p. synthesis
... REALLY ITS _______________________________I N THE DNA DETERMINE THE CHARACTERISTIC. BUT SOMETIMES PROBLEMS ARISE…. ...
... REALLY ITS _______________________________I N THE DNA DETERMINE THE CHARACTERISTIC. BUT SOMETIMES PROBLEMS ARISE…. ...
Genetic Engineering
... primer will attach to the wrong thing, an incorrect DNA sequence would result. • The nucleotide sequence must be known in order to create the correct primers. • Did I mention contamination? ...
... primer will attach to the wrong thing, an incorrect DNA sequence would result. • The nucleotide sequence must be known in order to create the correct primers. • Did I mention contamination? ...
Research Fast Facts: BRCA
... BRCA1 and BRCA2 (breast cancer susceptibility) are genes that help prevent cancer from developing. They repair cell damage so breast cells can grow normally. Everyone has BRCA genes. But, when BRCA is mutated, it cannot function normally and breast cancer risk increases. Most inherited breast cancer ...
... BRCA1 and BRCA2 (breast cancer susceptibility) are genes that help prevent cancer from developing. They repair cell damage so breast cells can grow normally. Everyone has BRCA genes. But, when BRCA is mutated, it cannot function normally and breast cancer risk increases. Most inherited breast cancer ...
dna
... Eukaryotes if their DNA was done by one polymerase molecule per chromosome would take about a month for the DNA to replicate. Multiple polymerase latch on the the replicating DNA simultaneously and as a result replication in humans takes about an hour. R ...
... Eukaryotes if their DNA was done by one polymerase molecule per chromosome would take about a month for the DNA to replicate. Multiple polymerase latch on the the replicating DNA simultaneously and as a result replication in humans takes about an hour. R ...
Replication is when DNA
... Read the information to the right of the picture. Once you have finished reading, click on the magnifying glass with the + sign in the middle. This will take you to the next screen where you will read more information. For each slide there will be several questions that you will need to answer below ...
... Read the information to the right of the picture. Once you have finished reading, click on the magnifying glass with the + sign in the middle. This will take you to the next screen where you will read more information. For each slide there will be several questions that you will need to answer below ...
High efficiency of site-directed mutagenesis mediated by a single
... mutagenesis of double-stranded plasmids. The method relies on a single PCR primer which incorporates both the mutations at the selection site and the desired single base substitutions at the mutant site. This primer is annealed to the denatured plasmid and directs the synthesis of the mutant strand. ...
... mutagenesis of double-stranded plasmids. The method relies on a single PCR primer which incorporates both the mutations at the selection site and the desired single base substitutions at the mutant site. This primer is annealed to the denatured plasmid and directs the synthesis of the mutant strand. ...
Biology- Semester 2 Final Exam Review 2012
... How would you know from a picture which is which? 5. Explain crossing-over and how it contributes to the production of unique individuals. 6. How many chromosomes are in a human somatic cell? In a gamete? 7. The diploid number of chromosomes for humans is ____. The haploid number is____. 8. What is ...
... How would you know from a picture which is which? 5. Explain crossing-over and how it contributes to the production of unique individuals. 6. How many chromosomes are in a human somatic cell? In a gamete? 7. The diploid number of chromosomes for humans is ____. The haploid number is____. 8. What is ...
Exam 2 tutorial
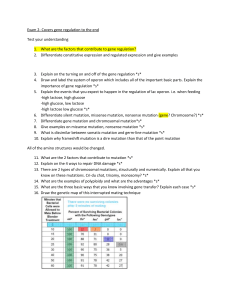
... 5. Explain the events that you expect to happen in the regulation of lac operon. i.e. when feeding -high lactose, high glucose -high glucose, low lactose -high lactose low glucose *s* 6. Differentiate silent mutation, missense mutation, nonsense mutation (gene? Chromosome?) *s* 7. Differentiate gene ...
... 5. Explain the events that you expect to happen in the regulation of lac operon. i.e. when feeding -high lactose, high glucose -high glucose, low lactose -high lactose low glucose *s* 6. Differentiate silent mutation, missense mutation, nonsense mutation (gene? Chromosome?) *s* 7. Differentiate gene ...
- Frimley VTS
... • After counselling John decides that he will NOT take a test at present due to the absence of treatment and the long time interval before any symptoms would arise. • Sarah comes to see you. She explains how distressed she is by witnessing the deterioration in John’s mother. She feels she needs to b ...
... • After counselling John decides that he will NOT take a test at present due to the absence of treatment and the long time interval before any symptoms would arise. • Sarah comes to see you. She explains how distressed she is by witnessing the deterioration in John’s mother. She feels she needs to b ...
Biology 105 Midterm 1 v. 1 Feb. 13, 2007
... c. There are 16 homologous pairs. d. A gamete from this species has 8 chromosomes. 41. In which phase of mitosis do the sister chromatids become separated? a. prophase b. interphase c. anaphase ...
... c. There are 16 homologous pairs. d. A gamete from this species has 8 chromosomes. 41. In which phase of mitosis do the sister chromatids become separated? a. prophase b. interphase c. anaphase ...
From Hard Drives to Flash Drives to DNA Drives
... and readable for millennia.5 For purposes of timeless storage, DNA may be dried and then protected from water and oxygen, which gives it a nearly infinite stability. DNA information storage is not new. It has been around since 1988, and one of the first successful projects came from the J. Craig Ven ...
... and readable for millennia.5 For purposes of timeless storage, DNA may be dried and then protected from water and oxygen, which gives it a nearly infinite stability. DNA information storage is not new. It has been around since 1988, and one of the first successful projects came from the J. Craig Ven ...
Mutations in human pathology - diss.fu
... Several mutations affect regulatory elements critical to the processing of mRNAs, such as poly-adenylation signals, splice sites or splicing enhancers. A.4.1. Mutations of the poly-adenylation signal Abolition of the canonical poly(A) signal. Pathogenicity through read-through transcripts and ...
... Several mutations affect regulatory elements critical to the processing of mRNAs, such as poly-adenylation signals, splice sites or splicing enhancers. A.4.1. Mutations of the poly-adenylation signal Abolition of the canonical poly(A) signal. Pathogenicity through read-through transcripts and ...
Mendel`s Contributions
... Mendel came to three important conclusions from these experimental results: 1. that the inheritance of each trait is determined by "units" or "factors" (now called genes) that are passed on to descendents unchanged 2. These units come in different forms called alleles 3. His Second conclusion was t ...
... Mendel came to three important conclusions from these experimental results: 1. that the inheritance of each trait is determined by "units" or "factors" (now called genes) that are passed on to descendents unchanged 2. These units come in different forms called alleles 3. His Second conclusion was t ...
Preview Sample 1
... 10) Assume that the somatic cells of a male contain one pair of 10) _____________ homologous chromosomes (e.g., AaAb), and an additional chromosome without a homolog (e.g., W). What chromosomal combinations would be expected in the meiotic products (spermatids) of a single primary spermatocyte? (The ...
... 10) Assume that the somatic cells of a male contain one pair of 10) _____________ homologous chromosomes (e.g., AaAb), and an additional chromosome without a homolog (e.g., W). What chromosomal combinations would be expected in the meiotic products (spermatids) of a single primary spermatocyte? (The ...
Exam3-1406_Fall2007ch9-10-11.doc
... A) 100 base pairs. B) 1000 base pairs. C) 10,000 base pairs. D) million base pairs. E) billion base pairs. 23) The DNA in your body's cells can accumulate errors for which of the following reasons? A) Mistakes are made during DNA replication. B) Some DNA spontaneously breaks down at normal body temp ...
... A) 100 base pairs. B) 1000 base pairs. C) 10,000 base pairs. D) million base pairs. E) billion base pairs. 23) The DNA in your body's cells can accumulate errors for which of the following reasons? A) Mistakes are made during DNA replication. B) Some DNA spontaneously breaks down at normal body temp ...
Document
... Telophase II: nuclear membrane forms around newly separated chromatids • Note that each new nucleus formed has ½ the amount of DNA as the original cell. • These cells are haploid cells. ...
... Telophase II: nuclear membrane forms around newly separated chromatids • Note that each new nucleus formed has ½ the amount of DNA as the original cell. • These cells are haploid cells. ...
Stem Cells, Cancer, and Human Health
... 1. Unambiguous: if I show you a codon, there’s no question which amino acid to use next 2. Redundant: most amino acids have more than one codon ...
... 1. Unambiguous: if I show you a codon, there’s no question which amino acid to use next 2. Redundant: most amino acids have more than one codon ...
BIO 110 Survey of Biology QZM 3 Q 150701abbr.2
... Reproduction and Inheritance 47. Most of an organism's DNA is carried by its _____. a. chromosomes b. endoplasmic reticulum c. mitochondria d. ribosomes e. nucleoli 48. Sister chromatids a. all of the below b. are attached at the centromere prior to division c. are separated during mitosis d. are cr ...
... Reproduction and Inheritance 47. Most of an organism's DNA is carried by its _____. a. chromosomes b. endoplasmic reticulum c. mitochondria d. ribosomes e. nucleoli 48. Sister chromatids a. all of the below b. are attached at the centromere prior to division c. are separated during mitosis d. are cr ...
Document
... Telophase II: nuclear membrane forms around newly separated chromatids • Note that each new nucleus formed has ½ the amount of DNA as the original cell. • These cells are haploid cells. ...
... Telophase II: nuclear membrane forms around newly separated chromatids • Note that each new nucleus formed has ½ the amount of DNA as the original cell. • These cells are haploid cells. ...
Document
... Telophase II: nuclear membrane forms around newly separated chromatids • Note that each new nucleus formed has ½ the amount of DNA as the original cell. • These cells are haploid cells. ...
... Telophase II: nuclear membrane forms around newly separated chromatids • Note that each new nucleus formed has ½ the amount of DNA as the original cell. • These cells are haploid cells. ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.