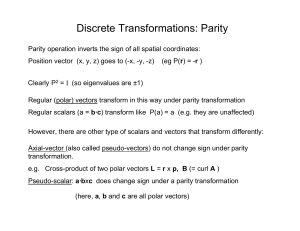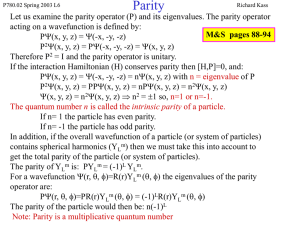
Lecture 6, Parity and Charge Conjugation
... Example: determination of the parity of the p using p-dnn. For this reaction we know many things: a) sp=0, sn=1/2, sd=1, orbital angular momentum Ld=0, Jd=1 b) We know (from experiment) that the p is captured by the d in an s-wave state. Thus the total angular momentum of the initial state is just ...
... Example: determination of the parity of the p using p-dnn. For this reaction we know many things: a) sp=0, sn=1/2, sd=1, orbital angular momentum Ld=0, Jd=1 b) We know (from experiment) that the p is captured by the d in an s-wave state. Thus the total angular momentum of the initial state is just ...
Jens Juul Rasmussen
... in geophysical beta-plane turbulence, due to the similarity between drift waves in plasmas and Rossby waves on the beta-plane. In general, we observe that the particle dispersion is strongly anisotropic, with the diffusion in the zonal direction much larger than the diffusion in the direction parall ...
... in geophysical beta-plane turbulence, due to the similarity between drift waves in plasmas and Rossby waves on the beta-plane. In general, we observe that the particle dispersion is strongly anisotropic, with the diffusion in the zonal direction much larger than the diffusion in the direction parall ...
Particle Conjugation and the 1/N_C Corrections to g_A
... require one to make a certain choice about the ordering of two collective space operators which appear in the expression for the current. An ambiguity arises when one replaces classical objects by quantum operators while doing the collective quantization. In the present note we show that particle co ...
... require one to make a certain choice about the ordering of two collective space operators which appear in the expression for the current. An ambiguity arises when one replaces classical objects by quantum operators while doing the collective quantization. In the present note we show that particle co ...
Particles and Fields
... It was first observed by Planck, that one can actually construct a fully natural system of units by also assigning a unit value to Newton’s constant: G = 1. The natural unit of mass then is the Planck mass ...
... It was first observed by Planck, that one can actually construct a fully natural system of units by also assigning a unit value to Newton’s constant: G = 1. The natural unit of mass then is the Planck mass ...
Nucleus Bubble Discovered
... milestone by many physicists and confirm the theory of the strong interaction. As one of the most powerful computers in the world, JUQUEEN at Forschungszentrum Jülich was decisive for the simulation. The existence and stability of atoms relies heavily on the fact that neutrons are slightly more mass ...
... milestone by many physicists and confirm the theory of the strong interaction. As one of the most powerful computers in the world, JUQUEEN at Forschungszentrum Jülich was decisive for the simulation. The existence and stability of atoms relies heavily on the fact that neutrons are slightly more mass ...