Living in an Active Zone
... Destructive Plate Margins Oceanic and continental Crust • Where it involves oceanic and continental crust, the oceanic crust is always subducted below the continental because it is denser. • The subduction of the oceanic crust creates a deep sea trench and earthquakes are formed at the subduction z ...
... Destructive Plate Margins Oceanic and continental Crust • Where it involves oceanic and continental crust, the oceanic crust is always subducted below the continental because it is denser. • The subduction of the oceanic crust creates a deep sea trench and earthquakes are formed at the subduction z ...
6th_Plate_Tectonics
... from a volcano or lava flow. * Bomb lava - Also known as volcanic bombs; lava chunk greater than 64mm in diameter which were ejected while still partially melted. * Pillow lava - Lava underwater forms long pillow-shaped formations. Shield volcanoes - shield volcanoes are tall and broad, with flat, r ...
... from a volcano or lava flow. * Bomb lava - Also known as volcanic bombs; lava chunk greater than 64mm in diameter which were ejected while still partially melted. * Pillow lava - Lava underwater forms long pillow-shaped formations. Shield volcanoes - shield volcanoes are tall and broad, with flat, r ...
Lecture #1
... pull apart. • Magma (molten rock) forced up through the cracks forms new oceanic crust that piles up underwater in mid-ocean ridges. ...
... pull apart. • Magma (molten rock) forced up through the cracks forms new oceanic crust that piles up underwater in mid-ocean ridges. ...
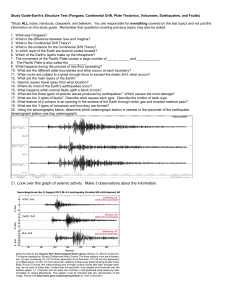
21. Look over this graph of seismic activity. Make 3 observations
... information on this study guide. Remember that questions covering previous topics may also be asked. 1. What was Pangaea? 2. What is the difference between lava and magma? 3. What is the Continental Drift Theory? 4. What is the evidence for the Continental Drift Theory? 5. In which layer of the Eart ...
... information on this study guide. Remember that questions covering previous topics may also be asked. 1. What was Pangaea? 2. What is the difference between lava and magma? 3. What is the Continental Drift Theory? 4. What is the evidence for the Continental Drift Theory? 5. In which layer of the Eart ...
3 TYPES OF FAULTS (MOTIONS) 3 TYPES OF VOLCANOES
... 9. geyeser A type of hot spring that shoots water into the air. This forms where water collects in an underground chamber then erupts through a narrow channel. 10. Tsunami: A water wave triggered by an earthquake, volcanic eruption, or landslide. 11. Pyroclastic flow: A dense cloud of super-hot gase ...
... 9. geyeser A type of hot spring that shoots water into the air. This forms where water collects in an underground chamber then erupts through a narrow channel. 10. Tsunami: A water wave triggered by an earthquake, volcanic eruption, or landslide. 11. Pyroclastic flow: A dense cloud of super-hot gase ...
Chapter_9-Volcanoes
... Associated with subduction zones Most are adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g., Cascade, Andes volcanoes) ...
... Associated with subduction zones Most are adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g., Cascade, Andes volcanoes) ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... – Gases expand near the surface – A vent is an opening in the surface of Earth through which molten rock and gases are released. – Provide the force to extrude lava – Violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma – Gases escape easily from fluid magma. – Viscous magma prod ...
... – Gases expand near the surface – A vent is an opening in the surface of Earth through which molten rock and gases are released. – Provide the force to extrude lava – Violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma – Gases escape easily from fluid magma. – Viscous magma prod ...
Plate Tectonics Test
... 3_______________ opening in the volcano 4_______________ approximately 15 large masses of rock 5_______________ long area of frequent plate activity 6_______________ innermost part of the earth 7_______________ outermost layer of the earth 8_______________ weathering due to wind, water, sand movemen ...
... 3_______________ opening in the volcano 4_______________ approximately 15 large masses of rock 5_______________ long area of frequent plate activity 6_______________ innermost part of the earth 7_______________ outermost layer of the earth 8_______________ weathering due to wind, water, sand movemen ...
Elaborating on a Preexisting Concept
... 19. If plates are moving apart two centimeters per year, that distance is so insignificant that it could never be noticed. ...
... 19. If plates are moving apart two centimeters per year, that distance is so insignificant that it could never be noticed. ...
S05_4359_L20
... 9. Number of Deaths/Type of hazards: 1790 K eruption from the active caldera killed ~100 people (lava and pumice flows and base surge). ML & K lavas have destroyed 100s of houses, villages & ranches. 1868 ML eruption produced lahars killing ~36 and tsunami killing 46. 10. Subsequent activity: ML las ...
... 9. Number of Deaths/Type of hazards: 1790 K eruption from the active caldera killed ~100 people (lava and pumice flows and base surge). ML & K lavas have destroyed 100s of houses, villages & ranches. 1868 ML eruption produced lahars killing ~36 and tsunami killing 46. 10. Subsequent activity: ML las ...
Geomorphic Comparison of Volcanoes on Earth
... Many volcanoes on Earth are asymmetric in shape in map view. This research examined volcanoes in different tectonic settings to assess possible influences of tectonics on terrestrial volcanoes. Volcanic regions studied are the Galapagos Islands (a hot spot), the Caribbean, the Philippines, and Java, ...
... Many volcanoes on Earth are asymmetric in shape in map view. This research examined volcanoes in different tectonic settings to assess possible influences of tectonics on terrestrial volcanoes. Volcanic regions studied are the Galapagos Islands (a hot spot), the Caribbean, the Philippines, and Java, ...
Unit 1 Project-Pompeii - Social Circle City Schools
... Goal: To learn the effect a major volcanic eruption has on earth’s surface and the people who live there. Standard: S6E5 Students will investigate the scientific view of how earth’s surface was formed. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the ear ...
... Goal: To learn the effect a major volcanic eruption has on earth’s surface and the people who live there. Standard: S6E5 Students will investigate the scientific view of how earth’s surface was formed. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the ear ...
4 Tectonics and Geologic Processes
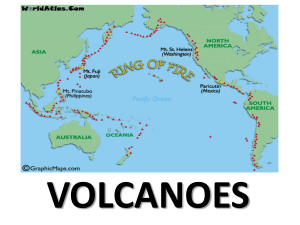
... with continental crust…in areas of subduction. The most dangerous result of a volcanic occurrence is not the viscous lava, but the ensuing flood of mud mixed with ash, and debris known as a “lahar”. Very few volcanoes actually produce lava!!! Pyroclastic flows are also dangerous. Again, the “Ring of ...
... with continental crust…in areas of subduction. The most dangerous result of a volcanic occurrence is not the viscous lava, but the ensuing flood of mud mixed with ash, and debris known as a “lahar”. Very few volcanoes actually produce lava!!! Pyroclastic flows are also dangerous. Again, the “Ring of ...
Virtual Volcano Lab Handout
... a. How are they made?____________________________________________ b. Look like—____________________________________________________ c. 2 famous cinder cone volcanoes & where they are located: i. _______________________________________________________ ii. _____________________________________________ ...
... a. How are they made?____________________________________________ b. Look like—____________________________________________________ c. 2 famous cinder cone volcanoes & where they are located: i. _______________________________________________________ ii. _____________________________________________ ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... Associated with subduction zones Most are adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g., Cascade, Andes volcanoes) ...
... Associated with subduction zones Most are adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g., Cascade, Andes volcanoes) ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.