Fysiikan historia
... particular, why quarks were never observed as free particles. There were also problems with Pauli’s exclusion princible: For example, in omega particle there are three s quarks with their spins parallel, a state of identical fermions forbidden by the exclusion princible. • American Oscar Greenberg ...
... particular, why quarks were never observed as free particles. There were also problems with Pauli’s exclusion princible: For example, in omega particle there are three s quarks with their spins parallel, a state of identical fermions forbidden by the exclusion princible. • American Oscar Greenberg ...
From Electrons to Quarks
... Observations on mountains and in balloon: intensity of cosmic radiation increases with height above surface of Earth – must come from “outer space” Much of cosmic radiation from sun (rather low energy protons) Very high energy radiation from outside solar ...
... Observations on mountains and in balloon: intensity of cosmic radiation increases with height above surface of Earth – must come from “outer space” Much of cosmic radiation from sun (rather low energy protons) Very high energy radiation from outside solar ...
Inclusive DIS in saturation models
... -- Multi-Pomeron interactions, Higher Twist effects, Saturation/CGC -- Rapidity Gaps, Energy loss, Multiple Scattering, Color Transparency -- Glasma, Quark Gluon Plasma What can this teach us about confinement, universal features of the theory (infrared fixed point?) -- hard vs soft Pomerons, Strong ...
... -- Multi-Pomeron interactions, Higher Twist effects, Saturation/CGC -- Rapidity Gaps, Energy loss, Multiple Scattering, Color Transparency -- Glasma, Quark Gluon Plasma What can this teach us about confinement, universal features of the theory (infrared fixed point?) -- hard vs soft Pomerons, Strong ...
Document
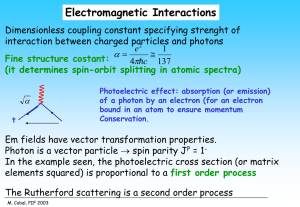
... in strong interactions they play similar role to the electric charge in em interactions. • A quark can carry one of the three colours (red, blue, green). An anti-quark one of the three anti-colours • All the observable particles are “white” (they do not carry colour) Hadrons: neutral mix of r,g,b co ...
... in strong interactions they play similar role to the electric charge in em interactions. • A quark can carry one of the three colours (red, blue, green). An anti-quark one of the three anti-colours • All the observable particles are “white” (they do not carry colour) Hadrons: neutral mix of r,g,b co ...