Nonrenewable Mineral Resources
... 14-1A Dynamic processes within the earth and on its surface produce the mineral resources we depend on. 14-1B Mineral resources are nonrenewable because they are produced and renewed over millions of years mostly by the earth’s rock cycle. 14-2A Nonrenewable mineral resources exist in finite amounts ...
... 14-1A Dynamic processes within the earth and on its surface produce the mineral resources we depend on. 14-1B Mineral resources are nonrenewable because they are produced and renewed over millions of years mostly by the earth’s rock cycle. 14-2A Nonrenewable mineral resources exist in finite amounts ...
Historical Geology - FacultyWeb Support Center
... and thus winds and weather systems Rapid plate spreading and hot-spot activity may release volcanic carbon dioxide and affect global climate ...
... and thus winds and weather systems Rapid plate spreading and hot-spot activity may release volcanic carbon dioxide and affect global climate ...
What Happens to Create the Lode?
... deposits build up, the overburden (or lithostatic) pressure squeezes the sediment into layered solids in a process known as lithification ("rock formation"). Sedimentary rocks contain important information about the history of the earth. They contain fossils, the preserved remains of ancient plants ...
... deposits build up, the overburden (or lithostatic) pressure squeezes the sediment into layered solids in a process known as lithification ("rock formation"). Sedimentary rocks contain important information about the history of the earth. They contain fossils, the preserved remains of ancient plants ...
Lecture 13
... many craters has not changed much in 3 billion years • Erosion can erase craters. Thus fewer craters indicate geological activity ...
... many craters has not changed much in 3 billion years • Erosion can erase craters. Thus fewer craters indicate geological activity ...
Plate tectonics: The main features are
... per year. The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. Convection currents in the mantle beneath the plates move the plates in different directions. The source of heat driving the convection currents is radioactive decay which is happening deep in the ...
... per year. The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. Convection currents in the mantle beneath the plates move the plates in different directions. The source of heat driving the convection currents is radioactive decay which is happening deep in the ...
Geography Answer Key
... b. The rocks equidistant on either sides of mid oceanic ridges show remarkable similarities in terms of period of formation, chemical compositions and magnetic properties. c. The ocean crust rocks are much younger than the continental rocks. The age of the rocks in the oceanic crust is nowhere more ...
... b. The rocks equidistant on either sides of mid oceanic ridges show remarkable similarities in terms of period of formation, chemical compositions and magnetic properties. c. The ocean crust rocks are much younger than the continental rocks. The age of the rocks in the oceanic crust is nowhere more ...
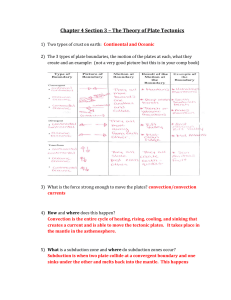
Chapter 4 Section 3 – The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... 3) What is the force strong enough to move the plates? convection/convection currents ...
... 3) What is the force strong enough to move the plates? convection/convection currents ...
Convergent Boundaries
... of how the earth’s surface is formed e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. Review: 1. List the geologic event(s) that can occur at each plate boundary. (What happens or is formed here?) • ____ & ____ @ Divergent Boundaries • _ ...
... of how the earth’s surface is formed e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. Review: 1. List the geologic event(s) that can occur at each plate boundary. (What happens or is formed here?) • ____ & ____ @ Divergent Boundaries • _ ...
Test Review Building Up and Wearing Down the Surface
... 5.) As a modern expert in the field of geography, specifically geology, explain the theory of Plate Tectonics. You are to include in your discussion who the scientist was that was a major contributor of the theory, then provide an explanation of how the crustal plates move, what happens at plate bo ...
... 5.) As a modern expert in the field of geography, specifically geology, explain the theory of Plate Tectonics. You are to include in your discussion who the scientist was that was a major contributor of the theory, then provide an explanation of how the crustal plates move, what happens at plate bo ...
Plate: a rigid slab of solid lithosphere rock that has defined
... parallel fault lines; also know as a graben. 1. What sets the continental plates in motion? Describe the process. Convention currents (heat rising) in the asthenosphere expand and migrate to the surface while cooler material flows to fill the void. 2. Briefly explain the difference between Convergin ...
... parallel fault lines; also know as a graben. 1. What sets the continental plates in motion? Describe the process. Convention currents (heat rising) in the asthenosphere expand and migrate to the surface while cooler material flows to fill the void. 2. Briefly explain the difference between Convergin ...
Name Date_________Core____ Inside the Restless Earth – Ch. 4
... When two tectonic plates push/crash/collide into one another; mountains can be formed a. Continental/oceanic When a tectonic plate with oceanic crust and tectonic plate with continental crust collide; Andes Mountains in S. America b. Oceanic/oceanic When tectonic plate with oceanic crust and tectoni ...
... When two tectonic plates push/crash/collide into one another; mountains can be formed a. Continental/oceanic When a tectonic plate with oceanic crust and tectonic plate with continental crust collide; Andes Mountains in S. America b. Oceanic/oceanic When tectonic plate with oceanic crust and tectoni ...
7 Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements:
... 7th Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements: Learning Target: I will be able to create & develop a Movie with Live Movie Maker by utilizing the knowledge I have been practicing over the last two weeks. I will explore and compile facts about an Earth Science topic that I am starting to study in ...
... 7th Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements: Learning Target: I will be able to create & develop a Movie with Live Movie Maker by utilizing the knowledge I have been practicing over the last two weeks. I will explore and compile facts about an Earth Science topic that I am starting to study in ...
Earth Science - Atlanta Public Schools
... substance becomes less dense, and it rises. As the substance cools, the molecules get closer together, the substance becomes more dense, and it sinks. 19. What do the convection currents in the asthenosphere cause on the Earth’s surface? ...
... substance becomes less dense, and it rises. As the substance cools, the molecules get closer together, the substance becomes more dense, and it sinks. 19. What do the convection currents in the asthenosphere cause on the Earth’s surface? ...
Goal-directed Instructional Design Plan
... pulling apart. The internal energy of the Earth drives the movement of the plates. The slow movement of materials within Earth results from heat flowing out from the deep interior and the action of gravity on regions of different density. Evidence for plate tectonics includes the spreading of the se ...
... pulling apart. The internal energy of the Earth drives the movement of the plates. The slow movement of materials within Earth results from heat flowing out from the deep interior and the action of gravity on regions of different density. Evidence for plate tectonics includes the spreading of the se ...
9 Geography Investigating Australia`s Physical Environments Term 1
... Many fossils have been found which link continents together and support the idea that the continents were once joined together. They show that a plant or animal lived on the edge of two (or more) continents. This shows that the two areas would have had to have a similar climate (and so a similar lat ...
... Many fossils have been found which link continents together and support the idea that the continents were once joined together. They show that a plant or animal lived on the edge of two (or more) continents. This shows that the two areas would have had to have a similar climate (and so a similar lat ...
- Google Sites
... become more dense and sink. The cycle continues and moves the plates. 3. How was the Grand Canyon formed? Flowing water eroded existing rock layers in a gradual, destructive process. 4. What causes rock to break apart? Roots of plants, weathering, freezing and melting, animals, water, human activity ...
... become more dense and sink. The cycle continues and moves the plates. 3. How was the Grand Canyon formed? Flowing water eroded existing rock layers in a gradual, destructive process. 4. What causes rock to break apart? Roots of plants, weathering, freezing and melting, animals, water, human activity ...
Inside the Earth
... The Taconian Orogeny, as viewed from above, about 450 million years ago. The Chopawamsic Terrane has begun to collide with ancestral North America, adding the volcanic rocks and sedimentary to the eastern margin of the continent. Map by Ron Blakey, Northern Arizona University. ...
... The Taconian Orogeny, as viewed from above, about 450 million years ago. The Chopawamsic Terrane has begun to collide with ancestral North America, adding the volcanic rocks and sedimentary to the eastern margin of the continent. Map by Ron Blakey, Northern Arizona University. ...
Studyguide_PTtest
... ~ The theory Harry Hess put forth – What did he find? What other evidence added to the idea that the seafloor was spreading? (new crust formed at mid-ocean ridge – younger closer to ridge, older farther away; trenches & subduction zones; magnetic striping of seafloor) ~ The 4 basic layers of the Ear ...
... ~ The theory Harry Hess put forth – What did he find? What other evidence added to the idea that the seafloor was spreading? (new crust formed at mid-ocean ridge – younger closer to ridge, older farther away; trenches & subduction zones; magnetic striping of seafloor) ~ The 4 basic layers of the Ear ...
Plate Tectonic Internet Activity
... 14. Next. How did he use the rock sequence as evidence for his theory? Explain. 15. Next. Which continents (5) had glaciations? 16. Look at the present day climate zones. Ice is found at _________________ latitudes. 17. What are his two possible explanations for the glaciers on these five continents ...
... 14. Next. How did he use the rock sequence as evidence for his theory? Explain. 15. Next. Which continents (5) had glaciations? 16. Look at the present day climate zones. Ice is found at _________________ latitudes. 17. What are his two possible explanations for the glaciers on these five continents ...
Understanding the Earth
... 2. Plates: huge blocks of Earth’s crust (includes ocean floor) Example: continents or parts of continents Forces of Earth’s Surface: a. Weathering: a process that breaks rocks down into tiny pieces ...
... 2. Plates: huge blocks of Earth’s crust (includes ocean floor) Example: continents or parts of continents Forces of Earth’s Surface: a. Weathering: a process that breaks rocks down into tiny pieces ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.