presentation source
... The W and Z are extremely short-lived, but can be identified by their decay modes, also predicted by electroweak theory ene ...
... The W and Z are extremely short-lived, but can be identified by their decay modes, also predicted by electroweak theory ene ...
Particle Zoo - University of Birmingham
... freedom which allowed formulation of Pauli exclusion principle. In 1925, it was suggested that it relates to self-rotation, but heavily criticised… only useful as a picture. In 1927 Pauli formulated theory of spin as a fully quantum object (non-relativistic). In 1928 Dirac described the relativistic ...
... freedom which allowed formulation of Pauli exclusion principle. In 1925, it was suggested that it relates to self-rotation, but heavily criticised… only useful as a picture. In 1927 Pauli formulated theory of spin as a fully quantum object (non-relativistic). In 1928 Dirac described the relativistic ...
2010 midterm exam - MIT OpenCourseWare
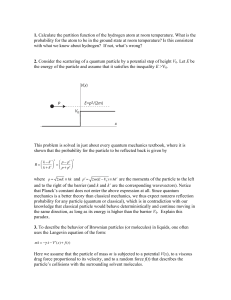
... 1. What is an observable in quantum mechanics and by which mathematical object is represented? 2. How are the possible values of measurement outcomes of an observable determined? 3. What is the probability of finding a particle described by the wavefunction ψ(x, y, z) in a small volume dV = dx dy dz ...
... 1. What is an observable in quantum mechanics and by which mathematical object is represented? 2. How are the possible values of measurement outcomes of an observable determined? 3. What is the probability of finding a particle described by the wavefunction ψ(x, y, z) in a small volume dV = dx dy dz ...
Reakcje jądrowe
... The is equal almost to 1 after reaching energy of a few MeV. Velocity of light is very high and equals about 3x108 m/s in a vacuum. We take the same value in the air. We can increase magnetic field or decrease frequency of potential difference applying to daunts, or both, to avoid increases of the ...
... The is equal almost to 1 after reaching energy of a few MeV. Velocity of light is very high and equals about 3x108 m/s in a vacuum. We take the same value in the air. We can increase magnetic field or decrease frequency of potential difference applying to daunts, or both, to avoid increases of the ...
Introduction: what is quantum field theory ?
... supernova lying 8 billion lightyears away. We compare this proton with one freshly minted in a particle accelerator here on Earth. And the two are exactly the same! How is this possible? Why aren’t there errors in proton production? How can two objects, manufactured so far apart in space and time, b ...
... supernova lying 8 billion lightyears away. We compare this proton with one freshly minted in a particle accelerator here on Earth. And the two are exactly the same! How is this possible? Why aren’t there errors in proton production? How can two objects, manufactured so far apart in space and time, b ...