Geologic Time - Bakersfield College
... Rocks from several localities have been dated at more than 3 billion years Confirms the idea that geologic time is immense Difficulties Not ...
... Rocks from several localities have been dated at more than 3 billion years Confirms the idea that geologic time is immense Difficulties Not ...
01 - Middletown Public Schools
... 23. Will a seismic wave traveling through a solid go faster or slower than a seismic wave traveling through ...
... 23. Will a seismic wave traveling through a solid go faster or slower than a seismic wave traveling through ...
Layers of the Earth Unit 5 ES.7 The student will investigate and
... respect to one another (because of convection currents in the mantle). The core, _______________, and crust of the Earth are dynamic systems that are constantly in motion Throughout the typical human lifespan the Earth’s surface appears to remain relatively _____________________ On the geologic time ...
... respect to one another (because of convection currents in the mantle). The core, _______________, and crust of the Earth are dynamic systems that are constantly in motion Throughout the typical human lifespan the Earth’s surface appears to remain relatively _____________________ On the geologic time ...
Word format
... processes have occurred throughout Earth history. Simply stated, this principle advocates “the present is the key to the past”. In order to better understand the long complex history of our planet, we must develop a strong understanding of its geologic complexity. This includes the evidence for how ...
... processes have occurred throughout Earth history. Simply stated, this principle advocates “the present is the key to the past”. In order to better understand the long complex history of our planet, we must develop a strong understanding of its geologic complexity. This includes the evidence for how ...
EGU2017
... This study investigates stratigraphy and structural features in the Cenozoic sedimentary sequence of the fold-thrust belt of the Nallıhan-Ankara region, located to the north of the İzmir-Ankara-Erzincan Suture Zone. PermianTriassic age marble intercalated with schist-phyllites, the upper Jurassic-l ...
... This study investigates stratigraphy and structural features in the Cenozoic sedimentary sequence of the fold-thrust belt of the Nallıhan-Ankara region, located to the north of the İzmir-Ankara-Erzincan Suture Zone. PermianTriassic age marble intercalated with schist-phyllites, the upper Jurassic-l ...
KEY
... Isochron map shows the age of the ocean-floor crust increases with distance from the ridge. It also shows the symmetry on both sides of the ridge. Ch 17.3, page 459 1. Explain the theory of plate tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large slabs call ...
... Isochron map shows the age of the ocean-floor crust increases with distance from the ridge. It also shows the symmetry on both sides of the ridge. Ch 17.3, page 459 1. Explain the theory of plate tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large slabs call ...
Eighth Grade ScienceEarth`s HistoryStudy Guide
... 4. Who proposed the theory of continental drift? Alfred Wegner 5. Why did scientists NOT support the theory of Continental Drift? Wegner could NOT explain how or why the plates moved. 6. What is subduction? When one plate goes under another plate and it is melted back into the mantle. 7. The Earth’s ...
... 4. Who proposed the theory of continental drift? Alfred Wegner 5. Why did scientists NOT support the theory of Continental Drift? Wegner could NOT explain how or why the plates moved. 6. What is subduction? When one plate goes under another plate and it is melted back into the mantle. 7. The Earth’s ...
Chapter 1
... Geology – the study of the Earth Physical Geology • materials that make up the Earth • processes that operate upon and beneath the surface of the Earth • this course is primarily a study of physical geology. ...
... Geology – the study of the Earth Physical Geology • materials that make up the Earth • processes that operate upon and beneath the surface of the Earth • this course is primarily a study of physical geology. ...
Chapter 4
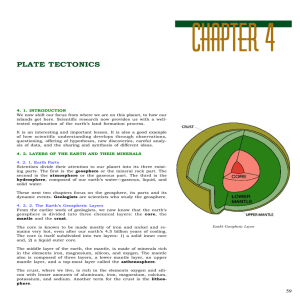
... 1) What is indirect evidence? 2) What are seismic waves? 3) How do geologist know about the Earth’s interior? 4) What happens to pressure and temperature as one descends through the Earth? 5) What is pressure? 6) Identify the four layers of the Earth from the outside and moving in. 7) Identify the p ...
... 1) What is indirect evidence? 2) What are seismic waves? 3) How do geologist know about the Earth’s interior? 4) What happens to pressure and temperature as one descends through the Earth? 5) What is pressure? 6) Identify the four layers of the Earth from the outside and moving in. 7) Identify the p ...
Chapter 10 * Plate Tectonics
... Fossil evidence has been used to support this hypothesis. Fossils of the same plants and animals have been found in areas that could have been joined together at one time. Geologic evidence also supports Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift. The ages and types of rocks in the coastal regions of ...
... Fossil evidence has been used to support this hypothesis. Fossils of the same plants and animals have been found in areas that could have been joined together at one time. Geologic evidence also supports Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift. The ages and types of rocks in the coastal regions of ...
8.4 Earth`s Layers
... Over 82 % of Earth’s volume is contained in the mantle Mantle – a solid, rocky shell that extends to a depth of 2890 km. The boundary between the crust & mantle shows a change in chemical composition. ...
... Over 82 % of Earth’s volume is contained in the mantle Mantle – a solid, rocky shell that extends to a depth of 2890 km. The boundary between the crust & mantle shows a change in chemical composition. ...
The Earth`s Formation
... The Nebular Hypothesis states _______________________________________________ called a nebula The cloud (nebula) was over 10 billion kilometers in diameter Originally a large ___________________________________ became unstable The most dense part of the cloud started to collapse under the __________ ...
... The Nebular Hypothesis states _______________________________________________ called a nebula The cloud (nebula) was over 10 billion kilometers in diameter Originally a large ___________________________________ became unstable The most dense part of the cloud started to collapse under the __________ ...
Continental Drift and Sea-Floor Spreading 7.2
... 1. Continents fit together like puzzle pieces (mountain ranges lined up) 2. Mesosaurus – Reptile fossil found on South America and Africa – It couldn’t swim! 3. Glossopteris – Tropical plant fossil that was found in Antarctica! ...
... 1. Continents fit together like puzzle pieces (mountain ranges lined up) 2. Mesosaurus – Reptile fossil found on South America and Africa – It couldn’t swim! 3. Glossopteris – Tropical plant fossil that was found in Antarctica! ...
Our Earth
... Bombardment melts surface, not the core. • Radioactive heating – trapped by insulating rocks - melts iron-rich rocks. • Gravity causes heavy iron to sink to centre. • Crust is cooling ‘skin’ on the surface. ...
... Bombardment melts surface, not the core. • Radioactive heating – trapped by insulating rocks - melts iron-rich rocks. • Gravity causes heavy iron to sink to centre. • Crust is cooling ‘skin’ on the surface. ...
Volcanoes Explosive-non explosive
... Most are adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g. Mt. Rainier, Mt. St. Helens) Large size Layered lava and pyroclastic debris both explosive and non-explosive Most violent type of activity ...
... Most are adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (e.g. Mt. Rainier, Mt. St. Helens) Large size Layered lava and pyroclastic debris both explosive and non-explosive Most violent type of activity ...
Vocabulary Activity - Stout Middle School
... 11. a theory that says the lithosphere is divided into plates that move around on top of the asthenosphere: ATPLE ICESTNOTC ...
... 11. a theory that says the lithosphere is divided into plates that move around on top of the asthenosphere: ATPLE ICESTNOTC ...
Inferred Properties about Earth`s Interior
... inner core: red outer core: orange stiffer mantle: purple (upper and lower) asthenosphere (top part of upper mantle):blue rigid mantle: yellow MOHO: yellow (darken slightly) Crust: greenShade in LIGHTLY with colored pencil. 3. See board for example. 4. Now we are ready to practice read ...
... inner core: red outer core: orange stiffer mantle: purple (upper and lower) asthenosphere (top part of upper mantle):blue rigid mantle: yellow MOHO: yellow (darken slightly) Crust: greenShade in LIGHTLY with colored pencil. 3. See board for example. 4. Now we are ready to practice read ...
Earthquakes
... • Stress: a force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume. – Because stress is a force, it adds energy to the rock. The energy is stored in the rock until the rock changes shape or breaks. – Most changes in the crust occur so slowly that they cannot be observed directly. But if you could spe ...
... • Stress: a force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume. – Because stress is a force, it adds energy to the rock. The energy is stored in the rock until the rock changes shape or breaks. – Most changes in the crust occur so slowly that they cannot be observed directly. But if you could spe ...
EVOLUTION OF EARTH
... The First 400 Million Years: The Earth was largely molten due to: (1) the residual heat of formation, (2) continuing impacts from asteroids, & (3) internal radioactivity, which cooked Earth from within. Differentiation occurred as the heavier elements sank towards the center, producing the core/ ...
... The First 400 Million Years: The Earth was largely molten due to: (1) the residual heat of formation, (2) continuing impacts from asteroids, & (3) internal radioactivity, which cooked Earth from within. Differentiation occurred as the heavier elements sank towards the center, producing the core/ ...
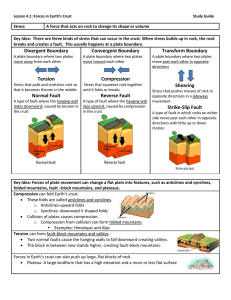
Chapter 4 lesson 1
... A type of fault in which rocks on either side move past each other in opposite directions with little up or down motion ...
... A type of fault in which rocks on either side move past each other in opposite directions with little up or down motion ...
Introduction to Earthquakes EASA
... Geology & The Plates Plates play an enormous role in geologic activity. Much of the action in geology occurs along the plate edges, or boundaries. The boundaries are the locus of – Earthquakes – Volcanoes – Heat loss – etc. ...
... Geology & The Plates Plates play an enormous role in geologic activity. Much of the action in geology occurs along the plate edges, or boundaries. The boundaries are the locus of – Earthquakes – Volcanoes – Heat loss – etc. ...
DYNAMIC EARTH NOTES
... especially along the ocean floor, magma is released. This iron-rich magma magnetizes towards the north & south pole. As the plates move & spread apart, newer magma is formed, again pointing to the poles, however, since the other older magma has moved (and still points in it’s original direction) the ...
... especially along the ocean floor, magma is released. This iron-rich magma magnetizes towards the north & south pole. As the plates move & spread apart, newer magma is formed, again pointing to the poles, however, since the other older magma has moved (and still points in it’s original direction) the ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.