$doc.title
... Then we study heat engines, the wording of the second law of thermodynamics, and the efficiency of heat engines and refrigerators, before moving on to the Carnot cycle. From both the practical and theoretical perspective, the Carnot cycle is of great importance as a heat engine operating with this i ...
... Then we study heat engines, the wording of the second law of thermodynamics, and the efficiency of heat engines and refrigerators, before moving on to the Carnot cycle. From both the practical and theoretical perspective, the Carnot cycle is of great importance as a heat engine operating with this i ...
Dry heat - Grainchain
... Foods which are baked, grilled or roasted undergo colour, odour and flavour changes. The process is called dextrinisation. ...
... Foods which are baked, grilled or roasted undergo colour, odour and flavour changes. The process is called dextrinisation. ...
SYNOPSES: A gas, completely insulated from its surroundings
... ∆ U is the internal energy of the system. Every equilibrium state of a thermodynamic system is completely described by specific values of some macroscopic variables, also called state variables. Examples of State Variables: (1) Pressure (P) (2) Volume (V) (3) Temperature (T) (4) Mass (m). Calorie is ...
... ∆ U is the internal energy of the system. Every equilibrium state of a thermodynamic system is completely described by specific values of some macroscopic variables, also called state variables. Examples of State Variables: (1) Pressure (P) (2) Volume (V) (3) Temperature (T) (4) Mass (m). Calorie is ...
Homework #1: Energy Unit Conversions
... Solve the following problems using the conversions listed below. Report your answer with the correct units. Conversions: 1 calorie = 4.18 joules 1 Calorie = 1000 calories 1kilocalorie= 1 Calorie (food) 1. How many calories are in 16.00 joules? ...
... Solve the following problems using the conversions listed below. Report your answer with the correct units. Conversions: 1 calorie = 4.18 joules 1 Calorie = 1000 calories 1kilocalorie= 1 Calorie (food) 1. How many calories are in 16.00 joules? ...
Experiment 5
... relevant heat exchanges is zero. The determination or use of thermal properties of the materials in a system consisting of objects exchanging heat is called calorimetry. Calorimetry experiments are generally difficult to analyze due to a source of error which is difficult to quantify – heat exchange ...
... relevant heat exchanges is zero. The determination or use of thermal properties of the materials in a system consisting of objects exchanging heat is called calorimetry. Calorimetry experiments are generally difficult to analyze due to a source of error which is difficult to quantify – heat exchange ...
Thermodynamics
... Analysis of the heat flow is more complex than for the coffee cup calorimeter because the heat flow into the metal parts of the calorimeter must be accounted for (heat capacity, Cp): qreaction = - (qwater + qbomb) where qwater = 4.18 J/(g·°C) x mwater x Δt qbomb = Cp x Δt ...
... Analysis of the heat flow is more complex than for the coffee cup calorimeter because the heat flow into the metal parts of the calorimeter must be accounted for (heat capacity, Cp): qreaction = - (qwater + qbomb) where qwater = 4.18 J/(g·°C) x mwater x Δt qbomb = Cp x Δt ...
ASLab_100Specific Heat Inquiry
... Heat, abbreviated as Cv. This quantity represents the amount of heat required to raise or lower a given quantity (a gram or a Kilogram) by one degree. Water has an extremely high Specific Heat (1 calorie per gram per degree C). That’s what makes it such a wonderful (and plentiful!) substance for hea ...
... Heat, abbreviated as Cv. This quantity represents the amount of heat required to raise or lower a given quantity (a gram or a Kilogram) by one degree. Water has an extremely high Specific Heat (1 calorie per gram per degree C). That’s what makes it such a wonderful (and plentiful!) substance for hea ...
Condensation and the Nusselt`s Film Theory
... As we can see from this equation, the heat transfer coefficients are large for small temperature differences ts-tw and heights L. In both cases the condensate film is thin and hence the heat transfer resistance is low. Equation (11) can also be used for film condensation at the inner or outer walls ...
... As we can see from this equation, the heat transfer coefficients are large for small temperature differences ts-tw and heights L. In both cases the condensate film is thin and hence the heat transfer resistance is low. Equation (11) can also be used for film condensation at the inner or outer walls ...
Thermochemistry
... temperature of 1 g of a substance 1oC. Water has a uniquely high specific heat compared to other substances. ...
... temperature of 1 g of a substance 1oC. Water has a uniquely high specific heat compared to other substances. ...
Specific Heat and Calculating Heat Absorbed - Varga
... The specific heat of concrete is 0.84 J/g°C, whereas the specific heat of water 4.184 J/g°C. If you have 1 kg of each substance at 0°C, which of them will take more energy to raise to a temperature of ...
... The specific heat of concrete is 0.84 J/g°C, whereas the specific heat of water 4.184 J/g°C. If you have 1 kg of each substance at 0°C, which of them will take more energy to raise to a temperature of ...
Power point about heat transfer
... • Heat: Heat is energy! Heat is the energy transferred (passed) from a hotter object to a cooler object. • Heat Transfer: The transfer (passing) of heat from one object to another. Heat always moves in the direction from: higher temperatures to lower temperatures. warm to cool • Always! Always! Alwa ...
... • Heat: Heat is energy! Heat is the energy transferred (passed) from a hotter object to a cooler object. • Heat Transfer: The transfer (passing) of heat from one object to another. Heat always moves in the direction from: higher temperatures to lower temperatures. warm to cool • Always! Always! Alwa ...
Heat, Temperature, and States of Matter
... 2. Radiation is the transfer of energy in the form of particles. ...
... 2. Radiation is the transfer of energy in the form of particles. ...
Equation-Based Modeling: Building your Equations from scratch
... All Heat Transfer conditions can be represented with the same interface Insulation: Heat Flux into domain: Convective condition: ...
... All Heat Transfer conditions can be represented with the same interface Insulation: Heat Flux into domain: Convective condition: ...
241 Lecture 11
... Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics • Remember with Thermal equilibrium • Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of heat between them when they are brought into thermal contact. • Temperature is the indicator of thermal equilibrium • Two systems individually in thermal e ...
... Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics • Remember with Thermal equilibrium • Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of heat between them when they are brought into thermal contact. • Temperature is the indicator of thermal equilibrium • Two systems individually in thermal e ...
Chapter Two Atoms & The Periodic Table
... Bclosed system (heat only pass through) Cisolated system (no heat or mass transfer) ...
... Bclosed system (heat only pass through) Cisolated system (no heat or mass transfer) ...
electrical heating - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... A heat pump uses an electric motor to drive a refrigeration cycle, drawing heat from a source such as ground water or outside air and directing it into the space to be warmed. Such systems can deliver two or three units of heating energy for every unit of purchased energy. ...
... A heat pump uses an electric motor to drive a refrigeration cycle, drawing heat from a source such as ground water or outside air and directing it into the space to be warmed. Such systems can deliver two or three units of heating energy for every unit of purchased energy. ...
Unit 3 Homework
... 1. Graphene ZA mode specific heat In the lectures, we obtained integral expressions for the specific heat of modes that can be approximated with a linear dispersion (Debye model) and constant dispersion (Einstein model). The ZA mode of graphene, which represents out-of-plane vibrations, is however c ...
... 1. Graphene ZA mode specific heat In the lectures, we obtained integral expressions for the specific heat of modes that can be approximated with a linear dispersion (Debye model) and constant dispersion (Einstein model). The ZA mode of graphene, which represents out-of-plane vibrations, is however c ...
Substance Specific Heat Capacity
... are better thermal conductors than materials that do not have this property such as wood, styrofoam, and gases. http://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation_348266&feature=iv&src _vid=yXT012us9ng&v=vqDbMEdLiCs ...
... are better thermal conductors than materials that do not have this property such as wood, styrofoam, and gases. http://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation_348266&feature=iv&src _vid=yXT012us9ng&v=vqDbMEdLiCs ...
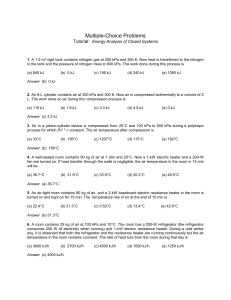
Multiple Choice Questions_1
... 3. Air in a piston-cylinder device is compressed from 25C and 100 kPa to 500 kPa during a polytropic process for which Pv1.3 = constant. The air temperature after compression is (a) 33C ...
... 3. Air in a piston-cylinder device is compressed from 25C and 100 kPa to 500 kPa during a polytropic process for which Pv1.3 = constant. The air temperature after compression is (a) 33C ...
Thermochemistry www.AssignmentPoint.com Thermochemistry is
... enclosed chamber within which the change to be examined occurs. The temperature of the chamber is monitored either using a thermometer or thermocouple, and the temperature plotted against time to give a graph from which fundamental quantities can be calculated. Modern calorimeters are ...
... enclosed chamber within which the change to be examined occurs. The temperature of the chamber is monitored either using a thermometer or thermocouple, and the temperature plotted against time to give a graph from which fundamental quantities can be calculated. Modern calorimeters are ...
Summary
... adding fins to the inside or outside the tubes? Why? 7. Hot air is to be cooled as it is forced through the tubes exposed to atmospheric air. Fins are to be attached in order to enhance heat transfer. Would you recommend adding fins to the inside or outside the tubes? Why? When would you recommend a ...
... adding fins to the inside or outside the tubes? Why? 7. Hot air is to be cooled as it is forced through the tubes exposed to atmospheric air. Fins are to be attached in order to enhance heat transfer. Would you recommend adding fins to the inside or outside the tubes? Why? When would you recommend a ...
Heat Transfer by Conduction
... For glass and most nonporous materials, the thermal conductivities are much lower, from about 0.35 to 3.5. For most liquid k is lower than that for solids, with typical values of about 0.17. k decreases by 3 ~ 4 %t for a 10 ºC rise in temperature, except water. ...
... For glass and most nonporous materials, the thermal conductivities are much lower, from about 0.35 to 3.5. For most liquid k is lower than that for solids, with typical values of about 0.17. k decreases by 3 ~ 4 %t for a 10 ºC rise in temperature, except water. ...