introduction to the standard model of particle physics
... Nuclei are made up of protons and neutrons (collectively nucleons). Nucleons are made from Quarks. Quarks and Electrons are (as far as we know) elementary particles. ...
... Nuclei are made up of protons and neutrons (collectively nucleons). Nucleons are made from Quarks. Quarks and Electrons are (as far as we know) elementary particles. ...
CH17 Self Assessment
... use hand rule to explain how to determine nature of charge or direction of magnetic field given the other and the track for subatomic particles compare tracks in terms of the mass, charge (size or nature), speed, or energy of the particle compare decreasing relative strengths and ranges of effect of ...
... use hand rule to explain how to determine nature of charge or direction of magnetic field given the other and the track for subatomic particles compare tracks in terms of the mass, charge (size or nature), speed, or energy of the particle compare decreasing relative strengths and ranges of effect of ...
some aspects of strange matter : stars and strangelets
... • Better notation: Isospin symmetry; • Strong interaction does not distinguish between n and p isospin conserved in strong interaction • BUT not in electromagnetic interaction ...
... • Better notation: Isospin symmetry; • Strong interaction does not distinguish between n and p isospin conserved in strong interaction • BUT not in electromagnetic interaction ...
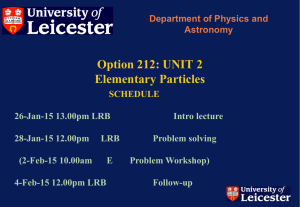
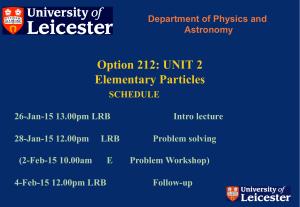
Option 212: UNIT 2 Elementary Particles - X
... Quarks in a baryon always have these three colours, such that when combined they are color-less ( qr , qy , qb ) In a meson, a red quark and its anti-red quark attract to form the particle ...
... Quarks in a baryon always have these three colours, such that when combined they are color-less ( qr , qy , qb ) In a meson, a red quark and its anti-red quark attract to form the particle ...