Some reflections on the charts of the ocean floor: Do they hide more
... plate tectonics theory and its explanatory power. Thus the bottom morphology presented by the first chart documents particularly well the existence of a world system of mid-oceanic ridges segmented by transform faults. Along these ridges new crust is continuously formed by outpouring of basaltic lav ...
... plate tectonics theory and its explanatory power. Thus the bottom morphology presented by the first chart documents particularly well the existence of a world system of mid-oceanic ridges segmented by transform faults. Along these ridges new crust is continuously formed by outpouring of basaltic lav ...
Intro Stream Processes
... The fossil record shows the same species of organisms in Africa and South America but the current organisms on the two continents are very different, why would that be? Separation of continents caused organisms to evolve separately on the different continents. ...
... The fossil record shows the same species of organisms in Africa and South America but the current organisms on the two continents are very different, why would that be? Separation of continents caused organisms to evolve separately on the different continents. ...
8-3 Unit Test - Darlington Middle School
... Scientists use the principle that the speed and direction of a seismic wave depends on the material it travels through. How does scientist know or study the Earth’s Core? Because of the behavior of these different waves, scientists have indirect evidence for the solid inner core and liquid outer cor ...
... Scientists use the principle that the speed and direction of a seismic wave depends on the material it travels through. How does scientist know or study the Earth’s Core? Because of the behavior of these different waves, scientists have indirect evidence for the solid inner core and liquid outer cor ...
Introduction: Tracking Past Plate Motions (2)
... Basaltic magma may rise into such a back-arc basin at a newly formed spreading center, and new oceanic crust may form. ...
... Basaltic magma may rise into such a back-arc basin at a newly formed spreading center, and new oceanic crust may form. ...
Chapter 8
... • Oceanic crust is almost entirely made up of mafic rocks (magnesium & iron) • Continental crust has two zones, the lower one is more dense and is largely mafic and the upper one that is lighter, felsic (aluminum, sodium, potassium, calcium) • Crust beneath continents much thicker than beneath ocean ...
... • Oceanic crust is almost entirely made up of mafic rocks (magnesium & iron) • Continental crust has two zones, the lower one is more dense and is largely mafic and the upper one that is lighter, felsic (aluminum, sodium, potassium, calcium) • Crust beneath continents much thicker than beneath ocean ...
Plate INteractions - Fellows
... earthquakes are common because parallel movement of the plates are not smooth. Elastic energy is stored within the rocks and when the rocks give way the energy is released. ...
... earthquakes are common because parallel movement of the plates are not smooth. Elastic energy is stored within the rocks and when the rocks give way the energy is released. ...
Plate Tectonics Unit Project
... this landform to the role it plays in forming two other landforms. Two of the landforms should be created at convergent boundaries and one should be created at a divergent boundary. Make sure to include vocabulary we have been using in this plate tectonics unit. ...
... this landform to the role it plays in forming two other landforms. Two of the landforms should be created at convergent boundaries and one should be created at a divergent boundary. Make sure to include vocabulary we have been using in this plate tectonics unit. ...
Volcanoes: lecture 1
... Increase temperature with depth Varies depending on tectonic setting Average increase is 25 degrees C/KM Yellow dotted line indicates 500 degrees centigrade ...
... Increase temperature with depth Varies depending on tectonic setting Average increase is 25 degrees C/KM Yellow dotted line indicates 500 degrees centigrade ...
Review for Science 10 Provincial Exam
... The Crosscutting rule says that any thing that disturbs other geologic features had to have happened after the layers were deposited. Here, the sill must have occurred after these layers were laid down. The top two layers might be more recent than the sill, although we would need more information t ...
... The Crosscutting rule says that any thing that disturbs other geologic features had to have happened after the layers were deposited. Here, the sill must have occurred after these layers were laid down. The top two layers might be more recent than the sill, although we would need more information t ...
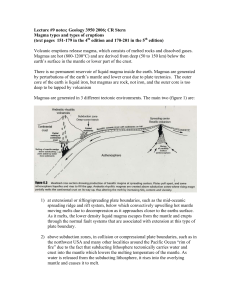
Lecture #10 -- Magma types and types of eruptions (text pages 151
... high iron content. They have low viscosity because they are hot (>1000°C) and have low silica content and have low volatile (H2O) contents. Therefore they erupt passively as lava flows, forming spatter cones and flows, shield volcanoes (like in Hawaii -- see figure below) and large lava plateaus (li ...
... high iron content. They have low viscosity because they are hot (>1000°C) and have low silica content and have low volatile (H2O) contents. Therefore they erupt passively as lava flows, forming spatter cones and flows, shield volcanoes (like in Hawaii -- see figure below) and large lava plateaus (li ...
Earth`s Skin: Plate Tectonics Document Contents
... Yellowstone is not near a plate boundary. You don’t have to be near a plate boundary to experience an earthquake, but chances are very small that you would experience one if you’re not. c) Locate your home town. Have many earthquakes occurred near it in the past 50 years? Why or why ...
... Yellowstone is not near a plate boundary. You don’t have to be near a plate boundary to experience an earthquake, but chances are very small that you would experience one if you’re not. c) Locate your home town. Have many earthquakes occurred near it in the past 50 years? Why or why ...
File - singhscience
... Convection currents can lead to earthquakes... • Radioactive decay takes place in the mantle, this produces a lot of heat, which causes the mantle to flow in convection currents. The hot rock rises then cools, causing the plates to move. As the plates move they slide past each other. There is frict ...
... Convection currents can lead to earthquakes... • Radioactive decay takes place in the mantle, this produces a lot of heat, which causes the mantle to flow in convection currents. The hot rock rises then cools, causing the plates to move. As the plates move they slide past each other. There is frict ...
Ring of Fire Around the edges of the Pacific Ocean, the plates of the
... down beneath the continents. Look at Figure 2 to see an example.The Nazca Plate, moving eastward from the East Pacific Ridge, slides down beneath the west coast of South America.The plate is heated as it sinks into the much hotter rocks of the deep Earth.The heat causes fluids, especially water, to ...
... down beneath the continents. Look at Figure 2 to see an example.The Nazca Plate, moving eastward from the East Pacific Ridge, slides down beneath the west coast of South America.The plate is heated as it sinks into the much hotter rocks of the deep Earth.The heat causes fluids, especially water, to ...
The Rock Cycle (1).
... These plates move past each other and occasionally slip above or below one another. As the plate sinks lower and lower beneath another plate, the heat and pressure it gives off causes the rock to melt. volcano Sometimes if one plate doesn’t slide underneath another, the the plates will collide and ...
... These plates move past each other and occasionally slip above or below one another. As the plate sinks lower and lower beneath another plate, the heat and pressure it gives off causes the rock to melt. volcano Sometimes if one plate doesn’t slide underneath another, the the plates will collide and ...
List and describe the 3 types of stress
... Ocean to ocean= (San Andreas Fault) foot wall as tension subduction stress pulls the Ocean to rocks apart. continental=subduction Continental to continental = mountain building The rocks move past each other. The shear Divergent: Mid stress pushes the rocks ocean ridges and horizontally rift valleys ...
... Ocean to ocean= (San Andreas Fault) foot wall as tension subduction stress pulls the Ocean to rocks apart. continental=subduction Continental to continental = mountain building The rocks move past each other. The shear Divergent: Mid stress pushes the rocks ocean ridges and horizontally rift valleys ...
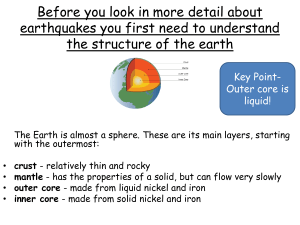
docx: Earth`s Interior Pre Assessment
... 1. As you travel from the Earth’s crust to its center, pressure and temperature do what? a. Temperature increases while pressure decreases. b. Both increase. c. Both stay pretty much the same. d. Both decrease. 2. The ________________________ is made of 13 tectonic plates. a. Lower mantle c. Lithosp ...
... 1. As you travel from the Earth’s crust to its center, pressure and temperature do what? a. Temperature increases while pressure decreases. b. Both increase. c. Both stay pretty much the same. d. Both decrease. 2. The ________________________ is made of 13 tectonic plates. a. Lower mantle c. Lithosp ...
presentation source
... As the concept of sea floor spreading gained acceptance in the late 60's, the consequences for geology gradually began to dawn. One of the first to recognise how plate tectonics could be applied to the geological record was J. Tuzo Wilson. If continents rift apart to form ocean basins, other oceans ...
... As the concept of sea floor spreading gained acceptance in the late 60's, the consequences for geology gradually began to dawn. One of the first to recognise how plate tectonics could be applied to the geological record was J. Tuzo Wilson. If continents rift apart to form ocean basins, other oceans ...
ES18-Understanding the Asthenosphere
... Lithosphere – the rigid, outermost layer of the Earth, composed of the crust and the solid upper part of the mantle Asthenosphere – the semi-solid part of the mantle immediately below the lithosphere Tectonic plate – an irregularly-shaped piece of the lithosphere ...
... Lithosphere – the rigid, outermost layer of the Earth, composed of the crust and the solid upper part of the mantle Asthenosphere – the semi-solid part of the mantle immediately below the lithosphere Tectonic plate – an irregularly-shaped piece of the lithosphere ...
Instructor`s Notes: Chapter 17 Earth`s Interior Earth`s Interior Indirect
... Increased temp- chemical bonds weaken lowering mechanical strength- deformation Melting- chemical bonds destroyed Pressure increases with depth making rock more dense –increasing strength- pressure raises the melting point because of confining pressure ...
... Increased temp- chemical bonds weaken lowering mechanical strength- deformation Melting- chemical bonds destroyed Pressure increases with depth making rock more dense –increasing strength- pressure raises the melting point because of confining pressure ...
What are 3 types of plate movements
... forming either a subduction zone or an orogenic belt. Convergent boundaries are also known as destructive boundaries. A subduction zone is when a dense oceanic plate thrusts under the less dense continental plate. This can create a mountain chain or a chain of volcanoes. Divergent movements occur wh ...
... forming either a subduction zone or an orogenic belt. Convergent boundaries are also known as destructive boundaries. A subduction zone is when a dense oceanic plate thrusts under the less dense continental plate. This can create a mountain chain or a chain of volcanoes. Divergent movements occur wh ...
tectonics2
... Most transform boundaries are associated with mid-ocean ridges (they form perpendicular to the rifts). One of the few major continental crustcontinental crust transform boundaries runs up the west coast of North ...
... Most transform boundaries are associated with mid-ocean ridges (they form perpendicular to the rifts). One of the few major continental crustcontinental crust transform boundaries runs up the west coast of North ...
Platemarginsandtheirassociatedvolcanoes 2.41
... undergoes ________melting producing basalt. This basaltic magma rises to the base of the continental crust. This magma has a temperature (1200°C-1400°C) much higher than the melting temperature of the crust (650°C-750°C), causing the crust to melt. • Melting of continental crust produces magmas with ...
... undergoes ________melting producing basalt. This basaltic magma rises to the base of the continental crust. This magma has a temperature (1200°C-1400°C) much higher than the melting temperature of the crust (650°C-750°C), causing the crust to melt. • Melting of continental crust produces magmas with ...
plate tectonics
... In areas where plates are moving apart Correct When plates move apart it is due to magma reaching the surface. When magma cools new land is formed. C. ...
... In areas where plates are moving apart Correct When plates move apart it is due to magma reaching the surface. When magma cools new land is formed. C. ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.