Name:
... Benchmark #3 Study Guide (Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Rocks) Name the three different types of volcanoes: a. b. c. Draw each type of volcano. a. ...
... Benchmark #3 Study Guide (Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Rocks) Name the three different types of volcanoes: a. b. c. Draw each type of volcano. a. ...
Cascade Volcanoes - Fort Hays State University
... Prior to its most recent eruption, the conical shape of Mount Saint Helens did not bear the marks of glaciers, which indicated that it was active more recently than other Cascade volcanoes, such as Mount Rainier. Mount Saint Helens erupted violently in May 1980, when a landslide on the north flank a ...
... Prior to its most recent eruption, the conical shape of Mount Saint Helens did not bear the marks of glaciers, which indicated that it was active more recently than other Cascade volcanoes, such as Mount Rainier. Mount Saint Helens erupted violently in May 1980, when a landslide on the north flank a ...
Shifting Plates Choice Board
... Apply what you know about the three types of movements at the plate boundaries and create models of the different geological formations that occur as a result of these movements. Plate Tectonics and the Formation of Mountains, Earthquakes, and Volcanoes ...
... Apply what you know about the three types of movements at the plate boundaries and create models of the different geological formations that occur as a result of these movements. Plate Tectonics and the Formation of Mountains, Earthquakes, and Volcanoes ...
Volcanic and Tectonic Landforms Landforms Landforms
... Stratovolcanoes The nature of volcanic eruptions, whether explosive or subdued, depends on the viscosity of the magma. Felsic lava (rhyolite and andesite) is highly viscous; it is thick and sticky, and resists flow. Consequently, volcanoes of felsic composition typically have steep slopes as the lav ...
... Stratovolcanoes The nature of volcanic eruptions, whether explosive or subdued, depends on the viscosity of the magma. Felsic lava (rhyolite and andesite) is highly viscous; it is thick and sticky, and resists flow. Consequently, volcanoes of felsic composition typically have steep slopes as the lav ...
Cornell Notes Template
... melts, forming magma o A major volcanic zone is around is around the Pacific Ring of Fire o Oceanic-oceanic → island arcs form in the ocean o Oceanic-continental → volcanoes form on land 2) Mid-ocean ridges- occur at divergent plate boundaries as plates pull apart and moves upward. As the magma reac ...
... melts, forming magma o A major volcanic zone is around is around the Pacific Ring of Fire o Oceanic-oceanic → island arcs form in the ocean o Oceanic-continental → volcanoes form on land 2) Mid-ocean ridges- occur at divergent plate boundaries as plates pull apart and moves upward. As the magma reac ...
Igneous Environments and Volcanoes - H
... Describe the following kinds of volcanic hazards: gases, ash and pumice fall, lava flows, pyroclastic flows, lahars and give examples of each. Identify some examples of composite, shield, dome, and scoria cone volcanoes from around the world. Summarize the type of eruptions that occurred at Vesuvius ...
... Describe the following kinds of volcanic hazards: gases, ash and pumice fall, lava flows, pyroclastic flows, lahars and give examples of each. Identify some examples of composite, shield, dome, and scoria cone volcanoes from around the world. Summarize the type of eruptions that occurred at Vesuvius ...
Dynamic Earth, Earthquakes and Volcanoes Webquest
... 3. List a destruction caused by volcanoes 4. List a benefit caused by volcanoes 5. Where do volcanoes occur? 6. About 5 % of volcanoes occur where there are lots of hot areas underneath. This is called a __. 7. Describe the Cinder Cone volcanoe 8. Describe the Composite Volcano 9. Describe the Shiel ...
... 3. List a destruction caused by volcanoes 4. List a benefit caused by volcanoes 5. Where do volcanoes occur? 6. About 5 % of volcanoes occur where there are lots of hot areas underneath. This is called a __. 7. Describe the Cinder Cone volcanoe 8. Describe the Composite Volcano 9. Describe the Shiel ...
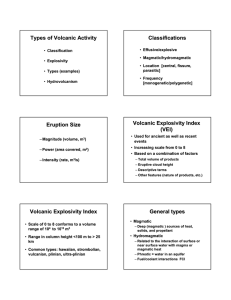
Types of Volcanic Activity Classifications Eruption Size Volcanic
... General types • Magmatic – Deep (magmatic ) sources of heat, solids, and propellant ...
... General types • Magmatic – Deep (magmatic ) sources of heat, solids, and propellant ...
Chapter 7.1
... surface. • Vent—the opening through which lava flows onto the surface. • Volcano—The structure formed by the vent and the built-up volcanic material on the surface around the vent. ...
... surface. • Vent—the opening through which lava flows onto the surface. • Volcano—The structure formed by the vent and the built-up volcanic material on the surface around the vent. ...
Plate Tectonics
... Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites Lava flow ...
... Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites Lava flow ...
Orientation and Conferencing Plan Stage 6
... the upper mantle is cracked into several giant pieces, or plates. The plates slowly push against or pull apart from one another, causing earthquakes. Magma is red-hot liquid rock from the upper mantle. It is under enormous pressure and it squeezes through the cracks in the crust to reach the surface ...
... the upper mantle is cracked into several giant pieces, or plates. The plates slowly push against or pull apart from one another, causing earthquakes. Magma is red-hot liquid rock from the upper mantle. It is under enormous pressure and it squeezes through the cracks in the crust to reach the surface ...
LANDFORMS
... • A cinder cone is a volcanic cone built almost entirely of loose volcanic fragments called cinders. They are built from particles and blobs of congealed lava ejected from a single vent. • As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall ...
... • A cinder cone is a volcanic cone built almost entirely of loose volcanic fragments called cinders. They are built from particles and blobs of congealed lava ejected from a single vent. • As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall ...
Volcano
... Composite Volcano (also know as Stratovolcano) –a taller, steep volcano. Eruption is lava and pyroclastic material. (lava and Tephra)- Felsic • Mt. St. Helens in Washington •Mt. Shasta in California •Mt. Fuji in Japan ...
... Composite Volcano (also know as Stratovolcano) –a taller, steep volcano. Eruption is lava and pyroclastic material. (lava and Tephra)- Felsic • Mt. St. Helens in Washington •Mt. Shasta in California •Mt. Fuji in Japan ...
Plate Tectonics
... causes Earth’s crust to move over time resulting in many of the landforms and geographic events that occur on Earth. ...
... causes Earth’s crust to move over time resulting in many of the landforms and geographic events that occur on Earth. ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.