Advanced Quantum Mechanics Syllabus and Introduction
... Office Hours: MWF 10:00 – 11:00 AM. You are welcome to stop by any other time when my door is open. Course Content: Advanced quantum mechanics (or “QM II” for short) begins where ordinary quantum mechanics leaves off in two very important respects. First there is the issue of relativity. Relativity ...
... Office Hours: MWF 10:00 – 11:00 AM. You are welcome to stop by any other time when my door is open. Course Content: Advanced quantum mechanics (or “QM II” for short) begins where ordinary quantum mechanics leaves off in two very important respects. First there is the issue of relativity. Relativity ...
Modern view of matter and the universe
... String + supersymmetry • One way to explain the “hierarchy” of particles by modifying the concept of “field” in Quantum physics. • The field (medium) at small length scale is replaced by loops of strings! • Different mode of oscillations of string + Supersymmetry Different particles ...
... String + supersymmetry • One way to explain the “hierarchy” of particles by modifying the concept of “field” in Quantum physics. • The field (medium) at small length scale is replaced by loops of strings! • Different mode of oscillations of string + Supersymmetry Different particles ...
PowerPoint
... Hard-wall AdS/QCD models contain the chiral symmetry breaking, the resulting mass spectra for the excited mesons are contrary to the experimental data. Soft-wall AdS/QCD models describe the linear confinement and desired mass spectra for the excited vector mesons, while the chiral symmetry breaking ...
... Hard-wall AdS/QCD models contain the chiral symmetry breaking, the resulting mass spectra for the excited mesons are contrary to the experimental data. Soft-wall AdS/QCD models describe the linear confinement and desired mass spectra for the excited vector mesons, while the chiral symmetry breaking ...
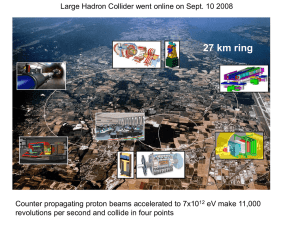
History of Particle Physics (lecture notes)
... Standard Model. It will be our main concern in this course. The Standard Model remains as the firm foundation for fundamental physics today, unshaken by scrutiny at far higher energies and wit ...
... Standard Model. It will be our main concern in this course. The Standard Model remains as the firm foundation for fundamental physics today, unshaken by scrutiny at far higher energies and wit ...
QCD with Isospin chemical potential
... • Adds another axis to the picture: μB induces quark/antiquark imbalance • Finite μI and μB : relevant for neutron stars ...
... • Adds another axis to the picture: μB induces quark/antiquark imbalance • Finite μI and μB : relevant for neutron stars ...
24.5 Nuclear Equations - The Free Learning Channel
... are each made of only up and down quarks, and they are made of three quarks each. The up quark carries a charge of + 23 , and the down quark carries a charge of − 31 . Determine by the final charge on the proton and neutron what combination of three up and down quarks are required to make a proton an ...
... are each made of only up and down quarks, and they are made of three quarks each. The up quark carries a charge of + 23 , and the down quark carries a charge of − 31 . Determine by the final charge on the proton and neutron what combination of three up and down quarks are required to make a proton an ...