
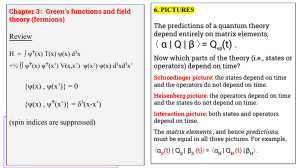
α | Q | β 〉= Q (t) . 〈 Review
... picture ... Assume H = H0 + H1 , where H0 is solvable and H1 is a set of interactions, possibly having small effects. {Usually H0 is a single particle operator; and H1 is a two-particle operator describing the interactions between particles.} ...
... picture ... Assume H = H0 + H1 , where H0 is solvable and H1 is a set of interactions, possibly having small effects. {Usually H0 is a single particle operator; and H1 is a two-particle operator describing the interactions between particles.} ...
Problem set 2
... 3. Find a matrix representation of the component of spin S~ · n̂ in the direction of the unit vector n̂ = (n x , ny , nz ), for a spin half particle. 4. Find the eigenvalues of the component of spin S~ · n̂ in any direction n̂ for a spin-half particle by evaluating the square of this operator and it ...
... 3. Find a matrix representation of the component of spin S~ · n̂ in the direction of the unit vector n̂ = (n x , ny , nz ), for a spin half particle. 4. Find the eigenvalues of the component of spin S~ · n̂ in any direction n̂ for a spin-half particle by evaluating the square of this operator and it ...
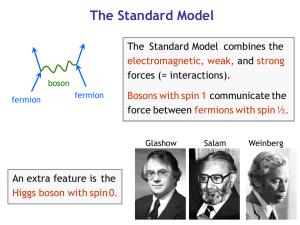
Inside A Particle Physicist`s Toolbox
... Early 1900’s: omnipresent radiation discharges electroscopes ...
... Early 1900’s: omnipresent radiation discharges electroscopes ...
量子力學
... (c) Explain why the ground-state energy of a particle in the potential given in (a) is different from zero. 12. Suppose we have two particles, both of mass m, confined in 0 < x < a described by a potential V = 0 for 0 < x < a and V = for x < 0 and x > a. Assume that these two particles are not int ...
... (c) Explain why the ground-state energy of a particle in the potential given in (a) is different from zero. 12. Suppose we have two particles, both of mass m, confined in 0 < x < a described by a potential V = 0 for 0 < x < a and V = for x < 0 and x > a. Assume that these two particles are not int ...
IMFUFA- Roskilde Universitetscenter- postbox 260
... series is divergent. Formally, we can put z=-1, whereby the infinite sum becomes the previously mentioned sum of all positive integers, and we can assign it a value given by the analytical continuation of the zetafunction to z=-1. In this way we get at the renormalized value ζ(-1) = -1/124 , i.e., n ...
... series is divergent. Formally, we can put z=-1, whereby the infinite sum becomes the previously mentioned sum of all positive integers, and we can assign it a value given by the analytical continuation of the zetafunction to z=-1. In this way we get at the renormalized value ζ(-1) = -1/124 , i.e., n ...











![[a,b]! - Nikhef](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000147861_1-4659b0cc203c9fe99ee5f554409aa79c-300x300.png)









