Document
... The maximum KE depends only on the frequency and the work function, not on the intensity The maximum KE increases with increasing frequency The effect is instantaneous since there is a one-to-one interaction between the photon and the electron ...
... The maximum KE depends only on the frequency and the work function, not on the intensity The maximum KE increases with increasing frequency The effect is instantaneous since there is a one-to-one interaction between the photon and the electron ...
Particles and their decays
... rot, buildings fall into ruins… we call it decay In microscopic world, some particles turn themselves into combinations of other particles – this is called particle decay › E.g. a free neutron (outside a nucleus) turns itself into ...
... rot, buildings fall into ruins… we call it decay In microscopic world, some particles turn themselves into combinations of other particles – this is called particle decay › E.g. a free neutron (outside a nucleus) turns itself into ...
August 2010 Regents Exam part 1
... 9 The percent composition by mass of nitrogen in NH4OH (gram-formula mass = 35 grams/mole) is equal to Nitrogen is 14 g out of 35 g molar mass ...
... 9 The percent composition by mass of nitrogen in NH4OH (gram-formula mass = 35 grams/mole) is equal to Nitrogen is 14 g out of 35 g molar mass ...
Planck`s “quantum of action” from the photoelectric effect (line
... As can be seen on the graph in Fig.2, when the value of V is high and positive, the current i is a constant. This occurs because all the photoelectrons formed at the cathode are reaching the anode. By increasing the intensity I, a higher constant value and current is obtained, because more electrons ...
... As can be seen on the graph in Fig.2, when the value of V is high and positive, the current i is a constant. This occurs because all the photoelectrons formed at the cathode are reaching the anode. By increasing the intensity I, a higher constant value and current is obtained, because more electrons ...
Monday, Apr. 14, 2014
... Classically, the particle would speed up passing the well region, because K = mv2 / 2 = E - V0. According to quantum mechanics, reflection and transmission may occur, but the wavelength inside the potential well is shorter than outside. When the width of the potential well is precisely equal to half ...
... Classically, the particle would speed up passing the well region, because K = mv2 / 2 = E - V0. According to quantum mechanics, reflection and transmission may occur, but the wavelength inside the potential well is shorter than outside. When the width of the potential well is precisely equal to half ...
The One-Dimensional Finite-Difference Time
... For anyone who has ever studied quantum mechanics, it is well-known that the Schrödinger equation can be very difficult to solve analytically. Occasionally, certain complex systems allow for approximate solutions through the use of the WKB method or pertubation theory, but the vast majority of phys ...
... For anyone who has ever studied quantum mechanics, it is well-known that the Schrödinger equation can be very difficult to solve analytically. Occasionally, certain complex systems allow for approximate solutions through the use of the WKB method or pertubation theory, but the vast majority of phys ...
Honors-Final-Review-2014
... _____ boiling point _____ surfactant _____ viscosity _____ solution _____ surface tension ...
... _____ boiling point _____ surfactant _____ viscosity _____ solution _____ surface tension ...
Document
... Atoms gain electrons (negatives) and become more negative. Atoms with 2-3 valence electrons will LOSE electrons and become more positive. Who will lose and who will gain an electron? ...
... Atoms gain electrons (negatives) and become more negative. Atoms with 2-3 valence electrons will LOSE electrons and become more positive. Who will lose and who will gain an electron? ...
Quantum interference in the classically forbidden region: A parametric oscillator
... and classical fluctuations cause transitions between coexisting vibrational states. The transitions are not described by the conventional theory of metastable decay, because the states are periodic in time and the systems lack detailed balance. Experimentally, classical transition rates have been st ...
... and classical fluctuations cause transitions between coexisting vibrational states. The transitions are not described by the conventional theory of metastable decay, because the states are periodic in time and the systems lack detailed balance. Experimentally, classical transition rates have been st ...
Electron Transport in a Double Quantum Dot Governed by a... Oleg N. Jouravlev* and Yuli V. Nazarov
... [8]. The quantum dots are commonly fabricated in GaAsbased semiconductor heterostructures. The specifics of GaAs is a strong hyperfine interaction between electron and nuclear spins [9]. Therefore, the spin of an electron localized in a quantum dot can be strongly affected by the effective spin magn ...
... [8]. The quantum dots are commonly fabricated in GaAsbased semiconductor heterostructures. The specifics of GaAs is a strong hyperfine interaction between electron and nuclear spins [9]. Therefore, the spin of an electron localized in a quantum dot can be strongly affected by the effective spin magn ...
What is LIGHT? Atomic Physics and
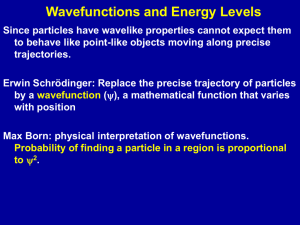
... The lowest energy level is called the ground state (closest to nucleus). To move "up", the electron must absorb a certain (exact) amount of energy from a photon. This new "excited" state for the electron is unstable and the electron returns to ground state. As it falls, the electron emits a pho ...
... The lowest energy level is called the ground state (closest to nucleus). To move "up", the electron must absorb a certain (exact) amount of energy from a photon. This new "excited" state for the electron is unstable and the electron returns to ground state. As it falls, the electron emits a pho ...