Explain the different soil types (bedrock/compact soil/loose sand
... Giant X-Ray Gun? • How do scientists know what layers are under the earth’s crust? • Earthquake waves travel through the earth and the speeds and locations help us determine what materials they are traveling through. ...
... Giant X-Ray Gun? • How do scientists know what layers are under the earth’s crust? • Earthquake waves travel through the earth and the speeds and locations help us determine what materials they are traveling through. ...
Slide 1
... b. the Earth was about 6000 years old c. there was no evidence to suggest that the Earth was changing d. all rocks on Earth were of the same age ...
... b. the Earth was about 6000 years old c. there was no evidence to suggest that the Earth was changing d. all rocks on Earth were of the same age ...
Hot spots can be used to track plate movements.
... columns, from the mantle. Volcanoes often develop above the plume. Although most hot spots occur far from plate boundaries, they offer a way to measure plate movement. This is because a hot spot generally stays in one place while the tectonic plate above it keeps moving. At a hot spot, the heat from ...
... columns, from the mantle. Volcanoes often develop above the plume. Although most hot spots occur far from plate boundaries, they offer a way to measure plate movement. This is because a hot spot generally stays in one place while the tectonic plate above it keeps moving. At a hot spot, the heat from ...
Internal Structure of the Earth File
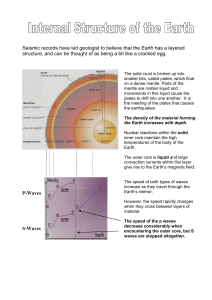
... Seismic records have led geologist to believe that the Earth has a layered structure, and can be thought of as being a bit like a cracked egg. ...
... Seismic records have led geologist to believe that the Earth has a layered structure, and can be thought of as being a bit like a cracked egg. ...
Document
... • Since new material is created at the midocean ridges and Earth is not expanding, somewhere material must be removed from the surface. • It turns out that old ocean floor is “subducted” into the mantle at subduction zones. ...
... • Since new material is created at the midocean ridges and Earth is not expanding, somewhere material must be removed from the surface. • It turns out that old ocean floor is “subducted” into the mantle at subduction zones. ...
2. Plate tectonics
... Explains many of Earth’s large-scale surface features and related phenomena Central idea of the theory Earth’s surface is broken up into some large pieces called tectonic plates Earth plate is composed of Crust and part of upper Mantle Ocean plates: 8-10 km thickness with dense rock ...
... Explains many of Earth’s large-scale surface features and related phenomena Central idea of the theory Earth’s surface is broken up into some large pieces called tectonic plates Earth plate is composed of Crust and part of upper Mantle Ocean plates: 8-10 km thickness with dense rock ...
PLATE TECTONICS - Part I
... Determines the numeric age of rock forming events Only appropriate for ages of igneous rocks and minerals Primary method is the radiometric technique Used in conjunction with stratigraphic principles and fossils ...
... Determines the numeric age of rock forming events Only appropriate for ages of igneous rocks and minerals Primary method is the radiometric technique Used in conjunction with stratigraphic principles and fossils ...
Origin of Oceanic Islands
... • Highly controversial; ridiculed, esp. in U.S. • Finally accepted by mainstream geology in 1960s. ...
... • Highly controversial; ridiculed, esp. in U.S. • Finally accepted by mainstream geology in 1960s. ...
The mechanics of tectonics
... The mechanics of tectonics When the plates of the earth’s crust exert pressure on one another as they move, the rocks that make up these plates are subject to extreme stress. During a latent period, this stress is absorbed by a certain elasticity. But beyond a particular point, a sudden rupture occu ...
... The mechanics of tectonics When the plates of the earth’s crust exert pressure on one another as they move, the rocks that make up these plates are subject to extreme stress. During a latent period, this stress is absorbed by a certain elasticity. But beyond a particular point, a sudden rupture occu ...
GG 101 Objectives Chapter Links
... 1. Recognize the importance of volcanic activity to the science of geology 2. Describe how volcanism relates to the origin of the atmosphere and affects Earth's climate 3. Contrast the beneficial and catastrophic effects of volcanism on humans. 4. Indicate the factors that control the explosive viol ...
... 1. Recognize the importance of volcanic activity to the science of geology 2. Describe how volcanism relates to the origin of the atmosphere and affects Earth's climate 3. Contrast the beneficial and catastrophic effects of volcanism on humans. 4. Indicate the factors that control the explosive viol ...
The inner solar system has rocky planets.
... an opening called a volcano. On Earth, lava often builds up into mountains. Volcanoes are found on Earth, Venus, and Mars. Lava can also flow onto large areas and cool into flat plains like the lunar maria. When the inside of a planet cools enough, no more molten rock reaches the surface. You have r ...
... an opening called a volcano. On Earth, lava often builds up into mountains. Volcanoes are found on Earth, Venus, and Mars. Lava can also flow onto large areas and cool into flat plains like the lunar maria. When the inside of a planet cools enough, no more molten rock reaches the surface. You have r ...
Catastrophic Events End of Book Review Game Questions (unedited
... thousands degrees C, the hot temperatures Inside the earths mantle can melt rock, this is Magma. 62. What is a P-wave? What is a S-wave? A. A P-wave is a push, pull wave. An Swave is a side, to side wave. 63. What is Aftershock? A. Aftershock happens after an earthquake happens. Aftershock is a eart ...
... thousands degrees C, the hot temperatures Inside the earths mantle can melt rock, this is Magma. 62. What is a P-wave? What is a S-wave? A. A P-wave is a push, pull wave. An Swave is a side, to side wave. 63. What is Aftershock? A. Aftershock happens after an earthquake happens. Aftershock is a eart ...
Continental Drift - CoconinoHighSchool
... Continental crust. It is constantly being formed and destroyed at ocean ridges and trenches. 3. Continental crust can carry on beyond the edges of the land and finally end far below the sea. This explains why the edges of all the continents don't have deep trenches right up against their coastlines. ...
... Continental crust. It is constantly being formed and destroyed at ocean ridges and trenches. 3. Continental crust can carry on beyond the edges of the land and finally end far below the sea. This explains why the edges of all the continents don't have deep trenches right up against their coastlines. ...
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators
... Rock that has been broken down can be eroded. Erosion is the movement of rock and soil by wind, water, ice, or gravity. Erosion can be fast or slow. For example, land is eroded quickly when hurricane waves carry away large amounts of sand from a beach. Gravity can quickly carry away large amounts of ...
... Rock that has been broken down can be eroded. Erosion is the movement of rock and soil by wind, water, ice, or gravity. Erosion can be fast or slow. For example, land is eroded quickly when hurricane waves carry away large amounts of sand from a beach. Gravity can quickly carry away large amounts of ...
volcanoes - Math/Science Nucleus
... were all once melted, and have since cooled down and become solid. Igneous rocks look different because of two factors: they cooled at different rates and the "Mother" Magma (original melted rock) was different. In addition, volcanoes erupt in different ways. Some extrude quiet lava flows, while oth ...
... were all once melted, and have since cooled down and become solid. Igneous rocks look different because of two factors: they cooled at different rates and the "Mother" Magma (original melted rock) was different. In addition, volcanoes erupt in different ways. Some extrude quiet lava flows, while oth ...
test - Scioly.org
... 3. He originated the theory of uniformitarianism—a fundamental principle of geology—which explains the features of the Earth's crust by means of natural processes over geologic time. His work established geology as a proper science, a ...
... 3. He originated the theory of uniformitarianism—a fundamental principle of geology—which explains the features of the Earth's crust by means of natural processes over geologic time. His work established geology as a proper science, a ...
Continental Drift
... Continental crust. It is constantly being formed and destroyed at ocean ridges and trenches. 3. Continental crust can carry on beyond the edges of the land and finally end far below the sea. This explains why the edges of all the continents don't have deep trenches right up against their coastlines. ...
... Continental crust. It is constantly being formed and destroyed at ocean ridges and trenches. 3. Continental crust can carry on beyond the edges of the land and finally end far below the sea. This explains why the edges of all the continents don't have deep trenches right up against their coastlines. ...
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE
... Cratons are large areas of stable rock older than 540 million years that exist on all continents today. Cratons that have been exposed at the Earth’s surface are called shields. Cratons are the cores around which the modern continents are formed. Rifting is the process by which Earth’s crust breaks ...
... Cratons are large areas of stable rock older than 540 million years that exist on all continents today. Cratons that have been exposed at the Earth’s surface are called shields. Cratons are the cores around which the modern continents are formed. Rifting is the process by which Earth’s crust breaks ...
THE ELKHEAD MOUNTAINS VOLCANIC FIELD, NORTHWESTERN
... which a number of rock samples collected from loca: ties throughout the volcanic field are described; A Je of the descriptions include chemical analyses. Ro (l926), in addition to his descriptions of the ro~ samples collected from the Fortification dike, includ~ in his report descriptions of an anal ...
... which a number of rock samples collected from loca: ties throughout the volcanic field are described; A Je of the descriptions include chemical analyses. Ro (l926), in addition to his descriptions of the ro~ samples collected from the Fortification dike, includ~ in his report descriptions of an anal ...
Geology of the Proposed Radioactive Waste Repository at Yucca
... Yucca Mountain (YM), in southern Nevada, is the proposed site of the nation’s sole high-level radioactive waste repository and lies within the middle to upper Miocene southwestern Nevada volcanic field (SWNVF) in the Walker Lane tectonic zone near the SW margin of the Basin and Range province. Rocks ...
... Yucca Mountain (YM), in southern Nevada, is the proposed site of the nation’s sole high-level radioactive waste repository and lies within the middle to upper Miocene southwestern Nevada volcanic field (SWNVF) in the Walker Lane tectonic zone near the SW margin of the Basin and Range province. Rocks ...
Developing a Theory of Plate Tectonics
... •Mountains are created as a massive mountain range when landmasses collide and their edges fold upward. •These landmasses had to be connected to create the Appalachian chain because they line up when pieced together. ...
... •Mountains are created as a massive mountain range when landmasses collide and their edges fold upward. •These landmasses had to be connected to create the Appalachian chain because they line up when pieced together. ...
Transform boundaries
... Transform boundaries – The plates move past each other, but because of friction, they cannot just glide past each other so build up stress, which is released as an earthquake. Divergent boundaries – The plates slide apart from each other and the space that this creates is filled with new crust fro ...
... Transform boundaries – The plates move past each other, but because of friction, they cannot just glide past each other so build up stress, which is released as an earthquake. Divergent boundaries – The plates slide apart from each other and the space that this creates is filled with new crust fro ...
TEST REVIEW KEY – Cat Events, W-E
... Wind erosion (movement) can build sand DUNES along beaches and in deserts. Water causes erosion in rivers. A quickly moving river will cause MORE or LESS (circle one) erosion than a river moving slowly. ...
... Wind erosion (movement) can build sand DUNES along beaches and in deserts. Water causes erosion in rivers. A quickly moving river will cause MORE or LESS (circle one) erosion than a river moving slowly. ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.