ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL
... 1. What are “plates” 2. What impact can colliding plates have on the earth? 3. Define Subduction 4. What can subduction cause? 5. What causes earthquakes? 6. What happens when plates pull apart? 7. Define Pangea ...
... 1. What are “plates” 2. What impact can colliding plates have on the earth? 3. Define Subduction 4. What can subduction cause? 5. What causes earthquakes? 6. What happens when plates pull apart? 7. Define Pangea ...
Lecture 3 Review Sheet
... Magnetic field, magnetic field lines, geodynamo, solenoid, solar wind, magnetosphere, inner core, outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, asthenospheric mantle, lithosphere, lithospheric mantle, continental crust, oceanic crust, the Moho, seismic analysis, seismic shadow zone, lava geochemistry, m ...
... Magnetic field, magnetic field lines, geodynamo, solenoid, solar wind, magnetosphere, inner core, outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, asthenospheric mantle, lithosphere, lithospheric mantle, continental crust, oceanic crust, the Moho, seismic analysis, seismic shadow zone, lava geochemistry, m ...
Earth Science - SC.7.E.6.2: First Assessment 1) Beaches and barrier
... 8) Lori is learning about two parts of the rock cycle: weathering and erosion. She needs to explain how weathering and erosion are different. Which of the following correctly describes the difference between weathering and erosion? a. Weathering is the movement of rocks by wind; erosion is the movem ...
... 8) Lori is learning about two parts of the rock cycle: weathering and erosion. She needs to explain how weathering and erosion are different. Which of the following correctly describes the difference between weathering and erosion? a. Weathering is the movement of rocks by wind; erosion is the movem ...
How old is the Earth really? THE AGE OF THE EARTH- 1850
... that radioactive decay produced heat. This discovery proved that the calculations of GeorgeLouis Leclerc and Lord Kelvin could not be accurate because these scientist had assumed that heat was always being lost; they did not know that heat could also be created. During the first few years of the 20t ...
... that radioactive decay produced heat. This discovery proved that the calculations of GeorgeLouis Leclerc and Lord Kelvin could not be accurate because these scientist had assumed that heat was always being lost; they did not know that heat could also be created. During the first few years of the 20t ...
earth
... – Igneous: cooled magma/lava – Sedimentary: particles deposited by water flow. Organic/inorganic matter (fossils) – Metamorphic: as layers build up, this rock is formed when pressure and heat become great enough to change the rock chemically • The rock cycle is completed through the tectonic process ...
... – Igneous: cooled magma/lava – Sedimentary: particles deposited by water flow. Organic/inorganic matter (fossils) – Metamorphic: as layers build up, this rock is formed when pressure and heat become great enough to change the rock chemically • The rock cycle is completed through the tectonic process ...
View the Sample
... This vibration cause the earth to move A fault is the fracture in the earth crust and slipped rock. These faults are divided into three – Normal Faults-is pulling or tension -Thrust faults- squeezing of compression -Strike Slip faults- Blocks move past each other After a earthquakes another can occu ...
... This vibration cause the earth to move A fault is the fracture in the earth crust and slipped rock. These faults are divided into three – Normal Faults-is pulling or tension -Thrust faults- squeezing of compression -Strike Slip faults- Blocks move past each other After a earthquakes another can occu ...
The Structure of the Earth
... The earth has a solid inner core made mostly of iron and nickel. It is solid because it is under so much pressure: all the rest of the earth is pressing down on it. Its temperature is about 7000 degrees Kelvin (about 12,000 degrees Fahrenheit) -- hotter than the surface of the sun! The outer core is ...
... The earth has a solid inner core made mostly of iron and nickel. It is solid because it is under so much pressure: all the rest of the earth is pressing down on it. Its temperature is about 7000 degrees Kelvin (about 12,000 degrees Fahrenheit) -- hotter than the surface of the sun! The outer core is ...
The Interior of the Earth
... (The lithosphere is broken up into tectonic plates.) The asthenosphere is the semi-liquid layer of upper mantle. (The plates are believed to flow slowly on top of the asthenosphere.) ...
... (The lithosphere is broken up into tectonic plates.) The asthenosphere is the semi-liquid layer of upper mantle. (The plates are believed to flow slowly on top of the asthenosphere.) ...
Earth Science SOL Review Facts Word document
... The layers of the atmosphere are, from bottom up are : troposphere (where we live and where the weather is), Stratosphere (Ozone layer), Mesosphere, and Thermosphere. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels has increased CO2 levels. High CO2 levels produce the Greenhouse effect. CFC's ar ...
... The layers of the atmosphere are, from bottom up are : troposphere (where we live and where the weather is), Stratosphere (Ozone layer), Mesosphere, and Thermosphere. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels has increased CO2 levels. High CO2 levels produce the Greenhouse effect. CFC's ar ...
Name____________________________
... Brittle: Likely to break, snap, or crack, as when subjected to pressure. Ductile: Easily molded or shaped. Density: The amount of matter in a given volume. Viscosity: The extent to which a fluid resists a tendency to flow. ...
... Brittle: Likely to break, snap, or crack, as when subjected to pressure. Ductile: Easily molded or shaped. Density: The amount of matter in a given volume. Viscosity: The extent to which a fluid resists a tendency to flow. ...
Name:___ANSWER KEY
... America and Africa provide evidence for plate tectonics? Explain: Animals live in similar regions. Fossils of these animals supports the idea that these regions were once similar and therefore were connected at a similar location and time. ...
... America and Africa provide evidence for plate tectonics? Explain: Animals live in similar regions. Fossils of these animals supports the idea that these regions were once similar and therefore were connected at a similar location and time. ...
– Circle the response that best answers the question.
... If the statement is true, write true. If it is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 11 Continental crust is made of rocks such as granite. 12 Slow movements of mantle rock called radiation transfer heat in the mantle. 13 The single landmass that broke apart 250 mil ...
... If the statement is true, write true. If it is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 11 Continental crust is made of rocks such as granite. 12 Slow movements of mantle rock called radiation transfer heat in the mantle. 13 The single landmass that broke apart 250 mil ...
Geology Study Guide
... The division of Earth’s history is the Geological Time Scale- from most recent to oldest time periods: Cenozoic (Age of Mammals), Mesozoic (Age of Reptiles), Paleozoic (Age of Marine Life), Proterozoic Eon (where first organism appeared), Archean Eon (where first rock appeared), and Hadean Eon.(Page ...
... The division of Earth’s history is the Geological Time Scale- from most recent to oldest time periods: Cenozoic (Age of Mammals), Mesozoic (Age of Reptiles), Paleozoic (Age of Marine Life), Proterozoic Eon (where first organism appeared), Archean Eon (where first rock appeared), and Hadean Eon.(Page ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... The magnitude of geologic time Involves vast times – millions or billions of years An appreciation for the magnitude of geologic time is important because many processes are very gradual The big difference between geology and other sciences: TIME (Geologically speaking, not much happens in a human l ...
... The magnitude of geologic time Involves vast times – millions or billions of years An appreciation for the magnitude of geologic time is important because many processes are very gradual The big difference between geology and other sciences: TIME (Geologically speaking, not much happens in a human l ...
Integrated Science Chapter 19 Notes Section 1: Earth`s Interior and
... • Earthquakes generally occur at the boundaries of tectonic plates, where the plates shift with respect to one another ⇒ As the plates move the rocks along their edges experience immense pressure ⇒ When the pressure is great enough the rocks break along the fault line, and the energy is released in ...
... • Earthquakes generally occur at the boundaries of tectonic plates, where the plates shift with respect to one another ⇒ As the plates move the rocks along their edges experience immense pressure ⇒ When the pressure is great enough the rocks break along the fault line, and the energy is released in ...
Study Guide: Plate tectonics TEST 2/soil Rocks/Weathering and
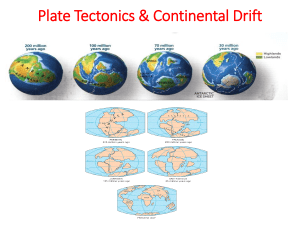
... 17. What are the theories of Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics? The earth’s crust is cracked into plates that move, the earth was once one supercontinent called pangaea. 18. List 3 pieces of evidence that prove our tectonic plates move. Fossils-similar fossils in Africa and South America, geology- ...
... 17. What are the theories of Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics? The earth’s crust is cracked into plates that move, the earth was once one supercontinent called pangaea. 18. List 3 pieces of evidence that prove our tectonic plates move. Fossils-similar fossils in Africa and South America, geology- ...
!GLG-101-Chapter 1-Illustrated Vocabulary copyright 2003
... *a rock that enters the Earth's atmosphere from outer space and falls to the ground. *[Iron Meteorite-Argentina-1] *[Widmanstatten Pattern-1] !meteorite impact crater *large meteorites, travelling at great speeds, are capable of creating craters when they strike the Earth. *[Meteor Crater-Rim-1] *[M ...
... *a rock that enters the Earth's atmosphere from outer space and falls to the ground. *[Iron Meteorite-Argentina-1] *[Widmanstatten Pattern-1] !meteorite impact crater *large meteorites, travelling at great speeds, are capable of creating craters when they strike the Earth. *[Meteor Crater-Rim-1] *[M ...
Plate Tectonics DQ - Biloxi Public Schools
... A. Faults on tectonic plates are in constant motion, but volcanoes may not erupt for many years. B. Faults and volcanoes existed long before there were tectonic plates. C. Tectonic plates that have many faults do not usually have volcanoes. D. Faults and volcanoes are often found at tectonic plate b ...
... A. Faults on tectonic plates are in constant motion, but volcanoes may not erupt for many years. B. Faults and volcanoes existed long before there were tectonic plates. C. Tectonic plates that have many faults do not usually have volcanoes. D. Faults and volcanoes are often found at tectonic plate b ...
Introduction to Earth Science Ch. 01
... Intrusive Igneous Activity • Plutons result from the cooling and hardening of magma within the earth • Exposed at surface after uplift and erosion • Pluton refers to Pluto, the Roman god of the underworld ...
... Intrusive Igneous Activity • Plutons result from the cooling and hardening of magma within the earth • Exposed at surface after uplift and erosion • Pluton refers to Pluto, the Roman god of the underworld ...
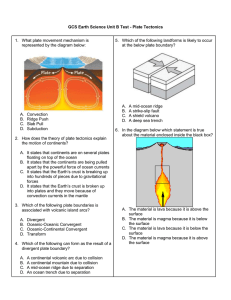
GCS Earth Science Unit B Test
... C. The Indian Ocean is the most tectonically active place on Earth D. North America and Europe are moving ...
... C. The Indian Ocean is the most tectonically active place on Earth D. North America and Europe are moving ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.