...
... the huge icecaps in Greenland and Antarctica. It has two major components: continental or land ice and sea ice. 4. The Biosphere (life sphere) includes all living things. The biosphere is a life-supporting global ecosystem, where each living things depends on each other and the environment. The ecos ...
crust
... • Geomagnetic north is located by a deposit of lodestone (a magnetic rock) in northern Canada. The position of this has changed many times over the years. It is about 250 miles from True North. A compass points toward this. ...
... • Geomagnetic north is located by a deposit of lodestone (a magnetic rock) in northern Canada. The position of this has changed many times over the years. It is about 250 miles from True North. A compass points toward this. ...
Plate Tectonics.common.assessment.studyguide
... 3. by recording and studying seismic waves 4. they both increase 5. a layer of hot rock and a dense ball of solid metal 6. When you touch a hot pot or pan, the heat moves from the pot to your hand (example) 7. Mantle or asthenosphere 8. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years a ...
... 3. by recording and studying seismic waves 4. they both increase 5. a layer of hot rock and a dense ball of solid metal 6. When you touch a hot pot or pan, the heat moves from the pot to your hand (example) 7. Mantle or asthenosphere 8. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years a ...
Dimensions of the Earth
... The Earth is composed of a series of spheres. Each sphere has a different composition of materials and is held together by gravity. The spheres of Earth are arranged from least dense (atmosphere) to most dense (geosphere) depending on how close they are found to the Earth’s center. ...
... The Earth is composed of a series of spheres. Each sphere has a different composition of materials and is held together by gravity. The spheres of Earth are arranged from least dense (atmosphere) to most dense (geosphere) depending on how close they are found to the Earth’s center. ...
Phytoplankton - Madison County Schools
... Photosynthesis and the Cycles • The phytoplankton’s photosynthesis abilities impact the carbon and oxygen cycles in a big way! • There are so many of these organisms and they collect a vast amount of carbon dioxide. They use the carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and they also store it inside. They ...
... Photosynthesis and the Cycles • The phytoplankton’s photosynthesis abilities impact the carbon and oxygen cycles in a big way! • There are so many of these organisms and they collect a vast amount of carbon dioxide. They use the carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and they also store it inside. They ...
ch 13 PPT File
... and solid rocks that churn. The entire mantle is about 2,900 kilometers thick. • The outermost layer is the crust. Very thin and cold, 8-70 kilometers thick. The continents and oceans floor are part of the crust. ...
... and solid rocks that churn. The entire mantle is about 2,900 kilometers thick. • The outermost layer is the crust. Very thin and cold, 8-70 kilometers thick. The continents and oceans floor are part of the crust. ...
Evolution of Organisms and Landforms EOG review
... A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth. B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms. C. They compare the life histories of species that have used rocks as habitats. D. They correlate the existence of life on Earth 5.01 with geologi ...
... A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth. B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms. C. They compare the life histories of species that have used rocks as habitats. D. They correlate the existence of life on Earth 5.01 with geologi ...
Intro Stream Processes
... What might best explain homologous structures between the fins of whales and wings of bats? ...
... What might best explain homologous structures between the fins of whales and wings of bats? ...
Mass Extinctions
... the impact of an asteroid/comet) may have affected the conditions on Earth and the diversity of its life forms ...
... the impact of an asteroid/comet) may have affected the conditions on Earth and the diversity of its life forms ...
ScienceChapter6Study..
... How can wind cause erosion? Wind can move loose soil or sand, but it can also act like sandpaper or a sandblaster as it blows these loose particles against rock. What forces coastline changes? Waves beating against the coast. How can gravity and water change Earth’s surface? Causes landslides and mu ...
... How can wind cause erosion? Wind can move loose soil or sand, but it can also act like sandpaper or a sandblaster as it blows these loose particles against rock. What forces coastline changes? Waves beating against the coast. How can gravity and water change Earth’s surface? Causes landslides and mu ...
Component 4: Chemistry Oils, Earth and Atmosphere – Word Bank
... that is too small to be seen with the naked eye, but can be seen under a microscope. Microbes include bacteria, viruses and some fungi. Many microbes are very useful to us because they break down waste products. Recycling - as an alternative to burning or burying waste, sometimes it can be recycled. ...
... that is too small to be seen with the naked eye, but can be seen under a microscope. Microbes include bacteria, viruses and some fungi. Many microbes are very useful to us because they break down waste products. Recycling - as an alternative to burning or burying waste, sometimes it can be recycled. ...
early-earth1 - WordPress.com
... • Our galaxy was formed - _________ billion years ago • Our Universe was formed - ________ billion years ago • Life on earth began _______ billion years ago • Human life began _________ years ago – the last _____ _________________ of the cosmic calendar. ...
... • Our galaxy was formed - _________ billion years ago • Our Universe was formed - ________ billion years ago • Life on earth began _______ billion years ago • Human life began _________ years ago – the last _____ _________________ of the cosmic calendar. ...
Exam #1: study guide
... Phases of the Moon (what is the phase on September 26 th) Eclipses of the Sun and Moon: be able to diagram Why does the moon rise one hour later each night? Mean solar day Sidereal day Doppler effect: definition; applied to light; what does the red shift mean? How is it applied to the Bi ...
... Phases of the Moon (what is the phase on September 26 th) Eclipses of the Sun and Moon: be able to diagram Why does the moon rise one hour later each night? Mean solar day Sidereal day Doppler effect: definition; applied to light; what does the red shift mean? How is it applied to the Bi ...
earth structure ppt
... Crust – average depth 30 km outermost layer Low density rock Silicate minerals (silicate and oxygen) ...
... Crust – average depth 30 km outermost layer Low density rock Silicate minerals (silicate and oxygen) ...
Earthquake Crossword - Science
... 1 The fracture along which blocks of crust move relative to each other. (5) 2 City destroyed by earthquake in 1923. (5) 4 The place where two plates collide and one goes over top the other. (10,4) 5 Sudden stress changes in the earth that cause ground shaking. They occur at fault lines and near volc ...
... 1 The fracture along which blocks of crust move relative to each other. (5) 2 City destroyed by earthquake in 1923. (5) 4 The place where two plates collide and one goes over top the other. (10,4) 5 Sudden stress changes in the earth that cause ground shaking. They occur at fault lines and near volc ...
Comparison of the rocky planets
... gases that formed the original atmosphere were derived from volcanic eruptions, which, similar to present-day eruptions, brought water vapor, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and sulfur to the surface from deep in the earth (no free oxygen). The abundance of oxygen was much lower and did not begi ...
... gases that formed the original atmosphere were derived from volcanic eruptions, which, similar to present-day eruptions, brought water vapor, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and sulfur to the surface from deep in the earth (no free oxygen). The abundance of oxygen was much lower and did not begi ...