Heart Rhythms, Let`s Keep It Simple! Linda Latour, RN/CN III 7100
... node, hypoxemia, MI, digitalis toxicity, ischemia, and increased vagal tone. This conduction usually does not progress to higher degree heart blocks. No treatment needed if patient is asymptomatic Rhythm: Irregular PRI: progressive lengthening of PRI until dropped beat. (long, longer, drop) QRS is u ...
... node, hypoxemia, MI, digitalis toxicity, ischemia, and increased vagal tone. This conduction usually does not progress to higher degree heart blocks. No treatment needed if patient is asymptomatic Rhythm: Irregular PRI: progressive lengthening of PRI until dropped beat. (long, longer, drop) QRS is u ...
Two-dimensional echocardiography in cardiac tamponade
... sector scanner (Advanced Technical Laboratories). This series of II patients comprised 7 men and 4 women, whose ages ranged from 31 to 73 years (mean 59). The original cardiac operation was coronary artery bypass grafting in eight, mitral valve replacement in two and atrial septal defect repair in o ...
... sector scanner (Advanced Technical Laboratories). This series of II patients comprised 7 men and 4 women, whose ages ranged from 31 to 73 years (mean 59). The original cardiac operation was coronary artery bypass grafting in eight, mitral valve replacement in two and atrial septal defect repair in o ...
Randomized Control of Sympathetic Drive With Continuous
... BACKGROUND Elevated sympathetic drive has a detrimental effect on patients with acute STEMI. The effect of beta-blocker-induced heart rate mediated sympathetic control on myocardial damage is unknown. METHODS The authors conducted a prospective, randomized, single-blind trial involving patients with ...
... BACKGROUND Elevated sympathetic drive has a detrimental effect on patients with acute STEMI. The effect of beta-blocker-induced heart rate mediated sympathetic control on myocardial damage is unknown. METHODS The authors conducted a prospective, randomized, single-blind trial involving patients with ...
geometric changes - The International Heart Institute of Montana
... TA, with 3.1 ± 1.1° of the rotation occurring during ejection. Conclusion: The tricuspid valve is not a passive structure but rather forms a dynamic part of the right ventricle. Its orifice area changes not only due to the contraction and expansion of its perimeter but also to changes in its saddle ...
... TA, with 3.1 ± 1.1° of the rotation occurring during ejection. Conclusion: The tricuspid valve is not a passive structure but rather forms a dynamic part of the right ventricle. Its orifice area changes not only due to the contraction and expansion of its perimeter but also to changes in its saddle ...
Diastolic closure rate of normal mitral valve - Heart
... The mitral valve echogram was recorded using a Smith- crystal microphone placed in the second intercostal Kline Instruments Ekoline 20 ultrasound recorder pro- space at the left sternal edge. A small cannula was introviding a repetition rate of iooo pulses a second with a duced into a vein on the do ...
... The mitral valve echogram was recorded using a Smith- crystal microphone placed in the second intercostal Kline Instruments Ekoline 20 ultrasound recorder pro- space at the left sternal edge. A small cannula was introviding a repetition rate of iooo pulses a second with a duced into a vein on the do ...
Assessment of longitudinal left ventricular systolic function by
... Patient characteristics and study protocol We enrolled 57 consecutive patients (30 men and 27 women; mean age 48±9 years) with newly diagnosed and never treated mild-to-moderate hypertension and 48 normotensive control subjects (26 men and 22 women; mean age 46±9 years) in this cross-sectional and o ...
... Patient characteristics and study protocol We enrolled 57 consecutive patients (30 men and 27 women; mean age 48±9 years) with newly diagnosed and never treated mild-to-moderate hypertension and 48 normotensive control subjects (26 men and 22 women; mean age 46±9 years) in this cross-sectional and o ...
SUDDEN DEATH IN YOUNG ATHLETES
... cause of the enhanced mortality, but it triggers cardiac arrest in those athletes who have cardiovascular conditions that predispose to life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias during physical exercise such as cardiomyopathy (primarily hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and ARVC/D), premature coronary arte ...
... cause of the enhanced mortality, but it triggers cardiac arrest in those athletes who have cardiovascular conditions that predispose to life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias during physical exercise such as cardiomyopathy (primarily hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and ARVC/D), premature coronary arte ...
Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Pressure-Volume
... To estimate changes in compliance, we evaluated the effects of sepsis on the end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship (EDPVR) in the left ventricle of rats that had undergone an open thorax procedure. Sepsis was induced in male Wistar Hannover rats (n 7; 240 to 270 g) by intraperitoneal administra ...
... To estimate changes in compliance, we evaluated the effects of sepsis on the end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship (EDPVR) in the left ventricle of rats that had undergone an open thorax procedure. Sepsis was induced in male Wistar Hannover rats (n 7; 240 to 270 g) by intraperitoneal administra ...
Hyperoxia causes oxygen free radical
... varying durations can occur (1, 2, 35, 41). For example, during ECMO or CPB, systemic oxygen levels can reach an arterial PO2 (PaO2) of up to 500 mmHg, which can last several days during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or for 2–5 h during a cardiac operation (1, 35). The original rationale for t ...
... varying durations can occur (1, 2, 35, 41). For example, during ECMO or CPB, systemic oxygen levels can reach an arterial PO2 (PaO2) of up to 500 mmHg, which can last several days during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or for 2–5 h during a cardiac operation (1, 35). The original rationale for t ...
Downloaded
... myocardial infarction, history of heart failure, and prior aspirin use. A recommendation with Level of Evidence B or C does not imply that the recommendation is weak. Many important clinical questions addressed in the guidelines do not lend themselves to clinical trials. Even though randomized trial ...
... myocardial infarction, history of heart failure, and prior aspirin use. A recommendation with Level of Evidence B or C does not imply that the recommendation is weak. Many important clinical questions addressed in the guidelines do not lend themselves to clinical trials. Even though randomized trial ...
Practice Guideline: Focused Update 2009 Focused Update
... Many important clinical questions addressed in the guidelines do not lend themselves to clinical trials. Even though randomized trials are not available, there may be a very clear clinical consensus that a particular test or therapy is useful or effective. †In 2003, the ACC/AHA Task Force on Practic ...
... Many important clinical questions addressed in the guidelines do not lend themselves to clinical trials. Even though randomized trials are not available, there may be a very clear clinical consensus that a particular test or therapy is useful or effective. †In 2003, the ACC/AHA Task Force on Practic ...
1 - Livemedia
... fatigue with a decreased ability to tolerate the daily regimen may represent cardiac impairment and should be investigated. •Development of dilated cardiomyopathy usually precedes the development of heart-failure symptoms by years and must be identified at its earliest onset. ...
... fatigue with a decreased ability to tolerate the daily regimen may represent cardiac impairment and should be investigated. •Development of dilated cardiomyopathy usually precedes the development of heart-failure symptoms by years and must be identified at its earliest onset. ...
2009 Focused Update: ACCF/AHA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management... Heart Failure in Adults: A Report of the American College...
... myocardial infarction, history of heart failure, and prior aspirin use. A recommendation with Level of Evidence B or C does not imply that the recommendation is weak. Many important clinical questions addressed in the guidelines do not lend themselves to clinical trials. Even though randomized trial ...
... myocardial infarction, history of heart failure, and prior aspirin use. A recommendation with Level of Evidence B or C does not imply that the recommendation is weak. Many important clinical questions addressed in the guidelines do not lend themselves to clinical trials. Even though randomized trial ...
Clyde W. Yancy Donna M. Mancini, Peter S. Rahko, Marc A. Silver
... myocardial infarction, history of heart failure, and prior aspirin use. A recommendation with Level of Evidence B or C does not imply that the recommendation is weak. Many important clinical questions addressed in the guidelines do not lend themselves to clinical trials. Even though randomized trial ...
... myocardial infarction, history of heart failure, and prior aspirin use. A recommendation with Level of Evidence B or C does not imply that the recommendation is weak. Many important clinical questions addressed in the guidelines do not lend themselves to clinical trials. Even though randomized trial ...
ACCF/AHA Practice Guideline: Focused Update
... The ACCF/AHA practice guidelines are intended to assist healthcare providers in clinical decision making by describing a range of generally acceptable approaches for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of specific diseases or conditions. The guidelines attempt to define practices that meet the ...
... The ACCF/AHA practice guidelines are intended to assist healthcare providers in clinical decision making by describing a range of generally acceptable approaches for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of specific diseases or conditions. The guidelines attempt to define practices that meet the ...
Cindarella - Gastaldi Congressi
... Impaired renal function is a risk factor for hyperkalemia during treatment with aldosterone antagonists. The risk of hyperkalemia increases progressively when sCr exceeds 1.6 mg/dL.* In elderly patients or others with low muscle mass in whom sCr does not accurately reflect GFR, determination that GF ...
... Impaired renal function is a risk factor for hyperkalemia during treatment with aldosterone antagonists. The risk of hyperkalemia increases progressively when sCr exceeds 1.6 mg/dL.* In elderly patients or others with low muscle mass in whom sCr does not accurately reflect GFR, determination that GF ...
De novo sirolimus with low-dose tacrolimus versus full
... RESULTS: Freedom from treatment switch was less in the lowTAC/SIR group than in the TAC/MMF group (51.7% vs 73.0%, p ¼ 0.038) 8 years after HTX. Freedom from acute rejection was 90.6% in the lowTAC/SIR group vs 80.3% in the TAC/MMF group (p ¼ 0.100). There was no difference in freedom from Internati ...
... RESULTS: Freedom from treatment switch was less in the lowTAC/SIR group than in the TAC/MMF group (51.7% vs 73.0%, p ¼ 0.038) 8 years after HTX. Freedom from acute rejection was 90.6% in the lowTAC/SIR group vs 80.3% in the TAC/MMF group (p ¼ 0.100). There was no difference in freedom from Internati ...
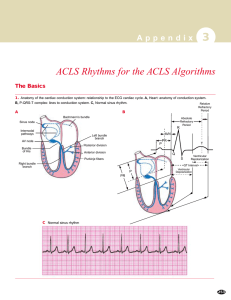
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms
... ■ Palpitations felt by patient at the paroxysmal onset; becomes anxious, uncomfortable ■ Exercise tolerance low with very high rates ■ Symptoms of unstable tachycardia may occur ...
... ■ Palpitations felt by patient at the paroxysmal onset; becomes anxious, uncomfortable ■ Exercise tolerance low with very high rates ■ Symptoms of unstable tachycardia may occur ...
Causes of sudden death in competitive athletes
... The exact mechanism by which this coronary anomaly may produce sudden death is not definitively known, How• ever, it has been postulated (33,35) that the important an• atomic feature is the acute takeoff angle of the left main coronary artery from the right sinus, which results in a narrowing of the ...
... The exact mechanism by which this coronary anomaly may produce sudden death is not definitively known, How• ever, it has been postulated (33,35) that the important an• atomic feature is the acute takeoff angle of the left main coronary artery from the right sinus, which results in a narrowing of the ...
... Bronchial blood flow to the affected lung may be increased 15–25 fold and can account for up to one third of the left ventricular output [1, 6]. The incidence of pulmonary hypertension in the isolated cases is 19% [1]. The clinical presentation of these patients is variable: about 30% of patients re ...
Increased diastolic time fraction as beneficial adjunct of - AJP
... be closely related to stenosis severity at the onset of stressinduced myocardial ischemia in humans, whereas no such correlation was found with heart rate at the ischemic threshold (7). It has recently been reported that DTF also depends inversely on coronary pressure (24), which is an important det ...
... be closely related to stenosis severity at the onset of stressinduced myocardial ischemia in humans, whereas no such correlation was found with heart rate at the ischemic threshold (7). It has recently been reported that DTF also depends inversely on coronary pressure (24), which is an important det ...
Atrioventricular Nodal Function in the Immature Canine
... neonatal goat, the AVNFRP falls within 10 ms of the VFRP and, that because of this, ventricular arrhythmias were commonly induced during atrial extrastimulation. This functional immaturity of the neonatal AV conduction system has been implicated as a possible cause of sudden death in infancy (4). In ...
... neonatal goat, the AVNFRP falls within 10 ms of the VFRP and, that because of this, ventricular arrhythmias were commonly induced during atrial extrastimulation. This functional immaturity of the neonatal AV conduction system has been implicated as a possible cause of sudden death in infancy (4). In ...
Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter - MC2893
... usually related to blockages in the arteries serving your heart muscle (coronary arteries), and they do not mean you are having a heart attack or any other serious heart problems. However, most people with atrial fibrillation have another disease, such as any of the following: • High blood pressure ...
... usually related to blockages in the arteries serving your heart muscle (coronary arteries), and they do not mean you are having a heart attack or any other serious heart problems. However, most people with atrial fibrillation have another disease, such as any of the following: • High blood pressure ...
lained severe pulmonary hypertension in ... H J. L.O.
... hypertension such as right ventricular dilatation and hypertrophy, paradoxical septal motion and the leakage of the pulmonary and tricuspid valves are easy to detect on echocardiography [27, 28], its more widespread use helps in making an earlier diagnosis. Scmiquantitative measurement of pulmonary ...
... hypertension such as right ventricular dilatation and hypertrophy, paradoxical septal motion and the leakage of the pulmonary and tricuspid valves are easy to detect on echocardiography [27, 28], its more widespread use helps in making an earlier diagnosis. Scmiquantitative measurement of pulmonary ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.