Chemistry Review - pams-hoey
... 1. Binding energy: needed for the stability of a nucleus 2. Radioactive decay: The spontaneous breakdown of an unstable atomic nucleus 3. Decay Series: The series of steps by which a radioactive nucleus decays into a non-radioactive nucleus. 4. Alpha Decay: Occurs when a nucleus releases an alpha pa ...
... 1. Binding energy: needed for the stability of a nucleus 2. Radioactive decay: The spontaneous breakdown of an unstable atomic nucleus 3. Decay Series: The series of steps by which a radioactive nucleus decays into a non-radioactive nucleus. 4. Alpha Decay: Occurs when a nucleus releases an alpha pa ...
Chapter 5
... • DeBroglie, Einstein (and others) showed that electromagnetic radiation has properties of matter as well as waves. This is known as the wave-particle duality for light. • Wave-particle duality is perhaps one of the most confusing concepts in science, because it is so unlike anything we see in the o ...
... • DeBroglie, Einstein (and others) showed that electromagnetic radiation has properties of matter as well as waves. This is known as the wave-particle duality for light. • Wave-particle duality is perhaps one of the most confusing concepts in science, because it is so unlike anything we see in the o ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC EMISSION OF ATOMIC ELECTRONS
... INTERNAL bremsstrahlung in {3 decay and K capture was first considered by Knipp and Uhlenbeck[1J. Later Glauber and Martin developed a more consistent theory of radiative capture of orbital electrons [ 2• 3]; Lewis and Ford [ 4] took account of the contribution from the ''virtual intermediate state" ...
... INTERNAL bremsstrahlung in {3 decay and K capture was first considered by Knipp and Uhlenbeck[1J. Later Glauber and Martin developed a more consistent theory of radiative capture of orbital electrons [ 2• 3]; Lewis and Ford [ 4] took account of the contribution from the ''virtual intermediate state" ...
The Atom
... # of protons = the atomic number Atomic number = # of protons # of protons determines which element it is! Who is element # 15? Phosphorus How many protons does lithium have? 3 What is the atomic number of tin? 50 ...
... # of protons = the atomic number Atomic number = # of protons # of protons determines which element it is! Who is element # 15? Phosphorus How many protons does lithium have? 3 What is the atomic number of tin? 50 ...
Chapter 5
... • DeBroglie, Einstein (and others) showed that electromagnetic radiation has properties of matter as well as waves. This is known as the waveparticle duality for light. • Wave-particle duality is perhaps one of the most confusing concepts in science, because it is so unlike anything we see in the or ...
... • DeBroglie, Einstein (and others) showed that electromagnetic radiation has properties of matter as well as waves. This is known as the waveparticle duality for light. • Wave-particle duality is perhaps one of the most confusing concepts in science, because it is so unlike anything we see in the or ...
USING STANDARD SYSTE - The University of Iowa
... Laboratory dusty plasmas have recently proven to be useful in studying strongly coupled plasmas, plasma-dust interactions, and solid-liquid phase transitions. The dust particles are highly charged due to collection of plasma electrons and ions and strongly repel one another. Clouds of such particles ...
... Laboratory dusty plasmas have recently proven to be useful in studying strongly coupled plasmas, plasma-dust interactions, and solid-liquid phase transitions. The dust particles are highly charged due to collection of plasma electrons and ions and strongly repel one another. Clouds of such particles ...
Notes-15 - KSU Physics
... Homework15.1. Go to website of NIST to find out the energy levels of 1s2s states of helium, for singlet and triplet states and including the fine structure (i.e., for different J's). Do the same for 1s2p, and draw the energy levels to approximate correct relative scale. 15.2. For helium atom, if on ...
... Homework15.1. Go to website of NIST to find out the energy levels of 1s2s states of helium, for singlet and triplet states and including the fine structure (i.e., for different J's). Do the same for 1s2p, and draw the energy levels to approximate correct relative scale. 15.2. For helium atom, if on ...
Lecture Slides
... “According to relativity theory, the word “simultaneous” admits of a definition in no other way than through experiments in which the velocity of light propagation enters essentially. If there were a “sharper” definition of simultaneity, for example by signals that propagate infinitely fast, relati ...
... “According to relativity theory, the word “simultaneous” admits of a definition in no other way than through experiments in which the velocity of light propagation enters essentially. If there were a “sharper” definition of simultaneity, for example by signals that propagate infinitely fast, relati ...
MAGNETIC FORCE ON MOVING CHARGE
... AP Physics B Learning Objectives III.D.I. 1. Forces on moving charges in magnetic fields Students should understand the force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field, so they can: a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force in terms of q, v, and, B, and explain why the magne ...
... AP Physics B Learning Objectives III.D.I. 1. Forces on moving charges in magnetic fields Students should understand the force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field, so they can: a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force in terms of q, v, and, B, and explain why the magne ...
1993 AP Physics B Free-Response
... A particle of mass m and charge q is accelerated from rest in the plane of the page through a potential difference V between two parallel plates as shown above. The particle is injected through a hole in the right-hand plate into a region of space containing a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B o ...
... A particle of mass m and charge q is accelerated from rest in the plane of the page through a potential difference V between two parallel plates as shown above. The particle is injected through a hole in the right-hand plate into a region of space containing a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B o ...
CHAPTER 9: Statistical Physics
... Because bosons do not obey the Pauli exclusion principle, more bosons can fill lower energy states. Three graphs coincide at high energies – the classical limit. Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics may be used in the classical ...
... Because bosons do not obey the Pauli exclusion principle, more bosons can fill lower energy states. Three graphs coincide at high energies – the classical limit. Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics may be used in the classical ...
UNIT PLAN TEMPLATE
... C-2.1 Illustrate electron configurations by using orbital notation for representative elements. C-2.2 Summarize atomic properties (including electron configuration, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic size, and ionic size). C-2.3 Summarize the periodic table’s property trends (including ele ...
... C-2.1 Illustrate electron configurations by using orbital notation for representative elements. C-2.2 Summarize atomic properties (including electron configuration, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic size, and ionic size). C-2.3 Summarize the periodic table’s property trends (including ele ...
Atomic Theory - World of Teaching
... the mass of a ball of clay? The mass changes as the altitude of the ball of clay changes. The mass changes as the shape of the ball of clay changes. The mass of the ball of clay is unchanged by altitude or shape. The mass is doubled when the ball of clay is divided into two equal pieces. ...
... the mass of a ball of clay? The mass changes as the altitude of the ball of clay changes. The mass changes as the shape of the ball of clay changes. The mass of the ball of clay is unchanged by altitude or shape. The mass is doubled when the ball of clay is divided into two equal pieces. ...
Chemistry
... atoms combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms - changes in the way they are bound together. The atoms themselves are not changed in a chemical reaction. ...
... atoms combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms - changes in the way they are bound together. The atoms themselves are not changed in a chemical reaction. ...
Zharkova & Khabarova, ApJ (2012)
... The main idea of the [Zharkova & Khabarova, ApJ (2012)] paper: small- and medium-scale features of the IMF and plasma characteristics observed near the HCS may be explained simultaneously only if magnetic reconnection was assumed to occur simultaneously and re-currently in many places on the HCS. ...
... The main idea of the [Zharkova & Khabarova, ApJ (2012)] paper: small- and medium-scale features of the IMF and plasma characteristics observed near the HCS may be explained simultaneously only if magnetic reconnection was assumed to occur simultaneously and re-currently in many places on the HCS. ...
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Georgia
... Department of Physics and Astronomy ...
... Department of Physics and Astronomy ...
lec03
... at each point in space, is the vector sum of the original electric field vector at that point in space and the electric field vector, at that point in space, due to the point charge. So why would the point charge experience a constant acceleration to the right? ...
... at each point in space, is the vector sum of the original electric field vector at that point in space and the electric field vector, at that point in space, due to the point charge. So why would the point charge experience a constant acceleration to the right? ...
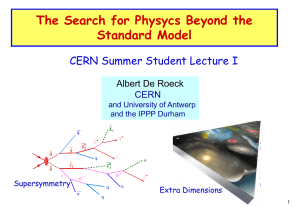
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.