ICCP Project 2 - Advanced Monte Carlo Methods
... must be chosen with the correct weight. In two dimensions it is chosen randomly on [0, 2π ]. The probability associated with the chosen angle is Pi = wi (θi ) = exp[− βE(θi )]/Zi , where Zi is the local partition function Zi = ∑i wi and is the sum of the weights due to all possible angles for the it ...
... must be chosen with the correct weight. In two dimensions it is chosen randomly on [0, 2π ]. The probability associated with the chosen angle is Pi = wi (θi ) = exp[− βE(θi )]/Zi , where Zi is the local partition function Zi = ∑i wi and is the sum of the weights due to all possible angles for the it ...
Document
... Thus Aeikx are eigenfunctions of the momentum operator with eigenvalues p = ±kћ. The particle in a box wavefunction ψ = D sin kx can be expressed as a linear combination of momentum eigenfunctions, i.e. ψ = D sin kx = D′ (eikx + e-ikx). A single measurement of the particle’s momentum must give a def ...
... Thus Aeikx are eigenfunctions of the momentum operator with eigenvalues p = ±kћ. The particle in a box wavefunction ψ = D sin kx can be expressed as a linear combination of momentum eigenfunctions, i.e. ψ = D sin kx = D′ (eikx + e-ikx). A single measurement of the particle’s momentum must give a def ...
quantum and stat approach
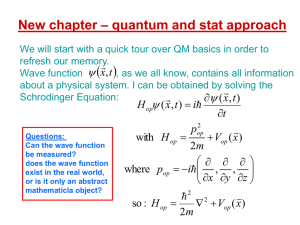
... Suppose that you perform measurements of a quantity associated with a Ωop operator, on a quantum system that at the time of each measurement is in the same state ψ . Each measurement yields an eigenvalue, but each time it may be a different one from the allowed ωn set. After collecting a sufficient ...
... Suppose that you perform measurements of a quantity associated with a Ωop operator, on a quantum system that at the time of each measurement is in the same state ψ . Each measurement yields an eigenvalue, but each time it may be a different one from the allowed ωn set. After collecting a sufficient ...
CHAPTER 2: THE ATOMS AND MOLECULES OF ANCIENT EARTH
... (3) Ball-and-stick model—3-D representation showing bond geometry. (4) Space-filling model—most accurate 3-D spatial depiction. f. Quantifying Molecules (1) Mole = 6.022 x 1023 molecules (Avogadro's number) (2) The mass of one mole of any molecule is the same as its molecular weight in grams. (3) Mo ...
... (3) Ball-and-stick model—3-D representation showing bond geometry. (4) Space-filling model—most accurate 3-D spatial depiction. f. Quantifying Molecules (1) Mole = 6.022 x 1023 molecules (Avogadro's number) (2) The mass of one mole of any molecule is the same as its molecular weight in grams. (3) Mo ...
Lecture 9
... count. The energy of course is not preserved because the Hamiltonian is changed. In addition the state given by this switch-on process will eventually decay into a collection of more complicated states (e.g. by exciting particle-hole pairs out of the Fermi sea) so that there is a finite lifetime. Th ...
... count. The energy of course is not preserved because the Hamiltonian is changed. In addition the state given by this switch-on process will eventually decay into a collection of more complicated states (e.g. by exciting particle-hole pairs out of the Fermi sea) so that there is a finite lifetime. Th ...
Bohr`s Model of the Atom - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... The Bohr model worked well for hydrogen. However, the equations could not be solved exactly for atoms with more than one electron, because of the additional effects that electrons exert on each other (Coulomb force kq q F d12 2 ). By the mid-1920s, quantum physics was changing. The concept of “all ...
... The Bohr model worked well for hydrogen. However, the equations could not be solved exactly for atoms with more than one electron, because of the additional effects that electrons exert on each other (Coulomb force kq q F d12 2 ). By the mid-1920s, quantum physics was changing. The concept of “all ...
SEMESTER 1 EXAM Prblms/Short Ans
... Chemistry EXAM – First Semester Eq, S, U, SF – Equations; Show all equations used in all calculations. Steps; show each step leading to each answer. Units; show the appropriate units with each number used in all calculations. SF; Use the correct significant figures when expressing all answers. Use S ...
... Chemistry EXAM – First Semester Eq, S, U, SF – Equations; Show all equations used in all calculations. Steps; show each step leading to each answer. Units; show the appropriate units with each number used in all calculations. SF; Use the correct significant figures when expressing all answers. Use S ...
Derivation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation from First Principles
... approach to quantum mechanics for the following reasons: a. In the conventional quantum mechanics the wave-function of a free particle is a complex plane wave. This wave, as a field, cannot be the carrier of the particle’s attributes since the energy and momentum densities will, then, be constant in ...
... approach to quantum mechanics for the following reasons: a. In the conventional quantum mechanics the wave-function of a free particle is a complex plane wave. This wave, as a field, cannot be the carrier of the particle’s attributes since the energy and momentum densities will, then, be constant in ...
... In section 2, a certain non self-adjoint Hamiltonian H with real eigenvalues, expressed as a quadratic combination of bosonic operators, is diagonalized by means of dynamical pseudo-bosons, which are determined by the EMM, with the help of a real and pseudo-Hermitian matrix M of size 2N. A complete ...