PULSE MODULATION
... transmitting channel depends on rise time of the pulse. Instantaneous power of transmitter varies. Noise interference is minimum. Simple to implement. Similar to F.M. ...
... transmitting channel depends on rise time of the pulse. Instantaneous power of transmitter varies. Noise interference is minimum. Simple to implement. Similar to F.M. ...
03-DataTransmission
... so increase strength using amplifiers/repeaters is also an increasing function of frequency so equalize attenuation across band of frequencies used ...
... so increase strength using amplifiers/repeaters is also an increasing function of frequency so equalize attenuation across band of frequencies used ...
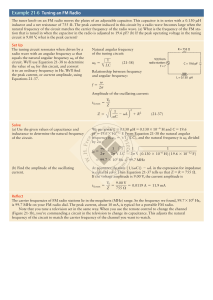
Example 21-6 Tuning an FM Radio
... equals the natural angular frequency v0 of the circuit. We’ll use Equation 21-38 to determine the value of v0 for this circuit, and convert it to an ordinary frequency in Hz. We’ll find the peak current, or current amplitude, using ...
... equals the natural angular frequency v0 of the circuit. We’ll use Equation 21-38 to determine the value of v0 for this circuit, and convert it to an ordinary frequency in Hz. We’ll find the peak current, or current amplitude, using ...
guided media (twisted pair, coaxial cable, and optical fiber)
... Intermodulation noise occurs when different frequencies share the same transmission medium. Intermodulation reduces frequency at a level equal to the sum or difference of the two original frequencies. For example, intermodulation can produce 12,000 Hz frequency from the two separate signals of 400 ...
... Intermodulation noise occurs when different frequencies share the same transmission medium. Intermodulation reduces frequency at a level equal to the sum or difference of the two original frequencies. For example, intermodulation can produce 12,000 Hz frequency from the two separate signals of 400 ...
Short Wave receiver
... I have inserted a switch which activates the spectrum monitor circuitry when set to SCAN. The monitor circuit settings were made in such a way that the ham band between 7.0 and 7.2 MHz can be visualized on the oscilloscope. ...
... I have inserted a switch which activates the spectrum monitor circuitry when set to SCAN. The monitor circuit settings were made in such a way that the ham band between 7.0 and 7.2 MHz can be visualized on the oscilloscope. ...
Principles of Electronic Communication Systems
... FM typically offers some significant benefits over AM. FM has superior immunity to noise, made possible by clipper limiter circuits in the receiver. In FM, interfering signals on the same frequency are rejected. This is known as the capture effect. FM signals have a constant amplitude and ther ...
... FM typically offers some significant benefits over AM. FM has superior immunity to noise, made possible by clipper limiter circuits in the receiver. In FM, interfering signals on the same frequency are rejected. This is known as the capture effect. FM signals have a constant amplitude and ther ...
Lab-05 Spectrum Analyzer Introduction
... Cables and Connectors: Used to connect the voltage source (input) to the analysis equipment (the spectrum analyzer). For this lab, one particular type of unique connecter is used: a Bayonet Neill-Concelman (BNC) (also known, most sources agree erroneously, as a British Naval ...
... Cables and Connectors: Used to connect the voltage source (input) to the analysis equipment (the spectrum analyzer). For this lab, one particular type of unique connecter is used: a Bayonet Neill-Concelman (BNC) (also known, most sources agree erroneously, as a British Naval ...
Principles of Electronic Communication Systems
... A standard AM broadcast station is allowed to transmit modulating frequencies up to 5 kHz. If the AM station is transmitting on a frequency of 980 kHz, what are sideband frequencies and total bandwidth? fUSB = 980 + 5 = 985 kHz fLSB = 980 – 5 = 975 kHz BW = fUSB – fLSB = 985 – 975 = 10 kHz BW = 2 (5 ...
... A standard AM broadcast station is allowed to transmit modulating frequencies up to 5 kHz. If the AM station is transmitting on a frequency of 980 kHz, what are sideband frequencies and total bandwidth? fUSB = 980 + 5 = 985 kHz fLSB = 980 – 5 = 975 kHz BW = fUSB – fLSB = 985 – 975 = 10 kHz BW = 2 (5 ...
Wireless Sensor Networks
... Channel models – analog • How to stochastically capture the behavior of a wireless ...
... Channel models – analog • How to stochastically capture the behavior of a wireless ...
Lab-in-a-Box
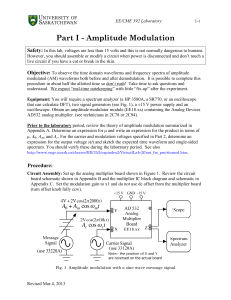
... 8. Construct the gyrator shown in Figure 1(b) of the text and simulated in step 5. 9. Connect the oscilloscope inputs with Channel 1 measuring the function generator output and the Channel 2 measuring the filter output. Be sure to use proper attenuation on the scope input to avoid saturating the sou ...
... 8. Construct the gyrator shown in Figure 1(b) of the text and simulated in step 5. 9. Connect the oscilloscope inputs with Channel 1 measuring the function generator output and the Channel 2 measuring the filter output. Be sure to use proper attenuation on the scope input to avoid saturating the sou ...
Blake`s Slides Chapter 7 File
... • TDM is used extensively in telephony • The most common standard is the DS-1 signal, which consists of 24 PCM voice channels, multiplexed using TDM • Each channel is sampled at 8 kHz with 8 bits per sample, which gives a bit rate of 64 kb/s for each voice channel • The samples must be transmitted a ...
... • TDM is used extensively in telephony • The most common standard is the DS-1 signal, which consists of 24 PCM voice channels, multiplexed using TDM • Each channel is sampled at 8 kHz with 8 bits per sample, which gives a bit rate of 64 kb/s for each voice channel • The samples must be transmitted a ...
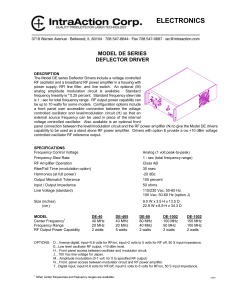
DE-70BM
... DEFLECTOR DRIVER DESCRIPTION The Model DE series Deflector Drivers include a voltage controlled RF oscillator and a broadband RF power amplifier in a housing with power supply, RFI line filter, and line switch. An optional (M) analog amplitude modulation circuit is available. Standard frequency line ...
... DEFLECTOR DRIVER DESCRIPTION The Model DE series Deflector Drivers include a voltage controlled RF oscillator and a broadband RF power amplifier in a housing with power supply, RFI line filter, and line switch. An optional (M) analog amplitude modulation circuit is available. Standard frequency line ...
Composite Analog Signals (cont.)
... Composite Signals and – no transmission medium is perfect – each medium passes some frequencies and ...
... Composite Signals and – no transmission medium is perfect – each medium passes some frequencies and ...
Introduction - Eastern Illinois University
... Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that starts at 50 watts and experiences a 10-watt loss over a given section of cable ? Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that loses half its power during the course of transmission ? Q: Do Week 6 Exercise available in the Notes section of the course webs ...
... Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that starts at 50 watts and experiences a 10-watt loss over a given section of cable ? Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that loses half its power during the course of transmission ? Q: Do Week 6 Exercise available in the Notes section of the course webs ...
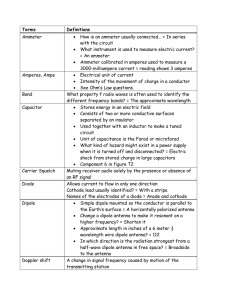
Terms
... Type of wave that carries radio signals between transmitting & receiving stations Usual name for electromagnetic waves that travel through space = Radio waves Basic unit of capacitance # of times alternating current flows back & forth in one second Hz = one time per second (or one cycle per seco ...
... Type of wave that carries radio signals between transmitting & receiving stations Usual name for electromagnetic waves that travel through space = Radio waves Basic unit of capacitance # of times alternating current flows back & forth in one second Hz = one time per second (or one cycle per seco ...
Chapter 6: Data Transmission
... ranging from 20Hz to 20kHz For practical purposes, the telephone system has a narrower bandwidth than human voice, from 300 to 3400Hz ...
... ranging from 20Hz to 20kHz For practical purposes, the telephone system has a narrower bandwidth than human voice, from 300 to 3400Hz ...
Chapter 2. Active Filter Design
... 5. A piece of communication equipment has two stages of amplification with gains of 40 and 60 and two loss stages with attenuation factor of 0.03 and 0.075. The output voltage is 2.2 V. What are the overall gain (or attenuation) and the input voltage? 21. What circuit Q is required to give a bandwid ...
... 5. A piece of communication equipment has two stages of amplification with gains of 40 and 60 and two loss stages with attenuation factor of 0.03 and 0.075. The output voltage is 2.2 V. What are the overall gain (or attenuation) and the input voltage? 21. What circuit Q is required to give a bandwid ...
405-line television system
The 405-line monochrome analogue television broadcasting system was the first fully electronic television system to be used in regular broadcasting.It was introduced with the BBC Television Service in 1936, suspended for the duration of World War II, and remained in operation in the UK until 1985, it was also used between 1961 and 1982 in Ireland as well as from 1957 to 1973 for the Rediffusion Television cable service in Hong Kong.Sometimes called the Marconi-EMI system, it was developed in 1934 by the EMI Research Team led by Sir Isaac Shoenberg. The figure of 405 lines had been chosen following discussions over Sunday lunch at the home of Alan Blumlein. The system was the first broadcast system in Britain to use interlacing, though EMI had been experimenting with a 243 line all-electronic interlaced system since 1933. In the 405 system the scanning lines were broadcast in two complementary fields, 50 times per second, creating 25 frames per second. The actual image was 377 lines high and interlaced, with additional unused lines making the frame up to 405 lines to give the slow circuitry time to prepare for the next frame; in modern terms it would be described as 377i.At the time of its introduction the 405-line system was referred to as ""high definition"", which it was compared to earlier systems, although of lower definition than 625-line and later standards.