Supercomputing in High Energy Physics
... Particle Physics “Everything in the universe seems to be made of simple, small objects which like to stick together” • Modern realization of this: The Standard Model – A quantum field theory in which point-like, spin-1/2 fermions interact through the exchange of spin-1 vector bosons – Electroweak i ...
... Particle Physics “Everything in the universe seems to be made of simple, small objects which like to stick together” • Modern realization of this: The Standard Model – A quantum field theory in which point-like, spin-1/2 fermions interact through the exchange of spin-1 vector bosons – Electroweak i ...
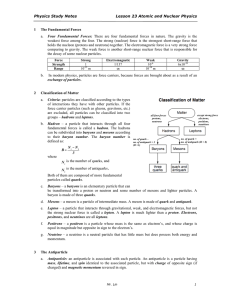
Study Notes Lesson 23 Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... produce two or more gamma ray photons. However, high-energy particle colliders produce annihilations where a wide variety of exotic heavy particles are created. ...
... produce two or more gamma ray photons. However, high-energy particle colliders produce annihilations where a wide variety of exotic heavy particles are created. ...
e - National Centre for Physics
... All hadrons are color singlet. Thus the color quantum number is hidden. This is the postulate of color confinement mentioned earlier and explains non-existence of free quark. Strong color charges are the sources of inter-quark force. Corresponding to three color charges of a quark, there are eight ...
... All hadrons are color singlet. Thus the color quantum number is hidden. This is the postulate of color confinement mentioned earlier and explains non-existence of free quark. Strong color charges are the sources of inter-quark force. Corresponding to three color charges of a quark, there are eight ...
The Standard Model - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... • Symmetries exist in the equations of the Standard Model – theorem: for each symmetry a conservation law A few most of us are familiar with • Mass-energy, momentum And some a little less familiar • Charge, Color, Spin, Angular Momentum, baryon #, lepton # These limit what is possible…. ...
... • Symmetries exist in the equations of the Standard Model – theorem: for each symmetry a conservation law A few most of us are familiar with • Mass-energy, momentum And some a little less familiar • Charge, Color, Spin, Angular Momentum, baryon #, lepton # These limit what is possible…. ...
Heisenburg uncertainty principle
... Fermions obey the Pauli exclusion principle – no 2 fermions in the same atom can have identical quantum numbers Bosons do not obey the Pauli principle ...
... Fermions obey the Pauli exclusion principle – no 2 fermions in the same atom can have identical quantum numbers Bosons do not obey the Pauli principle ...
The Strong interaction or the mystery of the nucleus - Pierre
... Hadrons are colourless objects ...
... Hadrons are colourless objects ...
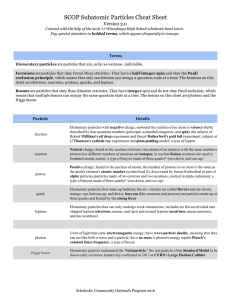
SCOP Subatomic Particles Cheat Sheet
... exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are electrons, neutrons, protons, quarks, and leptons. Bosons are particles that obey BoseEinstein statistics. T ...
... exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are electrons, neutrons, protons, quarks, and leptons. Bosons are particles that obey BoseEinstein statistics. T ...