Simplifying Expressions to Solve Linear Equations
... 4. Undo the operations of addition and subtraction to collect the variables on one side and the constants on the other. 5. Combine like terms and undo the operations of multiplication and division to isolate the variable. 6. Check the solution in the original equation. ...
... 4. Undo the operations of addition and subtraction to collect the variables on one side and the constants on the other. 5. Combine like terms and undo the operations of multiplication and division to isolate the variable. 6. Check the solution in the original equation. ...
GCSE Higher Paper Topics – Non Calculator
... 16. Standard Form 17. Sectors of Circles – areas / angle size etc 18. Reasons for Angle size – alternate etc / circle rules etc 19. Using calculators to solve to significant figures and decimal places. 20. Percentage / profit / loss – Interest 21. Estimated Mean 22. Bearings Pythagoras Trigonome ...
... 16. Standard Form 17. Sectors of Circles – areas / angle size etc 18. Reasons for Angle size – alternate etc / circle rules etc 19. Using calculators to solve to significant figures and decimal places. 20. Percentage / profit / loss – Interest 21. Estimated Mean 22. Bearings Pythagoras Trigonome ...
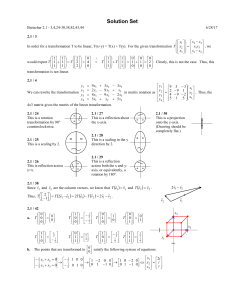
Solution Set - Harvard Math Department
... In proving the above two conditions, we have used a few properties of cross product. Since both conditions are satisfied, the cross product transformation is linear. Using the definition of cross product, we can write: v x v x 0 v3 v2 x1 v x ...
... In proving the above two conditions, we have used a few properties of cross product. Since both conditions are satisfied, the cross product transformation is linear. Using the definition of cross product, we can write: v x v x 0 v3 v2 x1 v x ...
8th Mathematics JSUNIL TUTORIAL,SAMASTIPUR
... 7. Two complementary angles are such that one is 14o more than three times the second angle. What is the measure of the larger angle. Solution : in two angles let a larger one and a smaller one = x . The larger one = 3 × + 14o The sum of two angles is 90o . 3 × + 14o + x = 90o 4 × r = 90 - 14 ...
... 7. Two complementary angles are such that one is 14o more than three times the second angle. What is the measure of the larger angle. Solution : in two angles let a larger one and a smaller one = x . The larger one = 3 × + 14o The sum of two angles is 90o . 3 × + 14o + x = 90o 4 × r = 90 - 14 ...
7th Grade Algebra Common Assessment
... 22. One of the systems in problem #21 above has no solution. How could you tell from just looking at the original equations? ...
... 22. One of the systems in problem #21 above has no solution. How could you tell from just looking at the original equations? ...
Slide 1.4
... Now, write the system of linear equations as a vector equation involving a linear combination of vectors. For example, the following system x1 2 x2 x3 4 ...
... Now, write the system of linear equations as a vector equation involving a linear combination of vectors. For example, the following system x1 2 x2 x3 4 ...
Semester Exam Review
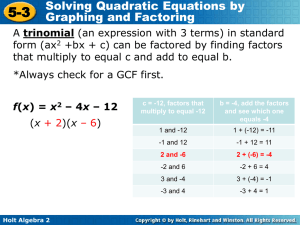
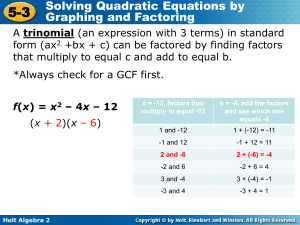
... Using the Zero-Product Property: Method to solve quadratic equations Zero-Product Property—If ab = 0, then a = 0 or b = 0 Steps: Set equation = 0, factor equation, use Zero-Product Property to find x Ex. x2 + x – 6 = 0; (x – 2)(x + 3) = 0; x – 2 = 0 or x + 3 = 0; x = 2 or x = -3 Solutions to a Quadr ...
... Using the Zero-Product Property: Method to solve quadratic equations Zero-Product Property—If ab = 0, then a = 0 or b = 0 Steps: Set equation = 0, factor equation, use Zero-Product Property to find x Ex. x2 + x – 6 = 0; (x – 2)(x + 3) = 0; x – 2 = 0 or x + 3 = 0; x = 2 or x = -3 Solutions to a Quadr ...
PowerPoint
... system of linear equations: substitution, elimination with equations, and elimination with matrices. You will now study one more method, Cramer’s Rule, named after Gabriel Cramer (1704–1752). This rule uses determinants to write the solution of a system of linear equations. ...
... system of linear equations: substitution, elimination with equations, and elimination with matrices. You will now study one more method, Cramer’s Rule, named after Gabriel Cramer (1704–1752). This rule uses determinants to write the solution of a system of linear equations. ...