Document
... solidifies, the lava within the pillow also cools and solidifies into solid rock forming a new section of ocean floor. Pillow basalt is not only formed at mid oceanic ridges. Pillow basalt forms anywhere where basalt is injected into water. Therefore, pillow basalt has also formed in places such as ...
... solidifies, the lava within the pillow also cools and solidifies into solid rock forming a new section of ocean floor. Pillow basalt is not only formed at mid oceanic ridges. Pillow basalt forms anywhere where basalt is injected into water. Therefore, pillow basalt has also formed in places such as ...
An Overview of Yellowstone Geologic History
... next page). The volume of rock produced by this eruption, known as the Huckleberry Ridge, produced approximately 600 cubic miles of rock and ash. In comparison to more recent volcanic activity, this is about 17 times the rock produced during the eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia, witnessed in A ...
... next page). The volume of rock produced by this eruption, known as the Huckleberry Ridge, produced approximately 600 cubic miles of rock and ash. In comparison to more recent volcanic activity, this is about 17 times the rock produced during the eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia, witnessed in A ...
Yellowstone Geologic History
... next page). The volume of rock produced by this eruption, known as the Huckleberry Ridge, produced approximately 600 cubic miles of rock and ash. In comparison to more recent volcanic activity, this is about 17 times the rock produced during the eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia, witnessed in A ...
... next page). The volume of rock produced by this eruption, known as the Huckleberry Ridge, produced approximately 600 cubic miles of rock and ash. In comparison to more recent volcanic activity, this is about 17 times the rock produced during the eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia, witnessed in A ...
Document
... Trenches are long, narrow, deep-cutting canyons (8 to 10 km deep) formed by slab pull (negative buoyancy) as the old, cold lithosphere descends into the hotter, less dense asthenosphere. The older, colder, denser the oceanic crust, the deeper the trench! (Basically, the mantle is pulling downwar ...
... Trenches are long, narrow, deep-cutting canyons (8 to 10 km deep) formed by slab pull (negative buoyancy) as the old, cold lithosphere descends into the hotter, less dense asthenosphere. The older, colder, denser the oceanic crust, the deeper the trench! (Basically, the mantle is pulling downwar ...
tectonics teachers notes
... Discuss the human response to the Bam earthquake. 92,000 tents and 200,000 blankets were supplied to help keep people warm. Other aid in the form of 56,000 items of clothing, 51,000 oil heaters and 400,000 ready meals, plus bread, rice, sugar and other food was supplied. Later a 250-bed emergency ho ...
... Discuss the human response to the Bam earthquake. 92,000 tents and 200,000 blankets were supplied to help keep people warm. Other aid in the form of 56,000 items of clothing, 51,000 oil heaters and 400,000 ready meals, plus bread, rice, sugar and other food was supplied. Later a 250-bed emergency ho ...
TWS Sample 7 Landforms 5th grade
... Convergent plate boundaries are where two separate plates collide into eachother. One plate is subducted beneath the other. The impact of the two plates colliding create landforms such as mountain ranges and uplift. 2) Explain a transform plate boundary. A transform plate boundary is where the two p ...
... Convergent plate boundaries are where two separate plates collide into eachother. One plate is subducted beneath the other. The impact of the two plates colliding create landforms such as mountain ranges and uplift. 2) Explain a transform plate boundary. A transform plate boundary is where the two p ...
PT Answers
... Drift - Wegener’s theory that says all of today’s continents were once part on one supercontinent which broke apart and the continents then moved into their present positions. 9. rocks, mountains, glaciers, continental shape, fossils, climate. 10. earthquakes and volcanoes occur on plate boundaries ...
... Drift - Wegener’s theory that says all of today’s continents were once part on one supercontinent which broke apart and the continents then moved into their present positions. 9. rocks, mountains, glaciers, continental shape, fossils, climate. 10. earthquakes and volcanoes occur on plate boundaries ...
File
... Roll your mouse over the image to find the definitions of the words below: Continental Crust - ______the earths crust that makes up the continents___ Mountain - __________a high large mass of earth and rock that rises above earths surface with steep or sloping sides._______ 2. At divergent boundarie ...
... Roll your mouse over the image to find the definitions of the words below: Continental Crust - ______the earths crust that makes up the continents___ Mountain - __________a high large mass of earth and rock that rises above earths surface with steep or sloping sides._______ 2. At divergent boundarie ...
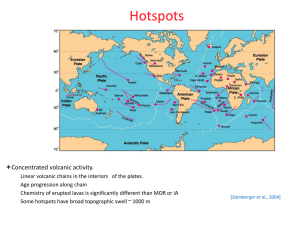
Hawaii, we thought we knew you
... "The crack model... was suggested for the Hawaiian volcanic chain as far back as 1849."4 In 1973, intraplate volcanism, including Hawaii, was proposed to be caused by lithospheric stress, with intermittent eruptions due to the shallowness of the source regions. "Cessation of volcanism in the absence ...
... "The crack model... was suggested for the Hawaiian volcanic chain as far back as 1849."4 In 1973, intraplate volcanism, including Hawaii, was proposed to be caused by lithospheric stress, with intermittent eruptions due to the shallowness of the source regions. "Cessation of volcanism in the absence ...
Go to a new page in your spiral and write the title “Volcanoes
... 12. What is the Ring of Fire? 13. How is Hawaii different? 14. Copy down what you see on the “Lesson Review” page. 15. A __________ is a region of volcanic activity in the middle of a tectonic plate. 16. How do hot spots form volcanic island arc? 17. Do you think that a quick lava flow is more dange ...
... 12. What is the Ring of Fire? 13. How is Hawaii different? 14. Copy down what you see on the “Lesson Review” page. 15. A __________ is a region of volcanic activity in the middle of a tectonic plate. 16. How do hot spots form volcanic island arc? 17. Do you think that a quick lava flow is more dange ...
Geology and geochronology of McMurdo Volcanic Group rocks
... of the geology of Mount Morning and describes in detail the rocks from ‘Gandalf Ridge’. Undersaturatedalkali volcanic rocks of late Cenozoic age in the McMurdo Sound area constitute the Erebus volcanic province of the McMurdo Volcanic Group (Kyle & Cole 1974, Kyle, in press). The rocks of the Erebus ...
... of the geology of Mount Morning and describes in detail the rocks from ‘Gandalf Ridge’. Undersaturatedalkali volcanic rocks of late Cenozoic age in the McMurdo Sound area constitute the Erebus volcanic province of the McMurdo Volcanic Group (Kyle & Cole 1974, Kyle, in press). The rocks of the Erebus ...
File
... Describe the geological manifestations of plate tectonics (e.g., earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building) that occur at plate boundaries. Purpose: To understand how geological features and phenomena relate to plate motions. To understand GPS vector data and how this information allows us to ...
... Describe the geological manifestations of plate tectonics (e.g., earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building) that occur at plate boundaries. Purpose: To understand how geological features and phenomena relate to plate motions. To understand GPS vector data and how this information allows us to ...
A short, data oriented summary of
... (shallower water). Even before plate tectonics, this long linear feature was described as a “midocean ridge.” This is because the lithosphere is hottest at a spreading center, so thermal expansion makes its elevation higher. Hot mantle rocks rise into the space left by the separating plates and form ...
... (shallower water). Even before plate tectonics, this long linear feature was described as a “midocean ridge.” This is because the lithosphere is hottest at a spreading center, so thermal expansion makes its elevation higher. Hot mantle rocks rise into the space left by the separating plates and form ...
Worksheets - Keep It Simple Science
... and sometimes produce huge i)........................ Since these occur under water, they may set off a j)........................... ...
... and sometimes produce huge i)........................ Since these occur under water, they may set off a j)........................... ...
La Yeguada Volcanic Complex - Michigan Technological University
... North America and South America plates slowly compresses the Caribbean plate, and is more pronounced along its western edge in Central America, which contributes to the zone of deformation along the northern, Caribbean coast of Panama, thus separating the Panama block from the larger Caribbean plate ...
... North America and South America plates slowly compresses the Caribbean plate, and is more pronounced along its western edge in Central America, which contributes to the zone of deformation along the northern, Caribbean coast of Panama, thus separating the Panama block from the larger Caribbean plate ...
Rocks ISM 22 2014 - AlmaMiddleSchoolScience
... to the atmosphere and hydrosphere they start to break down Weathering is the general term for all actions that break down or wear away rock Erosion is the carrying away of the sediment ...
... to the atmosphere and hydrosphere they start to break down Weathering is the general term for all actions that break down or wear away rock Erosion is the carrying away of the sediment ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.