Pharmaceutical suspension
... attracted towards to each other by van der-waals forces and forms loose agglomerates. ...
... attracted towards to each other by van der-waals forces and forms loose agglomerates. ...
TN156 Understanding and Interpreting Particle Siz
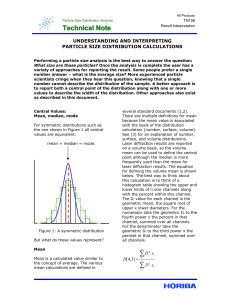
... distribution width is to normalize the standard deviation through division by the mean. This is the Coefficient of Variation (COV) (although it may also be referred to as the relative standard deviation, or RSD). Although included in HORIBA laser diffraction software this value is seldom used as oft ...
... distribution width is to normalize the standard deviation through division by the mean. This is the Coefficient of Variation (COV) (although it may also be referred to as the relative standard deviation, or RSD). Although included in HORIBA laser diffraction software this value is seldom used as oft ...
Multiscale theory of finite-size Bose systems: Implications for collective
... In a boson QC there are two types of processes to be accounted for. The QC-wide processes are either collective 共e.g., rotations, coherent density waves, or shape oscillations兲 or migrations of particlelike disturbances across the QC 共i.e., the coordinated motion of a given particle and a set of oth ...
... In a boson QC there are two types of processes to be accounted for. The QC-wide processes are either collective 共e.g., rotations, coherent density waves, or shape oscillations兲 or migrations of particlelike disturbances across the QC 共i.e., the coordinated motion of a given particle and a set of oth ...
AS_Unit1_Particle_10_Conservation_Rules
... Mesons have TWO quantum numbers that must be conserved in interactions. The charge is denoted by Q, the baryon number by B. Mesons have a baryon number of 0. Mesons have a lepton number of 0. This must be conserved in any interactions with leptons. Here is a typical decay: ...
... Mesons have TWO quantum numbers that must be conserved in interactions. The charge is denoted by Q, the baryon number by B. Mesons have a baryon number of 0. Mesons have a lepton number of 0. This must be conserved in any interactions with leptons. Here is a typical decay: ...
PPT - Florida Institute of Technology
... - LHC is the first opportunity to search for Z' in a high mass (TeV) range. - Z' → µ+ µ- is one of the most promising channel for its discovery( Clean signature, low ...
... - LHC is the first opportunity to search for Z' in a high mass (TeV) range. - Z' → µ+ µ- is one of the most promising channel for its discovery( Clean signature, low ...