amplitude modulation
... the carrier, leaving the upper and lower sidebands. – This type of signal is called a double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSSC) signal. No power is wasted on the carrier. – A balanced modulator is a circuit used to produce the sum and difference frequencies of a DSSC signal but to cancel or balance ...
... the carrier, leaving the upper and lower sidebands. – This type of signal is called a double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSSC) signal. No power is wasted on the carrier. – A balanced modulator is a circuit used to produce the sum and difference frequencies of a DSSC signal but to cancel or balance ...
Module 2 – Signals & Waves C2
... • Instead of varying the carrier’s amplitude, if we vary the frequency in step with the information waveform – FM is produced. • FM signals are much more resistant to the effects of noise but require more bandwidth. • FM bandwidth (for voice) is between 5 and 15 kHz. The higher the modulation level, ...
... • Instead of varying the carrier’s amplitude, if we vary the frequency in step with the information waveform – FM is produced. • FM signals are much more resistant to the effects of noise but require more bandwidth. • FM bandwidth (for voice) is between 5 and 15 kHz. The higher the modulation level, ...
A sensitive detection method for capacitive ultrasonic transducers
... values rather than using n sections with L and C values does not make any difference in terms of the phase length, but decreases the cutoff frequency. A very small capacitance change can be detected by measuring the phase length at a high rf frequency. An incident ultrasound signal of frequency v 1 ...
... values rather than using n sections with L and C values does not make any difference in terms of the phase length, but decreases the cutoff frequency. A very small capacitance change can be detected by measuring the phase length at a high rf frequency. An incident ultrasound signal of frequency v 1 ...
Helicity Clock Generator - JLab Tech Notes Home Page
... problem and provide a more accurate spin flip trigger we developed a circuit based on the a PLL design (fig. 1).1 ...
... problem and provide a more accurate spin flip trigger we developed a circuit based on the a PLL design (fig. 1).1 ...
Chapter 3 - William Stallings, Data and Computer Communications
... so increase strength using amplifiers/repeaters is also an increasing function of frequency so equalize attenuation across band of frequencies used ...
... so increase strength using amplifiers/repeaters is also an increasing function of frequency so equalize attenuation across band of frequencies used ...
6114.Output pulses after applying power through FETs
... This was measured at the HO and LO pin of the gate drive. As you can see the outputs were good. At this point, I have yet to supply 24V to the FETs ...
... This was measured at the HO and LO pin of the gate drive. As you can see the outputs were good. At this point, I have yet to supply 24V to the FETs ...
C. Wavelength
... frequencies. • When this complex mixture is embedded on a carrier, two sidebands are created that are mirror images. ...
... frequencies. • When this complex mixture is embedded on a carrier, two sidebands are created that are mirror images. ...
highpass filter - Jejaring Blog Unnes
... All materials are taken from “Fundamentals of electric circuits” ...
... All materials are taken from “Fundamentals of electric circuits” ...
Signal Theory
... noise is unpredictable in value, as next time step could take any value in its range. The plot is not smooth. Received signal = Actual signal + Noise This results in signal in a mixed form. The predictability depends on the S/N ratio, the ratio Var(S)/Var(N). Random noise is an unwanted signal, prod ...
... noise is unpredictable in value, as next time step could take any value in its range. The plot is not smooth. Received signal = Actual signal + Noise This results in signal in a mixed form. The predictability depends on the S/N ratio, the ratio Var(S)/Var(N). Random noise is an unwanted signal, prod ...
Fault Diagnosis
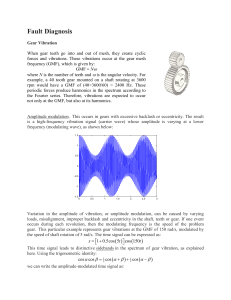
... When gear teeth go into and out of mesh, they create cyclic forces and vibrations. These vibrations occur at the gear mesh frequency (GMF), which is given by: GMF N where N is the number of teeth and is the angular velocity. For example, a 40 tooth gear mounted on a shaft rotating at 3600 rpm w ...
... When gear teeth go into and out of mesh, they create cyclic forces and vibrations. These vibrations occur at the gear mesh frequency (GMF), which is given by: GMF N where N is the number of teeth and is the angular velocity. For example, a 40 tooth gear mounted on a shaft rotating at 3600 rpm w ...
sidebands
... the carrier, leaving the upper and lower sidebands. This type of signal is called a double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSSC) signal. No power is wasted on the carrier. A balanced modulator is a circuit used to produce the sum and difference frequencies of a DSSC signal but to cancel or balance ...
... the carrier, leaving the upper and lower sidebands. This type of signal is called a double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSSC) signal. No power is wasted on the carrier. A balanced modulator is a circuit used to produce the sum and difference frequencies of a DSSC signal but to cancel or balance ...
angle modulation
... During the process of frequency modulations the frequency of carrier signal is changed in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of message signal .Therefore the frequency of carrier after modulation is written as ...
... During the process of frequency modulations the frequency of carrier signal is changed in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of message signal .Therefore the frequency of carrier after modulation is written as ...
chapter 2 - WordPress.com
... relatively high frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous value of modulating signal (information) A process of translating information signal from low band frequency to high band frequency. ...
... relatively high frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous value of modulating signal (information) A process of translating information signal from low band frequency to high band frequency. ...
chapter 2 - UniMAP Portal
... relatively high frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous value of modulating signal (information) A process of translating information signal from low band frequency to high band frequency. ...
... relatively high frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous value of modulating signal (information) A process of translating information signal from low band frequency to high band frequency. ...
AFM training quiz (this is a take home quiz, refer to your common
... T F When “Sum” signal is zero, “Amplitude” will also be zero. T F When “Sum” signal is large, “Amplitude” could still be zero. T F “Amplitude” is measured by looking the fdrive frequency component of the signal from the position-senstive photodetector (fdrive is the frequency that we shake the base ...
... T F When “Sum” signal is zero, “Amplitude” will also be zero. T F When “Sum” signal is large, “Amplitude” could still be zero. T F “Amplitude” is measured by looking the fdrive frequency component of the signal from the position-senstive photodetector (fdrive is the frequency that we shake the base ...
405-line television system
The 405-line monochrome analogue television broadcasting system was the first fully electronic television system to be used in regular broadcasting.It was introduced with the BBC Television Service in 1936, suspended for the duration of World War II, and remained in operation in the UK until 1985, it was also used between 1961 and 1982 in Ireland as well as from 1957 to 1973 for the Rediffusion Television cable service in Hong Kong.Sometimes called the Marconi-EMI system, it was developed in 1934 by the EMI Research Team led by Sir Isaac Shoenberg. The figure of 405 lines had been chosen following discussions over Sunday lunch at the home of Alan Blumlein. The system was the first broadcast system in Britain to use interlacing, though EMI had been experimenting with a 243 line all-electronic interlaced system since 1933. In the 405 system the scanning lines were broadcast in two complementary fields, 50 times per second, creating 25 frames per second. The actual image was 377 lines high and interlaced, with additional unused lines making the frame up to 405 lines to give the slow circuitry time to prepare for the next frame; in modern terms it would be described as 377i.At the time of its introduction the 405-line system was referred to as ""high definition"", which it was compared to earlier systems, although of lower definition than 625-line and later standards.