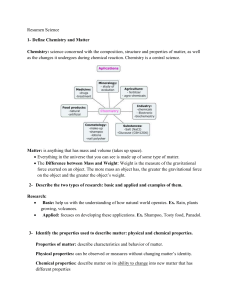
Coulomb`s Law - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... Hence draw an arrow, labelled R, on the figure above at P to represent the direction of the resultant electric field at P. ...
... Hence draw an arrow, labelled R, on the figure above at P to represent the direction of the resultant electric field at P. ...
the nuclear, plasma, and radiation universe
... If u is less than 10-3, Newtonian theory can be used. If u is around unity, General Relativity must be used. At intermediate values, the post Newtonian approximation is to be used. For the effect of the sun's gravity on Earth, u=10-8, and Newtonian law is adequate. For the universe, u = 10-2 to 1, a ...
... If u is less than 10-3, Newtonian theory can be used. If u is around unity, General Relativity must be used. At intermediate values, the post Newtonian approximation is to be used. For the effect of the sun's gravity on Earth, u=10-8, and Newtonian law is adequate. For the universe, u = 10-2 to 1, a ...
Dissecting Atoms 3 subatomic particles: , , Subatomic particle
... Sometimes, instead of one atom giving electrons to another, both atoms need electrons, so the atoms share electrons. This is called a _________________________ bond. They CO operate. They are CO nnected. _______________ is an example of covalent bonding. Water has ________________ bonding. Water’s c ...
... Sometimes, instead of one atom giving electrons to another, both atoms need electrons, so the atoms share electrons. This is called a _________________________ bond. They CO operate. They are CO nnected. _______________ is an example of covalent bonding. Water has ________________ bonding. Water’s c ...
Scales, verbs and verbal prefixes
... particle. The interpretation is always telic, but the event is mapped to different scales; the ambiguous event mapping is lexicalized by particles. With meg, the scale is the adjectival scale (6a). If the particle is not meg, then a non-scalar argument supplies the scale (6b). In (6b), the event is ...
... particle. The interpretation is always telic, but the event is mapped to different scales; the ambiguous event mapping is lexicalized by particles. With meg, the scale is the adjectival scale (6a). If the particle is not meg, then a non-scalar argument supplies the scale (6b). In (6b), the event is ...
I Examen I Trim Science
... A solid is the state of matter that has a definite shape and volume. The particles in a solid do not move fast enough to overcome the attraction between them. Each particle vibrates in place and is locked in place by the particles around it. 2 types of solids: Crystalline solids: have a very ...
... A solid is the state of matter that has a definite shape and volume. The particles in a solid do not move fast enough to overcome the attraction between them. Each particle vibrates in place and is locked in place by the particles around it. 2 types of solids: Crystalline solids: have a very ...
Pocket physics - Institute of Physics
... The strong nuclear force binds neutrons to neutrons, protons to protons and neutrons to protons. Number of neutrons (n) is approximately the same as the number of protons (p). Isotopes. Atoms with same atomic number Z (and so chemically similar), but different mass number A. Isotope shown as ZAK, w ...
... The strong nuclear force binds neutrons to neutrons, protons to protons and neutrons to protons. Number of neutrons (n) is approximately the same as the number of protons (p). Isotopes. Atoms with same atomic number Z (and so chemically similar), but different mass number A. Isotope shown as ZAK, w ...
Download PDF
... a denotes the particle radius; see ESI† for a discussion of this expression). In all of the following, we treat the external and interaction forces as scalars, acting opposite the direction of hydrodynamic drag. This assumption simplifies the model considerably and is consistent with an isotropic, u ...
... a denotes the particle radius; see ESI† for a discussion of this expression). In all of the following, we treat the external and interaction forces as scalars, acting opposite the direction of hydrodynamic drag. This assumption simplifies the model considerably and is consistent with an isotropic, u ...
Equation: Ψ(x,t) = X(x)T(t) with T(t) ∝ exp(− iEt ) and
... case, there are wiggling wavefunctions in all three regions that have to be smoothly matched at the well boundaries. Suppose that in region I there is a plane wave traveling to the right (“incident” on the well) of the form Ψ = exp[i(Kx − ω t)] . Plane waves can’t be normalized because their square ...
... case, there are wiggling wavefunctions in all three regions that have to be smoothly matched at the well boundaries. Suppose that in region I there is a plane wave traveling to the right (“incident” on the well) of the form Ψ = exp[i(Kx − ω t)] . Plane waves can’t be normalized because their square ...
ПРАКТИЧЕСКИЕ ЗАНЯТИЯ
... Everything these days seems to be computerized. That is one of the reasons why engineers are so desperately needed in the job force. A lot of people are realizing that an engineering career offers the potential for a great deal of money and the position is highly in demand. When you are interested i ...
... Everything these days seems to be computerized. That is one of the reasons why engineers are so desperately needed in the job force. A lot of people are realizing that an engineering career offers the potential for a great deal of money and the position is highly in demand. When you are interested i ...
Document
... figures (the most used being the dot, the triangle, the circle and the square). The drawing has spiritual and ritual meaning in both Buddhism and Hinduism. ...
... figures (the most used being the dot, the triangle, the circle and the square). The drawing has spiritual and ritual meaning in both Buddhism and Hinduism. ...
Determining Krypton Concentration is Xenon
... In the Millikan experiment there was a high percent difference and error. This probably is the result of the set up we used was very temperate an we constantly needed to adjust the camera and grid. Most problems during the experiment arose from focusing. The grid with the apparatus used was difficul ...
... In the Millikan experiment there was a high percent difference and error. This probably is the result of the set up we used was very temperate an we constantly needed to adjust the camera and grid. Most problems during the experiment arose from focusing. The grid with the apparatus used was difficul ...
Electric potential
... • Every atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. • Electrons all have same charge and same mass – same for protons. • Protons have an amount of positive charge equal to the negative charge on electrons, but about 1800 times as much mass. • Neutrons have almos ...
... • Every atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. • Electrons all have same charge and same mass – same for protons. • Protons have an amount of positive charge equal to the negative charge on electrons, but about 1800 times as much mass. • Neutrons have almos ...
Chapter 1 Quick Review
... The purpose of this review is to refresh your memory. Physics is a cumulative subject, so make it sure that you understand basic concepts and typical problem solving techniques in previous chapters before moving on to a new chapter. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... The purpose of this review is to refresh your memory. Physics is a cumulative subject, so make it sure that you understand basic concepts and typical problem solving techniques in previous chapters before moving on to a new chapter. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Homework #1 Solutions
... EVALUATE: Both the electrical force and the gravitational force are proportional to 1/r 2 . But in SI units the coefficient k in the electrical force is much greater than the coefficient G in the gravitational force. And a small mass of protons contains a large amount of charge. It would be impossib ...
... EVALUATE: Both the electrical force and the gravitational force are proportional to 1/r 2 . But in SI units the coefficient k in the electrical force is much greater than the coefficient G in the gravitational force. And a small mass of protons contains a large amount of charge. It would be impossib ...
t 1/2
... helium atoms. If radioactive material is placed at the bottom of a hole in a lead block, radiation will be emitted through the top. If the beam passes through an electric field, it will separate into the three types of radiation. ...
... helium atoms. If radioactive material is placed at the bottom of a hole in a lead block, radiation will be emitted through the top. If the beam passes through an electric field, it will separate into the three types of radiation. ...
June_Yong_Yang
... The garbage electron beam is put into a uniform magnetic field. Electrons are then curved by the field. Since the radius of the curve is related to their energies, we can classify the electrons by their energies. When an electron is detected by the tagger, it sends a signal to the main particle de ...
... The garbage electron beam is put into a uniform magnetic field. Electrons are then curved by the field. Since the radius of the curve is related to their energies, we can classify the electrons by their energies. When an electron is detected by the tagger, it sends a signal to the main particle de ...
TR-3
... maximum photon energy where we neglect the work function because it is normally so small compared to the potential energy of the electron. This yields the Duane-Hunt limit which was first found experimentally. The photon wavelength depends only on the accelerating voltage and is the same for all tar ...
... maximum photon energy where we neglect the work function because it is normally so small compared to the potential energy of the electron. This yields the Duane-Hunt limit which was first found experimentally. The photon wavelength depends only on the accelerating voltage and is the same for all tar ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.