Cubic Equations with Problems
... x1 = 3 A + 3 B − b/3 , so what are the other two solutions? x2 = 3 A 2 3 B − b/3 Well since (1cis 120)(1cis 240) = 1cis 360 = 1 + 0i … x3 = 2 3 A 3 B − b/3 I can see how the 'omegas' go away! Okay… Cardan's Formulas – Girolamo Cardano (1501-1576) Ars Magna 1545 http://www.geocities.com/d ...
... x1 = 3 A + 3 B − b/3 , so what are the other two solutions? x2 = 3 A 2 3 B − b/3 Well since (1cis 120)(1cis 240) = 1cis 360 = 1 + 0i … x3 = 2 3 A 3 B − b/3 I can see how the 'omegas' go away! Okay… Cardan's Formulas – Girolamo Cardano (1501-1576) Ars Magna 1545 http://www.geocities.com/d ...
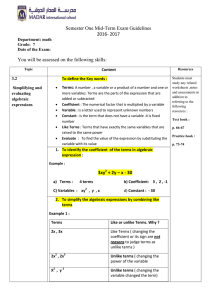
Mathematics - MADAR International School
... a) Equation that is true for all real numbers is called …………………………….. b) The algebraic equation that is True for some real numbers ……………………………………. c) ………………….........have exactly the same variables that are raised to the same power d) The value of the variable that makes the equation true is called ...
... a) Equation that is true for all real numbers is called …………………………….. b) The algebraic equation that is True for some real numbers ……………………………………. c) ………………….........have exactly the same variables that are raised to the same power d) The value of the variable that makes the equation true is called ...
MATH TODAY
... Engage New York material which is taught in the classroom. In Module 4, Topic G, students recognize that the solution can also be found using properties of operations. They make connections to the model and determine that 1 + a - 1 = 6 – 1 and , ultimately, that a = 5. Students represent two- step a ...
... Engage New York material which is taught in the classroom. In Module 4, Topic G, students recognize that the solution can also be found using properties of operations. They make connections to the model and determine that 1 + a - 1 = 6 – 1 and , ultimately, that a = 5. Students represent two- step a ...
SOLVING FIRST ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
... 7. Substitute this value into the previous expression containing g(y) and you have the solution, F(x, y). 8. The general solution is formed by setting the constant equal to the remaining expression. ...
... 7. Substitute this value into the previous expression containing g(y) and you have the solution, F(x, y). 8. The general solution is formed by setting the constant equal to the remaining expression. ...
Quadratic equations and complex numbers
... A complex number C is a number which can be written in the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers and i = 1 . a is the real part of C, and bi is the imaginary part of C. An imaginary number is a complex number whose imaginary part is not zero (i.e., b 0 ). A pure imaginary number is an imagi ...
... A complex number C is a number which can be written in the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers and i = 1 . a is the real part of C, and bi is the imaginary part of C. An imaginary number is a complex number whose imaginary part is not zero (i.e., b 0 ). A pure imaginary number is an imagi ...