Textbook - Chapter 17 File
... You are about to enter the world of undetectable particles that blink in and out of existence. You will see that a calculation by a theoretical physicist in the 1920s led to sophisticated new medical technology that uses a previously unknown form of matter (Figure 17.1). You will learn about the pec ...
... You are about to enter the world of undetectable particles that blink in and out of existence. You will see that a calculation by a theoretical physicist in the 1920s led to sophisticated new medical technology that uses a previously unknown form of matter (Figure 17.1). You will learn about the pec ...
John Dalton
... Ernest Rutherford - Discovered the nucleus using gold foil experiment James Chadwick - Discovered the neutron Henri Becquerel - discovered radiation emitted by Uranium Marie Curie - discovered two other elements that emitted radiation (Polonium and Radium) Niels Bohr - Proposed energy levels and the ...
... Ernest Rutherford - Discovered the nucleus using gold foil experiment James Chadwick - Discovered the neutron Henri Becquerel - discovered radiation emitted by Uranium Marie Curie - discovered two other elements that emitted radiation (Polonium and Radium) Niels Bohr - Proposed energy levels and the ...
vocab chap 6
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
e + + e
... Charged or neutral particle passage through matter → interaction of particle and matter. 1) Charged – electromagnetic interaction 2) Hadrons – strong interaction 3) Neutrina – only weak interaction A) Charged particles – electric charge is interacting with atoms of matter → escape of electrons from ...
... Charged or neutral particle passage through matter → interaction of particle and matter. 1) Charged – electromagnetic interaction 2) Hadrons – strong interaction 3) Neutrina – only weak interaction A) Charged particles – electric charge is interacting with atoms of matter → escape of electrons from ...
Teacher Guide
... Atoms of different elements are distinguished by the number of protons in the nucleus. For example, all carbon atoms have 6 protons. ...
... Atoms of different elements are distinguished by the number of protons in the nucleus. For example, all carbon atoms have 6 protons. ...
Element Builder Vocabulary
... The energy released by radioactive substances can be harnessed to produce electricity in a nuclear power plant. This energy also can be used to create a massive explosion in a nuclear bomb. ...
... The energy released by radioactive substances can be harnessed to produce electricity in a nuclear power plant. This energy also can be used to create a massive explosion in a nuclear bomb. ...
Document
... Let’s see what’s inside! Note: apparent excess of matter over antimatter can be traced to excess of the number of baryons over antibaryons. Thus our Big Problem is called Problem of Baryon Asymmetry of the Universe. ...
... Let’s see what’s inside! Note: apparent excess of matter over antimatter can be traced to excess of the number of baryons over antibaryons. Thus our Big Problem is called Problem of Baryon Asymmetry of the Universe. ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Elements are pure substances that are made up of one kind of atom. Pizza is not an element because it is a mixture of many substances. Water is a pure substance, but it contains two different kinds of atoms: oxygen and hydrogen. Iron is an element because it is composed of one kind of atom. Gizmo W ...
... Elements are pure substances that are made up of one kind of atom. Pizza is not an element because it is a mixture of many substances. Water is a pure substance, but it contains two different kinds of atoms: oxygen and hydrogen. Iron is an element because it is composed of one kind of atom. Gizmo W ...
If a pair of deuterium hydrinos fuse, or if two electrons are involved in
... the potential energy lost by the fall. If a point sized electron could magically be transported to the location of a point charge nucleus without gaining the corresponding kinetic energy, it would take an infinite amount of energy to separate them. Call such a system highly de-energized. As shown in ...
... the potential energy lost by the fall. If a point sized electron could magically be transported to the location of a point charge nucleus without gaining the corresponding kinetic energy, it would take an infinite amount of energy to separate them. Call such a system highly de-energized. As shown in ...
XII-1 - OP Jindal School, Raigarh
... A small ball of mass 2 x 10-3kg having a charge of 1µC is suspended by a string of length 0.8m. Another identical ball having the same charge is kept at the point of suspension. Determine the minimum horizontal velocity which should be imparted to the lower ball so that it can make complete revoluti ...
... A small ball of mass 2 x 10-3kg having a charge of 1µC is suspended by a string of length 0.8m. Another identical ball having the same charge is kept at the point of suspension. Determine the minimum horizontal velocity which should be imparted to the lower ball so that it can make complete revoluti ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do not have your first quarter review packet you can get another (and the answers) at: http://www.ncusd203.or ...
... you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do not have your first quarter review packet you can get another (and the answers) at: http://www.ncusd203.or ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do not have your first quarter review packet you can get another (and the answers) at: http://www.ncusd203.or ...
... you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do not have your first quarter review packet you can get another (and the answers) at: http://www.ncusd203.or ...
Lesson 17 - Motion of a Charged Particle in a Uniform Field
... magnetic field, it always experiences a force that is at right angles to the velocity This results in a change in the direction of the velocity but not its magnitude As a result, this force will provide a centripetal acceleration towards the centre of the circular path ...
... magnetic field, it always experiences a force that is at right angles to the velocity This results in a change in the direction of the velocity but not its magnitude As a result, this force will provide a centripetal acceleration towards the centre of the circular path ...
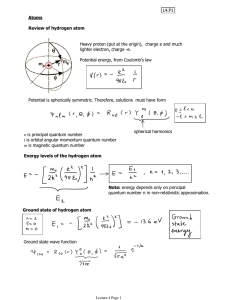
Lecture 4
... There are letters associated with values of orbital angular momentum. The first few are: For example, state with n=1 l=0 is referred to as 1s, n=2 l=0 is referred to as 2s, n=2 l=1 is referred to as 2p, and so on. While the energies are the same for the four n=2 states, the wave functions are not: ...
... There are letters associated with values of orbital angular momentum. The first few are: For example, state with n=1 l=0 is referred to as 1s, n=2 l=0 is referred to as 2s, n=2 l=1 is referred to as 2p, and so on. While the energies are the same for the four n=2 states, the wave functions are not: ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.