Experimental Aspects of Jet Reconstruction in Collider
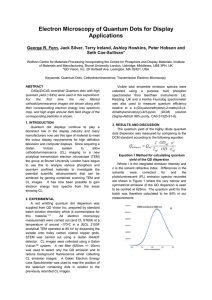
... Very precise for low pT measurements pT Only sensitive to charged particles Limited polar angle coverage Forward region in experiment excluded ...
... Very precise for low pT measurements pT Only sensitive to charged particles Limited polar angle coverage Forward region in experiment excluded ...
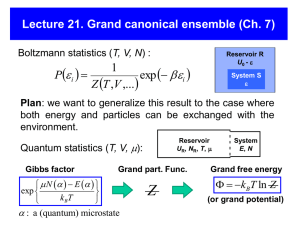
Symmetry and statistics
... Symmetry and statistics Two concepts, of fundamental importance to quantum mechanics, will be discussed in this chapter. The first is that of symmetry. Even though the concept of symmetry is familiar in a wide range of natural sciences, the way symmetry constrains the consequences of quantum mechani ...
... Symmetry and statistics Two concepts, of fundamental importance to quantum mechanics, will be discussed in this chapter. The first is that of symmetry. Even though the concept of symmetry is familiar in a wide range of natural sciences, the way symmetry constrains the consequences of quantum mechani ...
May 2001
... A particle of mass m moves in a one-dimensional potential V (x) = −ax2 + bx4 with very light damping. The particle is set in motion with a large initial velocity. Suppose now we measure the period of the motion for each full oscillation, and call these periods T1 , T2 , T3 , T4 , and so on. It is ob ...
... A particle of mass m moves in a one-dimensional potential V (x) = −ax2 + bx4 with very light damping. The particle is set in motion with a large initial velocity. Suppose now we measure the period of the motion for each full oscillation, and call these periods T1 , T2 , T3 , T4 , and so on. It is ob ...
Wavefunctions and Bound Systems
... • Operators tell us what we want to know: • Example: momentum – Classical: ...
... • Operators tell us what we want to know: • Example: momentum – Classical: ...
Particle Accelerators
... Einstein’s theory of special relativity states that as objects get faster, they get heavier. Therefore if the particles travel close to the speed of light, their mass will increase. As r = mv/BQ, an increase in mass, will cause the particle to have a circular path of a larger radius, therefore it wi ...
... Einstein’s theory of special relativity states that as objects get faster, they get heavier. Therefore if the particles travel close to the speed of light, their mass will increase. As r = mv/BQ, an increase in mass, will cause the particle to have a circular path of a larger radius, therefore it wi ...
Thermal Physics PH2001
... N indistinguishable atoms • 2nd stage N indistinguishable particles in the box that do not interact with each other the system energy is the sum of their individual energies. • The partition function is the sum of the Boltzmann factors over every possible state of the system (as always - this isn't ...
... N indistinguishable atoms • 2nd stage N indistinguishable particles in the box that do not interact with each other the system energy is the sum of their individual energies. • The partition function is the sum of the Boltzmann factors over every possible state of the system (as always - this isn't ...
PHY820 Homework Set 5
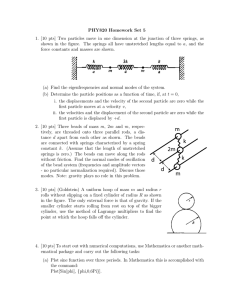
... (a) Find the eigenfrequencies and normal modes of the system. (b) Determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, i. the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the ...
... (a) Find the eigenfrequencies and normal modes of the system. (b) Determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, i. the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the ...