Review Sheet Answers Word Doc
... Vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral (bicuspid) valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, and aorta 18. What is a normal blood pressure reading? ...
... Vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral (bicuspid) valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, and aorta 18. What is a normal blood pressure reading? ...
Word
... heart, while also detecting previously undiagnosed and/or asymptomatic atrial fibrillation (AF), a condition that involves an irregular quivering or rapid heart rhythm in the upper chambers (atria) of the heart. Many patients rely on ICDs, small implantable heart devices placed under the skin, typic ...
... heart, while also detecting previously undiagnosed and/or asymptomatic atrial fibrillation (AF), a condition that involves an irregular quivering or rapid heart rhythm in the upper chambers (atria) of the heart. Many patients rely on ICDs, small implantable heart devices placed under the skin, typic ...
Boredom at its HEART by Dhravid - Fitz
... A heart attack is like a huge tidal wave in the ocean while a cardiac arrest is like a destructive Tsunami. A heart attack occurs when the heart does not receive sufficient blood because of blockage in the coronary artery. This causes the muscles of the heart (myocardium) to be damaged. Cardiac arr ...
... A heart attack is like a huge tidal wave in the ocean while a cardiac arrest is like a destructive Tsunami. A heart attack occurs when the heart does not receive sufficient blood because of blockage in the coronary artery. This causes the muscles of the heart (myocardium) to be damaged. Cardiac arr ...
Powerpoint version
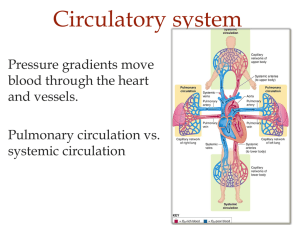
... Circulatory system Pressure gradients move blood through the heart and vessels. Pulmonary circulation vs. systemic circulation ...
... Circulatory system Pressure gradients move blood through the heart and vessels. Pulmonary circulation vs. systemic circulation ...
Coronary Artery Disease CAD: a global problem What is CAD
... coronary event and every minute someone dies from it.2 ...
... coronary event and every minute someone dies from it.2 ...
Mitral Valve Dysplasia in Cats - Veterinary Specialty Services
... being the heart murmur detected during physical examination. Other cats may develop symptoms, the nature and severity of which are variable between cats and depend upon how the condition progresses. If cardiac function becomes significantly impaired, intolerance to activity or exercise may be noted. ...
... being the heart murmur detected during physical examination. Other cats may develop symptoms, the nature and severity of which are variable between cats and depend upon how the condition progresses. If cardiac function becomes significantly impaired, intolerance to activity or exercise may be noted. ...
cardiac arrest heart attack
... More often, though, symptoms start slowly and persist for hours, days or weeks before a heart attack. Unlike with cardiac arrest, the heart usually does not stop beating during a heart attack. The longer the person goes without treatment, the greater the damage. ...
... More often, though, symptoms start slowly and persist for hours, days or weeks before a heart attack. Unlike with cardiac arrest, the heart usually does not stop beating during a heart attack. The longer the person goes without treatment, the greater the damage. ...
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
... 29. There is no history of renal trauma. Immunizations are up to date. She neither smokes nor drinks, but does take oral contraceptives. Her vision is fine, and she has no cough at all. There has been no personality change or excessive sweating. On physical examination you find that blood pressure ...
... 29. There is no history of renal trauma. Immunizations are up to date. She neither smokes nor drinks, but does take oral contraceptives. Her vision is fine, and she has no cough at all. There has been no personality change or excessive sweating. On physical examination you find that blood pressure ...
World Congress of Cardiology Scientific Sessions 2010 Featuring
... early after reperfusion and recover incompletely upon follow-up. “Accurate methods for the assessing cardiovascular function are crucial to reduce mortality and morbidity connected to cardiovascular diseases,” said Dr. Krasimira Hristova, MD, FESC, National Heart Hospital, Sofia, Bulgaria. “The pres ...
... early after reperfusion and recover incompletely upon follow-up. “Accurate methods for the assessing cardiovascular function are crucial to reduce mortality and morbidity connected to cardiovascular diseases,” said Dr. Krasimira Hristova, MD, FESC, National Heart Hospital, Sofia, Bulgaria. “The pres ...
Response to (resynchronization) therapy in chronic heart failure
... longitudinal cohort studies. Cohort studies are also unable to address the ‘ceiling effect’ commonly seen in older patients with comorbidities and in younger patients with mild disease. In both situations, patients with an excellent clinical outcome are labelled as ‘non-responders’. For example the ...
... longitudinal cohort studies. Cohort studies are also unable to address the ‘ceiling effect’ commonly seen in older patients with comorbidities and in younger patients with mild disease. In both situations, patients with an excellent clinical outcome are labelled as ‘non-responders’. For example the ...
File
... − A stronger pump, since it has to pump blood to the body • Cardiac output is the volume of blood that the left ventricle pumps per minute. o Cardiac output is about 5.25 L of blood per minute in a person with an average heart rate of 70 beats per minute o The pulse is a wave effect that passes down ...
... − A stronger pump, since it has to pump blood to the body • Cardiac output is the volume of blood that the left ventricle pumps per minute. o Cardiac output is about 5.25 L of blood per minute in a person with an average heart rate of 70 beats per minute o The pulse is a wave effect that passes down ...
CPVT - Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
... happened after conception. If this is the case, the gene change can be passed on to the affected child’s own children in the future, but their siblings are usually unaffected. There are currently four genes known to be associated with CPVT. Changes in the RYR2 (Ryanodine receptor 2 gene) gene causes ...
... happened after conception. If this is the case, the gene change can be passed on to the affected child’s own children in the future, but their siblings are usually unaffected. There are currently four genes known to be associated with CPVT. Changes in the RYR2 (Ryanodine receptor 2 gene) gene causes ...
Dia 1 - EPCCS
... I. Symptoms typical of heart failure and (not always!) II. Signs typical of heart failure and III. Objective evidence of a structural or functional abnormality of the heart at rest ...
... I. Symptoms typical of heart failure and (not always!) II. Signs typical of heart failure and III. Objective evidence of a structural or functional abnormality of the heart at rest ...
Heart Failiure and Valve disease
... Altered mental status Rising creatinine Liver enzyme abnormalities ...
... Altered mental status Rising creatinine Liver enzyme abnormalities ...
Doc - Medtronic
... The most common risk factor associated with AF is existing heart disease. AF is common among people who suffer from coronary heart disease, valve disease, an inflamed heart muscle or lining, or those who have had a heart attack, congestive heart failure or heart surgery. Other risk factors include h ...
... The most common risk factor associated with AF is existing heart disease. AF is common among people who suffer from coronary heart disease, valve disease, an inflamed heart muscle or lining, or those who have had a heart attack, congestive heart failure or heart surgery. Other risk factors include h ...
Cardiac Cycle (PPT#4)
... Cycle = “events of one complete heart beat” ► Mid-to-late diastole (relaxation) = blood flows into ventricles ► Ventricular systole (contraction) = blood pressure builds before ventricles contract pushing blood out ► Early diastole = atria finish re-filling; ventricular pressure is low ...
... Cycle = “events of one complete heart beat” ► Mid-to-late diastole (relaxation) = blood flows into ventricles ► Ventricular systole (contraction) = blood pressure builds before ventricles contract pushing blood out ► Early diastole = atria finish re-filling; ventricular pressure is low ...
Heart: Dilated Cardiomyopathy
... Before a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy is made, several tests are used that assess different aspects of heart function. Auscultation which is listening with a stethoscope. This allows us to identify murmurs due to the improper closure of heart valves based on the murmur’s location and intensit ...
... Before a diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy is made, several tests are used that assess different aspects of heart function. Auscultation which is listening with a stethoscope. This allows us to identify murmurs due to the improper closure of heart valves based on the murmur’s location and intensit ...
HEART FUNCTION AND HEART SOUNDS
... – Trouble relaxing between beats is a growing cause of heart failure • Why the heart can’t relax? – Open space inside the ventricles can be restricted by heart muscle that “bulks up” due to overwork or other causes or that stiffens and loses it flexibility. ...
... – Trouble relaxing between beats is a growing cause of heart failure • Why the heart can’t relax? – Open space inside the ventricles can be restricted by heart muscle that “bulks up” due to overwork or other causes or that stiffens and loses it flexibility. ...
Physiological basis of the care of the care of the elderly
... Evaluate BP bilaterally and in lying, sitting and standing positions Blood pressure varies with time of day and with activity Respond to “white coat ...
... Evaluate BP bilaterally and in lying, sitting and standing positions Blood pressure varies with time of day and with activity Respond to “white coat ...
ECG - Derriford ED
... 5. How can you tell the difference between an atrial or a ventricular premature conduction? 6. What HR may be on the cardiac monitor if patient is in PEA? 7. What is the normal length of time for the P-R interval? 8. What does the term Paroxysmal mean? There is a prize for the winning team!! ...
... 5. How can you tell the difference between an atrial or a ventricular premature conduction? 6. What HR may be on the cardiac monitor if patient is in PEA? 7. What is the normal length of time for the P-R interval? 8. What does the term Paroxysmal mean? There is a prize for the winning team!! ...
Keeping Healthy (B2)
... the sound made by the four valves of the heart closing A 12 week old foetus’ heart pumps 60 pints of blood a day ...
... the sound made by the four valves of the heart closing A 12 week old foetus’ heart pumps 60 pints of blood a day ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.