EC 6402-UNIT - 2 (Part-2 of 2) Teaching material
... • The tuned circuit is tuned so the fc, the nominal input frequency, is on the slope, not at the centre of the tuned circuits. As the FM signal deviates about fc on the tuned circuit slope, the amplitude of the output varies in proportion to the deviation from fc. Thus the FM signal is effectively c ...
... • The tuned circuit is tuned so the fc, the nominal input frequency, is on the slope, not at the centre of the tuned circuits. As the FM signal deviates about fc on the tuned circuit slope, the amplitude of the output varies in proportion to the deviation from fc. Thus the FM signal is effectively c ...
Power function generator with integral feedback voltage protection
... will not destroy its output stage. Furthermore, all front-panel inputs and outputs are no-load and short-circuit proof. The frequency settings are made using a decade switch, the frequency dial and the frequency offset potentiometer. The latter allows frequency settings with a reproducibility of < 0 ...
... will not destroy its output stage. Furthermore, all front-panel inputs and outputs are no-load and short-circuit proof. The frequency settings are made using a decade switch, the frequency dial and the frequency offset potentiometer. The latter allows frequency settings with a reproducibility of < 0 ...
Lab 1: AMPLITUDE MODULATION
... Generate an AM signal using the speech signal available from the Trunks Panel as your message. Observe the time domain waveform. The frequency spectrum will extend for about 3 kHz either side of the carrier. Since this is a stochastic (random) signal, the spectrum analyser may not give you much resp ...
... Generate an AM signal using the speech signal available from the Trunks Panel as your message. Observe the time domain waveform. The frequency spectrum will extend for about 3 kHz either side of the carrier. Since this is a stochastic (random) signal, the spectrum analyser may not give you much resp ...
Circuits for pulse shortening
... 1. Create circuit connections (Figures 1, 2 and 3) to shortening the pulse and determine the length of this impulse. 2. Make a report from these measuring. Theory: Monostable flip-flops These circuits have only one stable state, which is break by trigger pulse. Trigger pulse may be longer or shorter ...
... 1. Create circuit connections (Figures 1, 2 and 3) to shortening the pulse and determine the length of this impulse. 2. Make a report from these measuring. Theory: Monostable flip-flops These circuits have only one stable state, which is break by trigger pulse. Trigger pulse may be longer or shorter ...
ppt
... point in the transmission Typically measured at a receiver Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR, or S/N) signal power ( SNR) dB 10 log 10 noise power ...
... point in the transmission Typically measured at a receiver Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR, or S/N) signal power ( SNR) dB 10 log 10 noise power ...
ch2-stallings
... A signal may contain many frequencies. But most of the energy may concentrate in a narrow band of frequencies. These frequencies are effective bandwidth. ...
... A signal may contain many frequencies. But most of the energy may concentrate in a narrow band of frequencies. These frequencies are effective bandwidth. ...
Chapter 3: From lumped to distributed elements
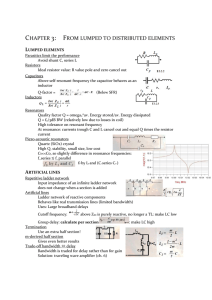
... Quality factor Q = omega0*av. Energy stored/av. Energy dissipated Q = f0/3dB BW (relatively low due to losses in coil) High tolerance on resonant frequency At resonance: currents trough C and L cancel out and equal Q times the resistor current Piezo-acoustic resonators Quartz (SiO2) crystal High Q, ...
... Quality factor Q = omega0*av. Energy stored/av. Energy dissipated Q = f0/3dB BW (relatively low due to losses in coil) High tolerance on resonant frequency At resonance: currents trough C and L cancel out and equal Q times the resistor current Piezo-acoustic resonators Quartz (SiO2) crystal High Q, ...
angle modulation
... receiver using a limiting circuit. Angle modulation is very effective in rejecting interference. (minimizes the effect of noise). Angle modulation allows the use of more efficient transmitter power in ...
... receiver using a limiting circuit. Angle modulation is very effective in rejecting interference. (minimizes the effect of noise). Angle modulation allows the use of more efficient transmitter power in ...
Radio Frequency Osc.
... meter, which indicates the signal level for the user. The entire instrument is contained in a shielded cabinet. Many laboratory-quality RF generators provide shielding for the oscillator plus shielding for the entire instrument. ...
... meter, which indicates the signal level for the user. The entire instrument is contained in a shielded cabinet. Many laboratory-quality RF generators provide shielding for the oscillator plus shielding for the entire instrument. ...
Subject: Video Surveillance Systems Topic: Driving Video Signals
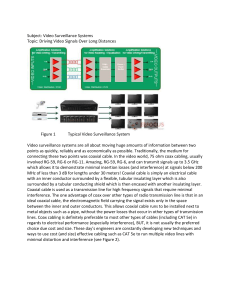
... in regards to length the signal can be transmitted and the pixel rate/frequency that sets the overall video resolution. As was previously discussed, insertion loss is a huge factor and is still probably the most dominant issue when transmitting single line CVBS with multiple high frequency component ...
... in regards to length the signal can be transmitted and the pixel rate/frequency that sets the overall video resolution. As was previously discussed, insertion loss is a huge factor and is still probably the most dominant issue when transmitting single line CVBS with multiple high frequency component ...
ECE 4117 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation ECE 4117
... filter. The filter does two things, it tunes the signal so that the carrier frequency is translated to 0 Hz and it uses a low pass filter to filter out the unwanted components of the spectrum of signals. Since our signal is being broadcast at 50KHz, the center frequency is at -50KHz. The bandwidth o ...
... filter. The filter does two things, it tunes the signal so that the carrier frequency is translated to 0 Hz and it uses a low pass filter to filter out the unwanted components of the spectrum of signals. Since our signal is being broadcast at 50KHz, the center frequency is at -50KHz. The bandwidth o ...
405-line television system
The 405-line monochrome analogue television broadcasting system was the first fully electronic television system to be used in regular broadcasting.It was introduced with the BBC Television Service in 1936, suspended for the duration of World War II, and remained in operation in the UK until 1985, it was also used between 1961 and 1982 in Ireland as well as from 1957 to 1973 for the Rediffusion Television cable service in Hong Kong.Sometimes called the Marconi-EMI system, it was developed in 1934 by the EMI Research Team led by Sir Isaac Shoenberg. The figure of 405 lines had been chosen following discussions over Sunday lunch at the home of Alan Blumlein. The system was the first broadcast system in Britain to use interlacing, though EMI had been experimenting with a 243 line all-electronic interlaced system since 1933. In the 405 system the scanning lines were broadcast in two complementary fields, 50 times per second, creating 25 frames per second. The actual image was 377 lines high and interlaced, with additional unused lines making the frame up to 405 lines to give the slow circuitry time to prepare for the next frame; in modern terms it would be described as 377i.At the time of its introduction the 405-line system was referred to as ""high definition"", which it was compared to earlier systems, although of lower definition than 625-line and later standards.