Heart Support
... stable cardiovascular hemodynamics and electrophysiologic function. In patients with congestive heart failure, the presence of adequate total-body magnesium stores serve as an important prognostic indicator because of an amelioration of arrhythmias, digitalis toxicity, and hemodynamic abnormalities. ...
... stable cardiovascular hemodynamics and electrophysiologic function. In patients with congestive heart failure, the presence of adequate total-body magnesium stores serve as an important prognostic indicator because of an amelioration of arrhythmias, digitalis toxicity, and hemodynamic abnormalities. ...
Mortality in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: an
... However, with each failed therapeutic clinical trial and the appearance of new basic studies (both animal and human) that delve deeper into the pathophysiology, some investigators are becoming more open minded to the possibility that both of these principles may not be true. Several well acknowledge ...
... However, with each failed therapeutic clinical trial and the appearance of new basic studies (both animal and human) that delve deeper into the pathophysiology, some investigators are becoming more open minded to the possibility that both of these principles may not be true. Several well acknowledge ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... and a systemic circuit supplied by the left. 2. The pulmonary circuit serves only to exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen in the lungs. The systemic circuit serves to deliver oxygen and nutrients to all organs. 3. The pulmonary circuit begins where the pulmonary trunk arises from the right ventricle, ...
... and a systemic circuit supplied by the left. 2. The pulmonary circuit serves only to exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen in the lungs. The systemic circuit serves to deliver oxygen and nutrients to all organs. 3. The pulmonary circuit begins where the pulmonary trunk arises from the right ventricle, ...
Slide ()
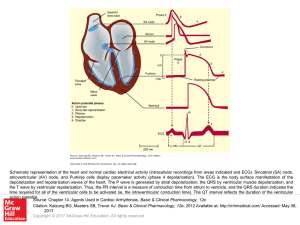
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
Sheep Heart Dissection Lab
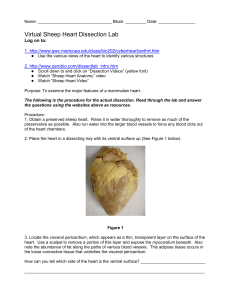
... 2. Place the heart in a dissecting tray with its ventral surface up (See Figure 2 below). Proceed as follows: Locate the visceral pericardium, which appears as a thin, transparent layer on the surface of the heart. Also note the abundance of fat along the paths of various blood vessels. This adipose ...
... 2. Place the heart in a dissecting tray with its ventral surface up (See Figure 2 below). Proceed as follows: Locate the visceral pericardium, which appears as a thin, transparent layer on the surface of the heart. Also note the abundance of fat along the paths of various blood vessels. This adipose ...
FACT SHEET Facts About Sudden Cardiac Arrest
... arrest episodes are caused by the rapid and/or chaotic activity of the heart known as ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF). These are abnormalities of the heart’s electrical conduction system. Sudden cardiac arrest is not a heart attack (myocardial infarction), which is c ...
... arrest episodes are caused by the rapid and/or chaotic activity of the heart known as ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF). These are abnormalities of the heart’s electrical conduction system. Sudden cardiac arrest is not a heart attack (myocardial infarction), which is c ...
Referring patients for LVAD Therapy
... III. Assessment of the Valves While aortic stenosis is not a definitive contraindication for LVAD therapy, aortic regurgitation may cause major problems by creating a circular blood flow loop between the inflow and outflow cannulas of the LVAD and restrict forward circulation. All regurgitation need ...
... III. Assessment of the Valves While aortic stenosis is not a definitive contraindication for LVAD therapy, aortic regurgitation may cause major problems by creating a circular blood flow loop between the inflow and outflow cannulas of the LVAD and restrict forward circulation. All regurgitation need ...
Document
... C. Fist size – 14cm X 9 cm D. lies in the mediastinum w/ apex On an angle pointing inferior/left 1. left side is thicker than right – 2/3 on the left fig. 18.1; pg. 662 II. Double pump A. Blood comes into Rt. atrium to Rt. ventricle B. goes to lungs exchanges CO2 &O2 C. Oxygenated blood comes back t ...
... C. Fist size – 14cm X 9 cm D. lies in the mediastinum w/ apex On an angle pointing inferior/left 1. left side is thicker than right – 2/3 on the left fig. 18.1; pg. 662 II. Double pump A. Blood comes into Rt. atrium to Rt. ventricle B. goes to lungs exchanges CO2 &O2 C. Oxygenated blood comes back t ...
L-2 heart sounds
... • It occurs at the last one third of Diastole (just before S1) • Cause of Fourth heart sound – Due to Atrial contraction which causes rapid flow of blood from Atria to Ventricle and vibration in the blood. • Frequency: < 20 Htz Note: • Third and Fourth heart sound are low pitched sounds therefore no ...
... • It occurs at the last one third of Diastole (just before S1) • Cause of Fourth heart sound – Due to Atrial contraction which causes rapid flow of blood from Atria to Ventricle and vibration in the blood. • Frequency: < 20 Htz Note: • Third and Fourth heart sound are low pitched sounds therefore no ...
MS Word - Wonderstruck
... and diastole respectively. When it contracts blood is pushed out and around the pulmonary and systemic circuits. When it relaxes, blood re-enters the heart ready to be pushed out again on the next contraction. Take a look at diagram 2 and go through the steps laid out below to see how it all works i ...
... and diastole respectively. When it contracts blood is pushed out and around the pulmonary and systemic circuits. When it relaxes, blood re-enters the heart ready to be pushed out again on the next contraction. Take a look at diagram 2 and go through the steps laid out below to see how it all works i ...
Circulation support part 1 dr. Horáček
... Cardiac output • preload = force strretching fibers before contraction = ED fiber lenght = EDV = EDP – blood volume, venous tone, ventricle compliance, contractility, afterload ...
... Cardiac output • preload = force strretching fibers before contraction = ED fiber lenght = EDV = EDP – blood volume, venous tone, ventricle compliance, contractility, afterload ...
Module 5 – Pediatric Cardiac Disorders
... than normal must be handled by the right side of the heart hypertrophy 3. Extra blood then passes through the pulmonary artery into the lungs, causing higher pressure than normal in the blood vessels in the lungs congestive heart failure ...
... than normal must be handled by the right side of the heart hypertrophy 3. Extra blood then passes through the pulmonary artery into the lungs, causing higher pressure than normal in the blood vessels in the lungs congestive heart failure ...
7 Conclusions and Future Perspectives F.S. de Man , N. Westerhof
... Hypertension (PH). In addition, we show that besides the pulmonary vasculature and right ventricle, also the diaphragm muscle is affected in PH. Exercise training is currently implemented in the recent treatment guidelines as therapeutic strategy to improve exercise capacity of patients with PH.1 Ho ...
... Hypertension (PH). In addition, we show that besides the pulmonary vasculature and right ventricle, also the diaphragm muscle is affected in PH. Exercise training is currently implemented in the recent treatment guidelines as therapeutic strategy to improve exercise capacity of patients with PH.1 Ho ...
congenital heart diseases
... pulmonary artery passes to the aorta through ductus arteriosus •PDA connects the proximal descending aorta with the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation •Left-to-right shunt •Marked increase in pulmonary blood flow results in left sided volume overload with increase in the size of the left atrium, le ...
... pulmonary artery passes to the aorta through ductus arteriosus •PDA connects the proximal descending aorta with the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation •Left-to-right shunt •Marked increase in pulmonary blood flow results in left sided volume overload with increase in the size of the left atrium, le ...
Cardiovascular System
... muscle to adjust size of vessel, adjustable vessel allows us to have adjustable flow. Like faucets on a sink. • Vasoconstriction: decreasing diameter of vessel • Vasodilation: increasing diameter of vessel. ...
... muscle to adjust size of vessel, adjustable vessel allows us to have adjustable flow. Like faucets on a sink. • Vasoconstriction: decreasing diameter of vessel • Vasodilation: increasing diameter of vessel. ...
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy for€Mild Heart Failure
... patients. Patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy ...
... patients. Patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy ...
Virtual Sheep Heart Dissection Lab Student Worksheet
... 4. The line running diagonally down from the right side (facing you) of the heart to the bottom left side is the coronary artery. The coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle tissue. The pointed bottom of the heart is called the apex. What do you think is the purpose of the coronary artery ...
... 4. The line running diagonally down from the right side (facing you) of the heart to the bottom left side is the coronary artery. The coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle tissue. The pointed bottom of the heart is called the apex. What do you think is the purpose of the coronary artery ...
Mechanisms underlying abnormal epicardium formation in the
... providing an outer protective layer to the heart), the embryonic epicardium is essential for normal heart development, contributing to structures such as cardiac valves and coronary vessels. Studies in our laboratory have shown that when a heartbeat is present but irregular, an abnormal epicardium c ...
... providing an outer protective layer to the heart), the embryonic epicardium is essential for normal heart development, contributing to structures such as cardiac valves and coronary vessels. Studies in our laboratory have shown that when a heartbeat is present but irregular, an abnormal epicardium c ...
Comprehending Cardiac Medications: Foundational Cardiac
... of the heart with each beat. The term stroke volume can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although it usually refers to the left ventricle. The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 70 mL in most adults. Stroke volume is influenced by the a ...
... of the heart with each beat. The term stroke volume can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although it usually refers to the left ventricle. The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 70 mL in most adults. Stroke volume is influenced by the a ...
Heart Failure
... divide. Under normal circumstances, functionally useful augmentation of myocyte number (hyperplasia) cannot occur. Increased mechanical load causes an increase in the content of subcellular components and a consequent increase in cell size (hypertrophy). Increased mechanical work owing to pressure o ...
... divide. Under normal circumstances, functionally useful augmentation of myocyte number (hyperplasia) cannot occur. Increased mechanical load causes an increase in the content of subcellular components and a consequent increase in cell size (hypertrophy). Increased mechanical work owing to pressure o ...
Author keywords
... 148 patients with a low (<5%) likelihood of coronary disease and normal tomograms were selected. No one of 148 patients had known coronary artery disease, typical angina, history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and smoking, any abnormality in echocardiography or hyperlipidemia. They were not tak ...
... 148 patients with a low (<5%) likelihood of coronary disease and normal tomograms were selected. No one of 148 patients had known coronary artery disease, typical angina, history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and smoking, any abnormality in echocardiography or hyperlipidemia. They were not tak ...
Tachycardia
... heartbeat. Problems with the heart that can also cause a fast heart rate are: Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT): PAT and PSVT are caused by changes in the natural electrical impulse that causes your heart to pump. Atrial fibrillation: The muscles ...
... heartbeat. Problems with the heart that can also cause a fast heart rate are: Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT): PAT and PSVT are caused by changes in the natural electrical impulse that causes your heart to pump. Atrial fibrillation: The muscles ...
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
... – Ventricles contract = increase pressure = valves open – Ventricles relax = blood flows back = close valves ...
... – Ventricles contract = increase pressure = valves open – Ventricles relax = blood flows back = close valves ...
Low-oxygen environment leads to heart
... Health Presbyterian Hospital Dallas, a joint program of UT Southwestern and Texas Health Resources. ...
... Health Presbyterian Hospital Dallas, a joint program of UT Southwestern and Texas Health Resources. ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.