Photo Album - Imperial Valley College
... same time (unlike a pure substance such as ice). This is called partial melting. Minerals with the highest silica content melt at the lowest temperatures (so magma is always richer in silica than the rock that produced it). Granite contains more silica than basalt and melts at a lower temp. So, basa ...
... same time (unlike a pure substance such as ice). This is called partial melting. Minerals with the highest silica content melt at the lowest temperatures (so magma is always richer in silica than the rock that produced it). Granite contains more silica than basalt and melts at a lower temp. So, basa ...
The Geology of Calavera Hills, North San Diego
... form distinct flows along the flanks of the extinct volcano. None of the volcanic plugs have been radiometrically dated but they are thought to have formed in the Miocene. This is a time when our coastline was transitioning from a convergent plate boundary (subduction) to a transform plate motion. T ...
... form distinct flows along the flanks of the extinct volcano. None of the volcanic plugs have been radiometrically dated but they are thought to have formed in the Miocene. This is a time when our coastline was transitioning from a convergent plate boundary (subduction) to a transform plate motion. T ...
The Geology of Calavera Hills, North San Diego County, California
... form distinct flows along the flanks of the extinct volcano. None of the volcanic plugs have been radiometrically dated but they are thought to have formed in the Miocene. This is a time when our coastline was transitioning from a convergent plate boundary (subduction) to a transform plate motion. T ...
... form distinct flows along the flanks of the extinct volcano. None of the volcanic plugs have been radiometrically dated but they are thought to have formed in the Miocene. This is a time when our coastline was transitioning from a convergent plate boundary (subduction) to a transform plate motion. T ...
Composition of Magma
... The silica content of magma determines not only its explosivity and viscosity, but also which type of volcanic rock it forms as lava cools. ...
... The silica content of magma determines not only its explosivity and viscosity, but also which type of volcanic rock it forms as lava cools. ...
C:\Users\Jim\Documents\school stuff\ses4u\Earth Materials Review
... typically is low and the lava flows out of the volcano and over the surrounding countryside for long distances. Thus, shield volcanoes are much wider than they are tall, although they can get quite high. The biggest are over 100 kilometres wide and many nearly several kilometres high. They are the t ...
... typically is low and the lava flows out of the volcano and over the surrounding countryside for long distances. Thus, shield volcanoes are much wider than they are tall, although they can get quite high. The biggest are over 100 kilometres wide and many nearly several kilometres high. They are the t ...
plate tectonics and associated hazards
... “The hazards presented by volcanic and seismic events have the greatest impact on the world’s poorest people.” To what extent do you agree with this view? (40 marks) ...
... “The hazards presented by volcanic and seismic events have the greatest impact on the world’s poorest people.” To what extent do you agree with this view? (40 marks) ...
Somma Vesuvius: the Volcano and the Observatory
... men and animals that left large. Stamping leaved deep imprints on the ash deposits (Fig. 9), which was filled in and preserved by larger-sized material of the following units. They consists of a succession of coarse-, medium- and fine-ash layers, and tends to mantle buildings and increase in thickne ...
... men and animals that left large. Stamping leaved deep imprints on the ash deposits (Fig. 9), which was filled in and preserved by larger-sized material of the following units. They consists of a succession of coarse-, medium- and fine-ash layers, and tends to mantle buildings and increase in thickne ...
Theoryofplatetectonics 1.91MB 2017-03-29 12
... The area where 2 tectonic plates meet is termed a plate boundary or plate margin. It is at plate boundaries that most of the world’s major landforms occur, and where earthquake, volcanic and mountain building zones are located. Key points related to plate boundaries: a. Due to its relatively low den ...
... The area where 2 tectonic plates meet is termed a plate boundary or plate margin. It is at plate boundaries that most of the world’s major landforms occur, and where earthquake, volcanic and mountain building zones are located. Key points related to plate boundaries: a. Due to its relatively low den ...
Part 1 – Plate Boundaries
... 4.1 – On the map on the previous page, indicate where the hot spot is currently located relative to the islands and seamounts in the chain. Hint: The “Big Island” of Hawaii has several active volcanoes. The other islands are extinct volcanoes. 4.2 – If hot spots are stationary mantle plumes, why is ...
... 4.1 – On the map on the previous page, indicate where the hot spot is currently located relative to the islands and seamounts in the chain. Hint: The “Big Island” of Hawaii has several active volcanoes. The other islands are extinct volcanoes. 4.2 – If hot spots are stationary mantle plumes, why is ...
Igneous Rock Formation, Compositions, and Textures
... make it less likely that gas pressure will build to the point of explosiveness. ...
... make it less likely that gas pressure will build to the point of explosiveness. ...
Earth and Space Sciences
... results in the formation of new oceanic crust (from magma that comes from within the Earth's mantle) along a mid-ocean ridge. Where the oceanic plates are moving away from each other is called a zone of divergence. Ocean floor spreading was first suggested by Harry Hess and Robert Dietz in the 1960' ...
... results in the formation of new oceanic crust (from magma that comes from within the Earth's mantle) along a mid-ocean ridge. Where the oceanic plates are moving away from each other is called a zone of divergence. Ocean floor spreading was first suggested by Harry Hess and Robert Dietz in the 1960' ...
Name ____Justin Powers______ Date ______ Period ____ Plate
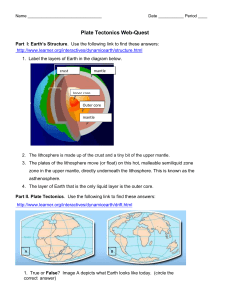
... Mountain – A high, large mass of earth and rock that rises above the Earth’s surface with steep or sloping sides 2. At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates are moving away from each other. One result of huge masses of crust moving apart is seafloor spreading. This occurs when two plates made of oce ...
... Mountain – A high, large mass of earth and rock that rises above the Earth’s surface with steep or sloping sides 2. At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates are moving away from each other. One result of huge masses of crust moving apart is seafloor spreading. This occurs when two plates made of oce ...
ICELAND
... valley system, occupied by a large outlet glacier or ice stream during repeated glaciations. The name Hvalfjörður means “Whale Fjord,” because whales were often seen in this area. (The local whaling station was closed in 1992.) The fjord is about 30 km long and up to 84 km deep. Along the way are ou ...
... valley system, occupied by a large outlet glacier or ice stream during repeated glaciations. The name Hvalfjörður means “Whale Fjord,” because whales were often seen in this area. (The local whaling station was closed in 1992.) The fjord is about 30 km long and up to 84 km deep. Along the way are ou ...
Plate Tectonics Webquest
... deeper into the earth, where high heat and pressure cause trapped water and other gasses to be released from it. This, in turn, makes the base of the crust melt, forming magma. The magma formed at a subduction zone rises up toward the earth's surface and builds up in magma chambers, where it feeds a ...
... deeper into the earth, where high heat and pressure cause trapped water and other gasses to be released from it. This, in turn, makes the base of the crust melt, forming magma. The magma formed at a subduction zone rises up toward the earth's surface and builds up in magma chambers, where it feeds a ...
Mercury, Venus and Mars Chapter 11 PowerPoint
... A. exhibits plate tectonic activity similar to that seen on Earth. B. exhibits a crust that has not broken up into moving plates but does exhibit hotspot volcanism. C. is relatively smooth and featureless. ...
... A. exhibits plate tectonic activity similar to that seen on Earth. B. exhibits a crust that has not broken up into moving plates but does exhibit hotspot volcanism. C. is relatively smooth and featureless. ...
Earth: Portrait of a Planet 3rd edition
... Plate motion is a dominant control on volcanism. Volcanic types are linked to tectonic settings ...
... Plate motion is a dominant control on volcanism. Volcanic types are linked to tectonic settings ...
2. Plate tectonics
... Two plates slide each other not smoothly Results are, 1) Earthquake San Andreas 2) No mountain building Fault in 3) No volcanic activities California ...
... Two plates slide each other not smoothly Results are, 1) Earthquake San Andreas 2) No mountain building Fault in 3) No volcanic activities California ...
Benchmark#5 Volcanoes, Rocks types, weathering
... boundary The island is directly over a divergent plate boundary The Big Island has existed for billions of years from vulcunism, and is now shrinking in size as the island is slowly weathered and eroded The Big Island presently sits directly above a hot spot ...
... boundary The island is directly over a divergent plate boundary The Big Island has existed for billions of years from vulcunism, and is now shrinking in size as the island is slowly weathered and eroded The Big Island presently sits directly above a hot spot ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.