
Biochemistry Introduction day 1
... Chemical Reactions: when elements and compounds interact with each other to form new substances. Reactant: A substance that undergoes a chemical reaction. Product: A substance formed from chemical reaction. Chemical Equations: Communicate what is happening in a chemical reaction. It can be done in a ...
... Chemical Reactions: when elements and compounds interact with each other to form new substances. Reactant: A substance that undergoes a chemical reaction. Product: A substance formed from chemical reaction. Chemical Equations: Communicate what is happening in a chemical reaction. It can be done in a ...
33 PARTICLE PHYSICS - Wright State University
... The pions, or π -mesons as they are also called, have masses close to those predicted and feel the strong nuclear force. Another previously unknown particle, now called the muon, was discovered during cosmic-ray experiments in 1936 (one of its discoverers, Seth Neddermeyer, also originated the idea ...
... The pions, or π -mesons as they are also called, have masses close to those predicted and feel the strong nuclear force. Another previously unknown particle, now called the muon, was discovered during cosmic-ray experiments in 1936 (one of its discoverers, Seth Neddermeyer, also originated the idea ...
Phys 111 CE1 2013 Fall
... First, write your name and section number on both the Scantron card and this exam sheet. Use the formula sheet (last exam booklet page) and no other materials. Budget your time. There are 18 multiple choice problems. For most, if not all, of the multiple choice problems, it will be difficult to arri ...
... First, write your name and section number on both the Scantron card and this exam sheet. Use the formula sheet (last exam booklet page) and no other materials. Budget your time. There are 18 multiple choice problems. For most, if not all, of the multiple choice problems, it will be difficult to arri ...
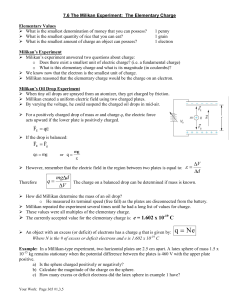
7.6 - Millikan Oil Drop Experiment
... How did Millikan determine the mass of an oil drop? o He measured its terminal speed (free fall) as the plates are disconnected from the battery. Millikan repeated the experiment several times until he had a long list of values for charge. These values were all multiples of the elementary char ...
... How did Millikan determine the mass of an oil drop? o He measured its terminal speed (free fall) as the plates are disconnected from the battery. Millikan repeated the experiment several times until he had a long list of values for charge. These values were all multiples of the elementary char ...
Mathematical Modelling and Computer Simulation of Electrical
... findings into a manufacturing process. It can assist in the process of de-signing and constructing a new type of an AC separatorsorter. It can also help to get it into practice and thus move research findings into the real-world conditions. The presented computer models may be applied both by projec ...
... findings into a manufacturing process. It can assist in the process of de-signing and constructing a new type of an AC separatorsorter. It can also help to get it into practice and thus move research findings into the real-world conditions. The presented computer models may be applied both by projec ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... 2. A substance’s _______ of matter depends on the freedom of ___________ and _______________ of Its particles (_________/molecules) a. (e.g.) the ____________ the attraction of the particles; the result is _____ freedom to _______ 3. The ________/molecules of ____ matter, even ________ substances, h ...
... 2. A substance’s _______ of matter depends on the freedom of ___________ and _______________ of Its particles (_________/molecules) a. (e.g.) the ____________ the attraction of the particles; the result is _____ freedom to _______ 3. The ________/molecules of ____ matter, even ________ substances, h ...
L01_5342_Sp02
... 3. There will be no make-up, or early exams given. Attendance is required for all tests. 4. See Americans with Disabilities Act statement 5. See academic dishonesty statement 6 ...
... 3. There will be no make-up, or early exams given. Attendance is required for all tests. 4. See Americans with Disabilities Act statement 5. See academic dishonesty statement 6 ...
Weak measurements [1] Pre and Post selection in strong measurements
... system can affect the environment when interacting with it at time t and that both have the same predictions for the system. The first questions that arises immediately is: Then how is it different? The philosophical side of the answer is that we want to understand the true interpretation of nature ...
... system can affect the environment when interacting with it at time t and that both have the same predictions for the system. The first questions that arises immediately is: Then how is it different? The philosophical side of the answer is that we want to understand the true interpretation of nature ...
quanta-and-waves-student-booklet-i-ror
... The solar wind, and its accompanying magnet field, is strong enough to interact with planets and their magnetic fields to shape magnetospheres. A magnetosphere is the region surrounding a planet where the planet's magnetic field has dominant control over the motions of gas and fast charged particles ...
... The solar wind, and its accompanying magnet field, is strong enough to interact with planets and their magnetic fields to shape magnetospheres. A magnetosphere is the region surrounding a planet where the planet's magnetic field has dominant control over the motions of gas and fast charged particles ...
Document
... charged particles via the space-charge fields, i.e., the fields produced by the space charge generated in the gap must be taken into account. In general, the space charge is characterized by large density gradients and dynamics range. In such conditions the gas properties such as the ionization coef ...
... charged particles via the space-charge fields, i.e., the fields produced by the space charge generated in the gap must be taken into account. In general, the space charge is characterized by large density gradients and dynamics range. In such conditions the gas properties such as the ionization coef ...
Chapter 2 Practice Questions
... B) Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. C) All atoms of a given element are identical. D) Atoms are indivisible in chemical reactions. E) All of these statements are true according to modern atomic theory. 4. Avogadro's hypothesis states that: A) Each atom of oxygen is 16 times ...
... B) Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. C) All atoms of a given element are identical. D) Atoms are indivisible in chemical reactions. E) All of these statements are true according to modern atomic theory. 4. Avogadro's hypothesis states that: A) Each atom of oxygen is 16 times ...
Lesson 13: Nuclear Propulsion Basics
... results from a redistribution of electric charge within a nucleus. • A g ray is a high energy photon. • For complex nuclei there are many different possible ways in which the neutrons and protons can be arranged within the nucleus. – Gamma rays can be emitted when a nucleus undergoes a transition fr ...
... results from a redistribution of electric charge within a nucleus. • A g ray is a high energy photon. • For complex nuclei there are many different possible ways in which the neutrons and protons can be arranged within the nucleus. – Gamma rays can be emitted when a nucleus undergoes a transition fr ...
About the Zero Point Energy, Zero Point Mass, Zero Point
... we get that the P has a its own inertial mass, which coincides with its ZPM [7]. It is certainly an extremely low value, yet 6= 0. Just incidentally let’s mention something about the neutrino. The neutrino too, up until short ago, was considered massless, though having a certain E (thus in contrast ...
... we get that the P has a its own inertial mass, which coincides with its ZPM [7]. It is certainly an extremely low value, yet 6= 0. Just incidentally let’s mention something about the neutrino. The neutrino too, up until short ago, was considered massless, though having a certain E (thus in contrast ...
The Atomic Theory
... The chemical action of an electric current is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity which passes through a solution. The weights of the substances deposited by the same quantity of electricity are proportional to their chemical equivalents. Stoney (1874) made the hypothesis that there ...
... The chemical action of an electric current is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity which passes through a solution. The weights of the substances deposited by the same quantity of electricity are proportional to their chemical equivalents. Stoney (1874) made the hypothesis that there ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.








![Weak measurements [1] Pre and Post selection in strong measurements](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008913441_1-7a0f5f5a1778eb5da686e2de8a47882f-300x300.png)













