In search of symmetry lost
... new particle, the so-called Higgs particle. More ambitious speculations suggest that there should be not just a single Higgs particle, but rather a complex of related particles. The very popular and attractive idea of low-energy supersymmetry7,8, to be discussed further below, requires at least five ...
... new particle, the so-called Higgs particle. More ambitious speculations suggest that there should be not just a single Higgs particle, but rather a complex of related particles. The very popular and attractive idea of low-energy supersymmetry7,8, to be discussed further below, requires at least five ...
QUANTROPY 1. Introduction There is a famous analogy between
... correct. Quantum mechanics is rife with complex numbers, and it makes no sense to maximize a complex function. But a complex function can still have stationary points, where its first derivative vanishes. So, a less naive program is to derive the amplitudes in quantum mechanics from a ‘principle of ...
... correct. Quantum mechanics is rife with complex numbers, and it makes no sense to maximize a complex function. But a complex function can still have stationary points, where its first derivative vanishes. So, a less naive program is to derive the amplitudes in quantum mechanics from a ‘principle of ...
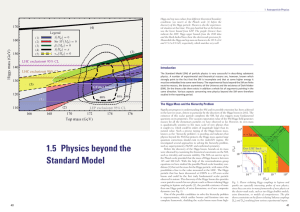
1.5 physics beyond the Standard Model
... in the last two years, driven in particular by the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012. The existence of this scalar particle completes the SM, but also triggers many fundamental questions on its properties. The vacuum expectation value of the SM Higgs field generates masses for all the elementary ...
... in the last two years, driven in particular by the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012. The existence of this scalar particle completes the SM, but also triggers many fundamental questions on its properties. The vacuum expectation value of the SM Higgs field generates masses for all the elementary ...
Quantum Cheshire Cat
... Figure 2: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup, which comprises of two beam splitters (BS1 and BS2 ), half wave plate (HWP), phase shifter (PS), a polarizing beam splitter (PBS) and three photon detectors (D1 , D2 , D3 ). Source: [2]. Components in this setup perform the following operations ...
... Figure 2: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup, which comprises of two beam splitters (BS1 and BS2 ), half wave plate (HWP), phase shifter (PS), a polarizing beam splitter (PBS) and three photon detectors (D1 , D2 , D3 ). Source: [2]. Components in this setup perform the following operations ...
Quantum computing
... based on NMR (Oxford; IBM, MIT, Stanford) 2000: quantum computer on 7 qubits, based on NMR ...
... based on NMR (Oxford; IBM, MIT, Stanford) 2000: quantum computer on 7 qubits, based on NMR ...
Statistics, Causality and Bell`s theorem
... Recall that quantum physics is a stochastic theory (the physists say: a statistical theory): it allows us to predict the probabilities of outcomes of measurements on quantum systems, not (in general) the actual outcomes. The EPR paradox and Bell’s theorem are two landmarks in the history of the ongo ...
... Recall that quantum physics is a stochastic theory (the physists say: a statistical theory): it allows us to predict the probabilities of outcomes of measurements on quantum systems, not (in general) the actual outcomes. The EPR paradox and Bell’s theorem are two landmarks in the history of the ongo ...
Solution of the Hard Problem of Consciousness
... Translocation of electrons in the brain The moment when the electrons gain enough energy to allow them to leave their position in the potential well, they, being in a quantum state, spill out of their original potential well in all directions, obeying the Schroedinger equation. The laws of classical ...
... Translocation of electrons in the brain The moment when the electrons gain enough energy to allow them to leave their position in the potential well, they, being in a quantum state, spill out of their original potential well in all directions, obeying the Schroedinger equation. The laws of classical ...
Common Exam - 2004 Department of Physics University of Utah August 28, 2004
... Please note that there is a separate booklet for each numbered question (i.e., use booklet #1 for problem #1, etc.). To receive full credit, not only should the correct solutions be given, but a sufficient number of steps should be given so that a faculty grader can follow your reasoning. Define all ...
... Please note that there is a separate booklet for each numbered question (i.e., use booklet #1 for problem #1, etc.). To receive full credit, not only should the correct solutions be given, but a sufficient number of steps should be given so that a faculty grader can follow your reasoning. Define all ...