unit 2 universal gravitation and circular motion
... 2. the force of attraction (Fg) between 2 masses (m1, m2)is directly proportional (if one goes up the other goes up) to the product of the masses: Fg m1m2 3. the force of attraction between 2 masses is indirectly proportional (if one goes up the other goes down) to the square of the distance (r) b ...
... 2. the force of attraction (Fg) between 2 masses (m1, m2)is directly proportional (if one goes up the other goes up) to the product of the masses: Fg m1m2 3. the force of attraction between 2 masses is indirectly proportional (if one goes up the other goes down) to the square of the distance (r) b ...
Factors That Affect Climate Change File
... radiation received by the earth varies due to a series of three variables. Milankovic’s calculations support the idea that earth’s climate is expected to change over long periods of time. ...
... radiation received by the earth varies due to a series of three variables. Milankovic’s calculations support the idea that earth’s climate is expected to change over long periods of time. ...
Grand Canyon - Personal.psu.edu
... movement of the continents and will form groups to answer the question, Why are the continents moving? -Students will look at the previous days information to form a conclusion -Discussion of ideas will take place and students will view a simulation of the plates and how they move on convective cu ...
... movement of the continents and will form groups to answer the question, Why are the continents moving? -Students will look at the previous days information to form a conclusion -Discussion of ideas will take place and students will view a simulation of the plates and how they move on convective cu ...
ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
... movement has occurred. When rocks are under stress along a fracture, they can sometimes snap as the stress is released. The vibrations which travel through the ground as a result of this release of energy are known as earthquakes. Earthquakes occur all the time, but most are not felt (only detected ...
... movement has occurred. When rocks are under stress along a fracture, they can sometimes snap as the stress is released. The vibrations which travel through the ground as a result of this release of energy are known as earthquakes. Earthquakes occur all the time, but most are not felt (only detected ...
8.4 Earth`s Layers
... Over 82 % of Earth’s volume is contained in the mantle Mantle – a solid, rocky shell that extends to a depth of 2890 km. The boundary between the crust & mantle shows a change in chemical composition. ...
... Over 82 % of Earth’s volume is contained in the mantle Mantle – a solid, rocky shell that extends to a depth of 2890 km. The boundary between the crust & mantle shows a change in chemical composition. ...
May the Force Be Qith You!
... a)Contact Forces: affect things they touch – Tension – force in a wire or rope when pulled. – Friction – slows down motion by rubbing. – Elastic – spring-like object restores itself to its normal shape after alteration. ...
... a)Contact Forces: affect things they touch – Tension – force in a wire or rope when pulled. – Friction – slows down motion by rubbing. – Elastic – spring-like object restores itself to its normal shape after alteration. ...
atoms - Waterford Public Schools
... In a given compound, the relative numbs and kinds of atoms are constant Based on In chemical reactions, the total mass of materials present before and after is the same ...
... In a given compound, the relative numbs and kinds of atoms are constant Based on In chemical reactions, the total mass of materials present before and after is the same ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... descend from that point, the temperature rises 1◦C. This rapid rise in temperature continues for several kilometers. After that, the temperature increases more slowly, but steadily. ...
... descend from that point, the temperature rises 1◦C. This rapid rise in temperature continues for several kilometers. After that, the temperature increases more slowly, but steadily. ...
common formative assessment planning template
... properties. Earthquake energy travels as waves through the Earth’s interior or as surface waves along the surface of the Earth. Connecticut shows evidence of continental collisions, rifting, and folding that have shaped its structure. ...
... properties. Earthquake energy travels as waves through the Earth’s interior or as surface waves along the surface of the Earth. Connecticut shows evidence of continental collisions, rifting, and folding that have shaped its structure. ...
Grade Seven - Science - Miami
... layers. You can imagine this as similar to a laundry hamper, where the clothes that were worn longest ago end up at the bottom at the hamper, while more recently used clothes are at the top. These layers of rocks (or clothes) maybe be shifted around to not stay in perfectly straight layers. Earthqua ...
... layers. You can imagine this as similar to a laundry hamper, where the clothes that were worn longest ago end up at the bottom at the hamper, while more recently used clothes are at the top. These layers of rocks (or clothes) maybe be shifted around to not stay in perfectly straight layers. Earthqua ...
procedure - Homework Market
... horizontal circular motion (of small radius), the mass will rotate in a larger circle at the end of the string. The string will describe a cone with the base of the cone being the imaginary flat surface about which the mass rotates. This phenomenon is called a conical pendulum because of its conical ...
... horizontal circular motion (of small radius), the mass will rotate in a larger circle at the end of the string. The string will describe a cone with the base of the cone being the imaginary flat surface about which the mass rotates. This phenomenon is called a conical pendulum because of its conical ...
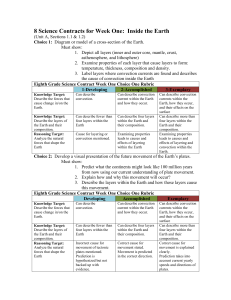
Science Contracts for Week 1
... Can describe more than four layers within the Earth and their composition. Examining properties leads to causes and effects of layering and convection within the Earth. ...
... Can describe more than four layers within the Earth and their composition. Examining properties leads to causes and effects of layering and convection within the Earth. ...
PRE-POSTTESTwithANSWERS
... 3. What occurs when an oceanic plate meets a continental plate? a. convection; b. subduction; c. diversion; d. transformation 4. What is formed when two continental plates collide? a. a trench; b. mountains; c. volcanoes; d. a rift 5. The collision of two oceanic plates forms: a. a mountain; b. conv ...
... 3. What occurs when an oceanic plate meets a continental plate? a. convection; b. subduction; c. diversion; d. transformation 4. What is formed when two continental plates collide? a. a trench; b. mountains; c. volcanoes; d. a rift 5. The collision of two oceanic plates forms: a. a mountain; b. conv ...
Plate Tectonics Chapter 1 Study Guide Section 1 Earth`s Interior In
... What is sonar used for? _________________________________________________________________ The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called _______________________. The process by which the ocean floor sinks into the mantle is called _____________________________. ...
... What is sonar used for? _________________________________________________________________ The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called _______________________. The process by which the ocean floor sinks into the mantle is called _____________________________. ...
Name: Date: : Aim#15b: Earth as a Planet
... of Earth? If we could travel through the layers of the Earth, what would our trip be like? In order to make this trip, we would need a special vehicle that could travel through both liquid and solid rock and that could withstand intense temperature and pressure changes! The deeper into the center of ...
... of Earth? If we could travel through the layers of the Earth, what would our trip be like? In order to make this trip, we would need a special vehicle that could travel through both liquid and solid rock and that could withstand intense temperature and pressure changes! The deeper into the center of ...
The Millikan Experiment
... the terminal velocity when it falls if the electric force is removed (gravity acts alone) ...
... the terminal velocity when it falls if the electric force is removed (gravity acts alone) ...
Section: The Geosphere - Environmental Science
... five layers. Earth’s outer layer is the lithosphere. It is a cool, rigid layer, 15 km to 300 km thick, and includes the crust and uppermost part of the mantle. It is divided into huge pieces called tectonic plates. The asthenosphere is the layer beneath the lithosphere. The asthenosphere is a plasti ...
... five layers. Earth’s outer layer is the lithosphere. It is a cool, rigid layer, 15 km to 300 km thick, and includes the crust and uppermost part of the mantle. It is divided into huge pieces called tectonic plates. The asthenosphere is the layer beneath the lithosphere. The asthenosphere is a plasti ...
Chapter 7 Earth`s Structure What are columns of steaming hot water
... 9. Lithosphere- area where Earth’s solid upper mantle and crust combine to form a shell. 10. Core- Earth’s innermost structure. 11. The lithosphere is not one solid shell of rock. It is actually broken up into giant slabs of rock called plates. 12. Plate Tectonics- idea that giant plates of rock are ...
... 9. Lithosphere- area where Earth’s solid upper mantle and crust combine to form a shell. 10. Core- Earth’s innermost structure. 11. The lithosphere is not one solid shell of rock. It is actually broken up into giant slabs of rock called plates. 12. Plate Tectonics- idea that giant plates of rock are ...
Schiehallion experiment

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of a pendulum due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. One of the triggers for the experiment were anomalies noted during the survey of the Mason–Dixon Line.The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation. However, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, were convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then so could the density of the Earth. Once this was known, then this would in turn yield approximate values for those of the other planets, their moons, and the Sun, previously known only in terms of their relative ratios. As an additional benefit, the concept of contour lines, devised to simplify the process of surveying the mountain, later became a standard technique in cartography.